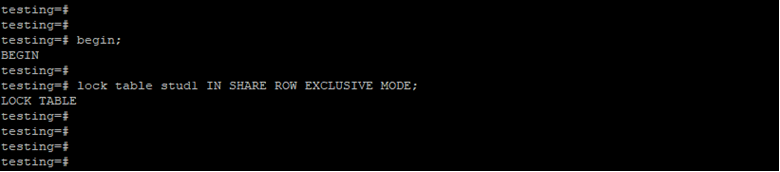Updated May 18, 2023
Introduction to PostgreSQL Lock Table
PostgreSQL lock table is defined as a lock table for access from the user, we can lock the table from read access or write access. A lock is very useful and important in PostgreSQL to prevent the user for modifying a single row or all tables. We can lock the table by using access share, row share, row exclusive, share, share update exclusive, exclusive, share row exclusive, and access exclusive mode in PostgreSQL. Using the lock command, we need to specify the table name and the name of the mode which we have applied to the table.
How to Lock Table in PostgreSQL?
Below is the way that defined how to lock the table in PostgreSQL.
Below syntax shows how to lock the table:
Lock table name_of_table IN [Mode of locking] [NOWAIT]- In the above example, the lock table is defined as a command used to lock the table by which mode we have used at the time of the locking table in PostgreSQL. After applying a lock on the table, it’s not accessible for read or write operations.
- The name of the table is defined as the table name on which we are applying the lock.
- Mode of locking is defined as the mode which was used while locking a table in PostgreSQL. If we have not used any lock mode, then the default mode of access exclusive is used in PostgreSQL.
- Now it is defined as do not wait for any lock to be released from the table. If the lock is not acquired, the transaction will be aborted directly without waiting in PostgreSQL.
- We can acquire a lock explicitly by using the lock command.
Mode of Locks:
- Access share
- Row share
- Row exclusive
- Share update exclusive
- Share
- Share row exclusive
- Exclusive
- Access exclusive
The above mode of lock will contain its specified function to lock the table in PostgreSQL as follows:
1. Access Share
- This lock in PostgreSQL conflicts with the only mode of access exclusive. Select command in PostgreSQL will acquire these locks on a specified table.
- This is defined as we can only read data from the table we cannot modify the table after acquiring these locks on the table.
2. Row Share
- This lock in PostgreSQL conflicts with the mode of access, exclusive and exclusive. The select for share and select for update statement will acquire these types of lock on the table.
3. Row Exclusive
- This lock in PostgreSQL conflicts with the mode of share row exclusive, share, access exclusive, and exclusive.
- The update deletes, and inserts will acquire the locks on the table. These locks are acquired on the lock, which modifies the statement in PostgreSQL.
4. Share Update Exclusive
- This lock in PostgreSQL conflicts with the mode of share row exclusive, share, access exclusive, share update exclusive, and exclusive.
- It will acquire command of vacuum, index creation, alter table, and validate command in PostgreSQL.
5. Share
- This lock in PostgreSQL conflicts with the mode of share row exclusive, share, access exclusive, share update exclusive, share, and exclusive.
- This lock mode will acquire locks from the create index command in PostgreSQL.
6. Share Row Exclusive
- This lock in PostgreSQL conflicts with the mode of share row exclusive, share, access exclusive, share update exclusive, share row exclusive, share, and exclusive.
- This mode is not automatically acquired on the table we have applied the same by using the lock command.
7. Exclusive
- This lock in PostgreSQL conflicts with the mode of share row exclusive, share, access exclusive, share update exclusive, share row exclusive, share, and exclusive.
- We acquire this lock by refreshing the materialized view.
8. Access Exclusive
- This lock in PostgreSQL conflicts with the mode of share row exclusive, share, access exclusive, share update exclusive, share row exclusive, share, access exclusive, and exclusive.
- While using this lock, only the user can access the table who applying a lock on the table.
Examples of PostgreSQL Lock Table
Given below are the examples of PostgreSQL Lock Table:
Example #1
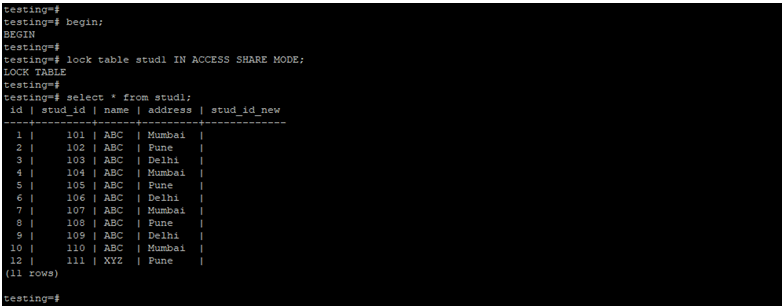
Lock Table by Using Access Share Lock Mode.
