Updated May 12, 2023
Introduction to PostgreSQL DDL
The PostgreSQL DDL is the acronym for Data Definition Language. The Data Definition Language is used to handle the database descriptions and schemas, and it is used to define as well as modify the structure of the data. With the help of the Data Definition Language, we decide how the data should be stored in the database. We can perform operations on the database by creating a new one, altering the existing one, and removing, truncating, or renaming the existing database.
How does the DDL Statement work in PostgreSQL?
- The Data Definition Language is used to define as well as modify the structure of the data.
- The Data Definition Language commands can be used to create, drop or modify tables within a database.
List of PostgreSQL DDL Statement
The Data Definition Language consists of the following statements:
- CREATE
- ALTER
- TRUNCATE
- DROP
1. CREATE Statement
The CREATE statement is used to create objects like (database, table, index, views, store procedure, function, and triggers).
Syntax:
CREATE TABLE <table_name>
(column_name_1 datatype,
column_name_2 datatype,
.
.
column_name_n datatype
);Example:
Code:
CREATE TABLE student
(
student_id INT,
student_name VARCHAR(30),
student_age INT,
student_address VARCHAR(25),
student_phone_no VARCHAR(20)
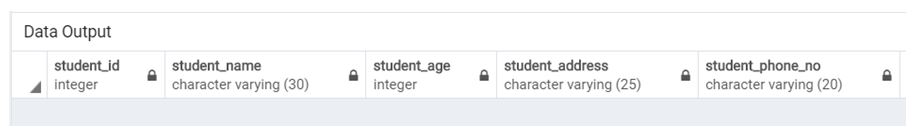
);Illustrate the result of the above Statement by using the following SQL statement and a snapshot:
Code:
Select * from student;Output:
2. ALTER Statement
The ALTER statement allows modifying the existing database objects. We can alter or modify the database structure by using an ALTER statement.
We can perform the following operations by using an ALTER statement:
- Add a column in the table.
- Drop the existing column.
- Change the data type of the column.
a. Consider the following ALTER statement syntax for adding a PRIMARY KEY on a column in the existing table.
Syntax:
ALTER TABLE
<tableName>
ADD PRIMARY KEY (<columnName>);Example:
Code:
ALTER TABLE
student
ADD PRIMARY KEY (student_id);b. Consider the following ALTER statement syntax for setting NOT NULL on a column in the existing table.
Syntax:
ALTER TABLE
<tableName>
ALTER COLUMN
<columnName>
SET NOT NULL;Example:
Code:
ALTER TABLE
student
ALTER COLUMN
student_name
SET NOT NULL;Output:
c. Consider the following ALTER statement syntax for dropping NOT NULL on a column in the existing table.
Syntax:
ALTER TABLE
<tableName>
ALTER COLUMN
<columnName>
DROP NOT NULL;Example:
Code:
ALTER TABLE
student
ALTER COLUMN
student_name
DROP NOT NULL;Output:
d. Consider the following ALTER statement syntax for adding a new column in the existing table.
Syntax:
ALTER TABLE
<tableName>
ADD <columnName data-type>;Example:
Code:
ALTER TABLE
student
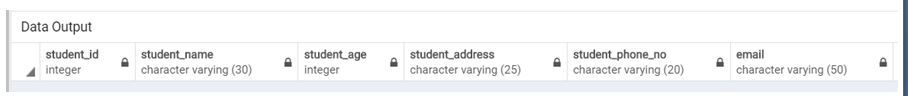
ADD email varchar(50);Illustrate the result of the above Statement by using the following SQL statement and a snapshot:
Code:
Select * from student;Output:
Consider the following ALTER statement syntax for renaming an existing column name to a new column name.
Syntax:
ALTER TABLE
<tableName>
RENAME COLUMN
<oldColumnName> TO <newColumnName>;Example:
Code:
ALTER TABLE
student
RENAME COLUMN
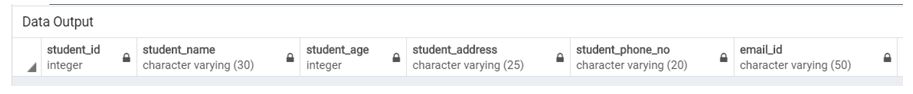
Email TO email_id;Illustrate the result of the above Statement by using the following SQL statement and a snapshot:
Code:
Select * from student;Output:
Consider the following ALTER statement syntax for removing an existing column from the table.
Syntax:
ALTER TABLE
<tableName>
DROP COLUMN
<columnName>;Example:
Code:
ALTER TABLE
student
DROP COLUMN
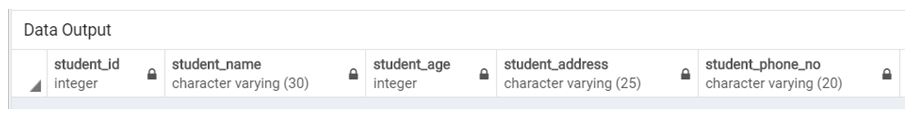
Email_id;Illustrate the result of the above Statement by using the following SQL statement and a snapshot:
Code:
Select * from student;Output:
We can rename the database objects. RENAME statement is used to rename the tables within the database.
Consider the following RENAME statement syntax for renaming the existing column from the table.
Syntax:
ALTER TABLE <oldName>
RENAME
TO
<newName>;Example:
Code:
ALTER TABLE
student
RENAME TO
studentInfo;3. TRUNCATE Statement
We can remove all rows from a table, including all spaces allocated for the rows.
Consider the following TRUNCATE statement syntax for removing all of the rows from the table.
Syntax:
TRUNCATE TABLE
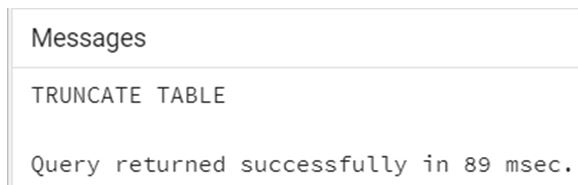
<tableName>;Example:
Code:
TRUNCATE TABLE studentInfo;Output:
4. DROP statement
We can delete database objects by using a DROP statement such as a table, index, view, etc.
Consider the following DROP statement syntax for removing the entire database object structure.
Syntax:
DROP TABLE
<tableName>;OR
DROP DATABASE
<databaseName>;Example:
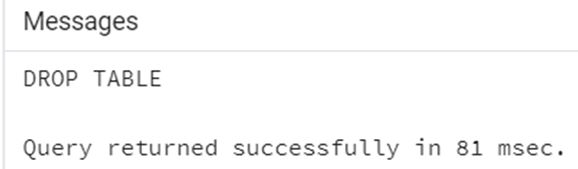
Code:
DROP TABLE studentInfo;Output:
Conclusion
In this article, we saw how to use the PostgreSQL DDL and how the PostgreSQL DDL works. Also, we have added several examples of each PostgreSQL DDL.
Recommended Articles
We hope that this EDUCBA information on “PostgreSQL DDL” was beneficial to you. You can view EDUCBA’s recommended articles for more information.