The below example shows the lock table by using access share lock mode.
Code:
begin;
lock table stud1 IN ACCESS SHARE MODE;
select * from stud1;Output:
Example #2
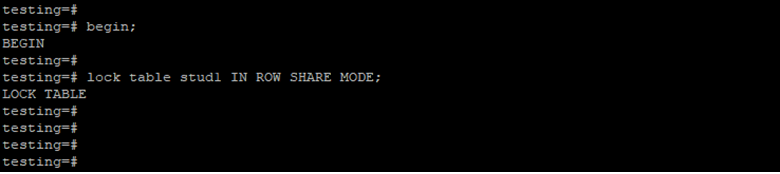
Lock Table by Using Row Share Lock Mode.
The below example shows that lock table by using row share lock mode.
Code:
begin;
lock table stud1 IN ROW SHARE MODE;Output:
Example #3
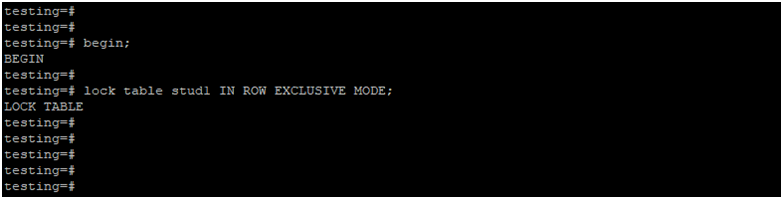
Lock Table by Using Rowexclusive Lockmode.
Below example shows that lock table by using row exclusive lock mode.
Code:
begin;
lock table stud1 IN ROW EXCLUSIVE MODE;Output:
Example #4
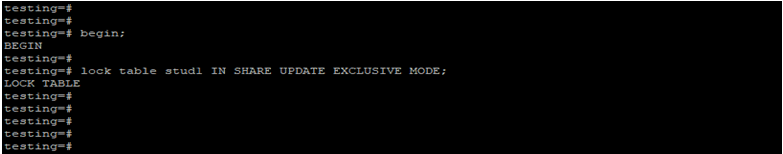
Lock Table by Using Share Updateexclusive Lock Mode.
Below example shows that lock table by using share update exclusive lock mode.
Code:
begin;
lock table stud1 IN SHARE UPDATE EXCLUSIVE MODE;Output:
Example #5
Lock Table by Using Share Lock Mode.
Below example shows that lock table by using share lock mode.
Code:
begin;
lock table stud1 IN SHARE MODE;Output:
Example #6
Lock Table by Using Share Row Exclusive Lock Mode.
Below example shows that lock table by using share row exclusive lock mode.
Code:
begin;
lock table stud1 IN SHARE ROW EXCLUSIVEMODE;Output:
Example #7
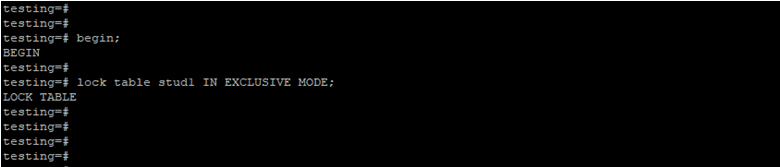
Lock Table by Using Exclusive Lock Mode.
Below example shows that lock table by using exclusive lock mode.
Code:
begin;
lock table stud1 IN EXCLUSIVE MODE;Output:
Example #8
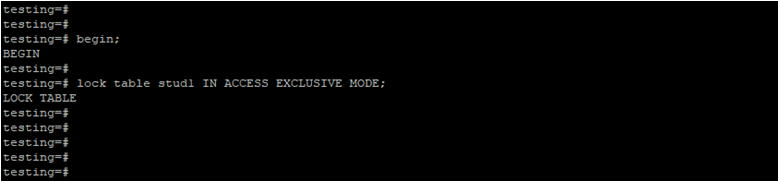
Lock Table by Using Access Exclusive Lock Mode.
Below example shows that lock table by using access exclusive lock mode.
Code:
begin;
lock table stud1 IN ACCESS EXCLUSIVE MODE;Output:
Recommended Articles
We hope that this EDUCBA information on “PostgreSQL Lock Table” was beneficial to you. You can view EDUCBA’s recommended articles for more information.