Updated May 17, 2023
Introduction to PostgreSQL DROP DATABASE
PostgreSQL drop database statement is used to drop the database; we can drop the database’s unwanted database using the drop database command in PostgreSQL. We can use the database name with the drop database command, which was we want to drop from the database server; this statement will delete or drop the catalog entries and physical data directory files from the server. We cannot undo the drop database statement, so we need to fire this command with caution. To execute this command on PostgreSQL, we have the permission of a superuser or admin user; another user cannot execute this command.
Syntax and Parameters
Below is the syntax :
- Drop database database_name (Name of database which was we have dropped from the database server);
OR
- Drop database [ IF EXISTS ] database_name (Name of database which was we have dropped from the database server);
OR
- Dropdb [options (We have used multiple options while dropping database in PostgreSQL)] database_name.
Below is the parameter description syntax of the drop database statements in PostgreSQL.
- Drop: Drop database statement in PostgreSQL basically used to drop the unused database from the server.
- Database name: The database name is the name we dropped from the database server.
- If exists: This is defined as dropping the database using if exists options; after using this option, if the database does not exist on a database server, it will not show the error.
- Dropdb: We can drop the database from the command line using the dropdb command. We can drop the database using the dropdb command in PostgreSQL.
- Options: We have used multiple options with the dropdb command. We have used multiple options while dropping the database in PostgreSQL.
We have used the below options while dropping the database using the dropdb command.
- –V: This option is used while we have to print the version of dropdb.
- –i: It will display the verification prompt before performing the command of dropdb.
- –help: It will display the dropdb command.
- –h: It is defined as drop the database as a specified host.
- –p: It is defined as drop the database as a specified port.
- –U: This is defined as use the username to drop the database.
- –W: It is defined as use the username password to drop the specified database.
How DROP DATABASE statement work in PostgreSQL?
- Below is the working of the drop database statement in PostgreSQL. We can drop the database using the drop database and dropdb command in PostgreSQL.
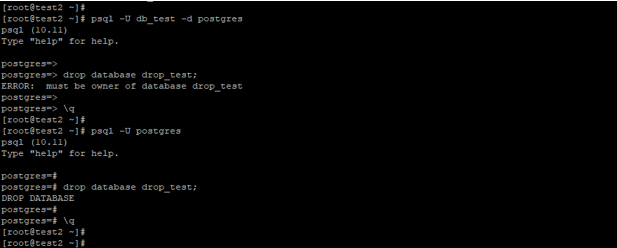
- To execute the command of drop database in PostgreSQL, we need to privileges database owners or privileges of admin privileges.
- This will issue the error like “ERROR: must be the owner of the database drop_test”. While dropping the drop_test database.
Code: The below example shows that we need to have privileges of the database owner or admin user in PostgreSQL.
psql -U db_test -d postgres
drop database drop_test;
psql -U postgres
drop database drop_test;Output:
- In the above first example, we have tried to drop the database using the db_test user; it will issue the error that we cannot drop the database because it will not owner of the database name of drop_test.
- In the second example, we have dropped the database using a Postgres user; it will not shows the error because it is an admin user.
- We cannot rollback the drop database transaction in PostgreSQL, so we need to use this statement with caution.
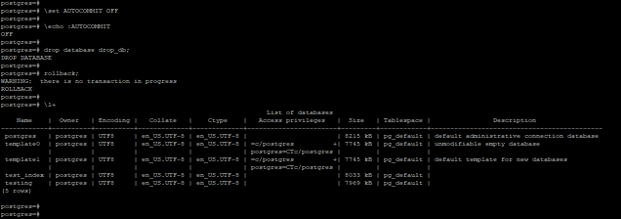
Code: The example below states that we cannot roll back the drop database transaction in PostgreSQL.
\set AUTOCOMMIT OFF
\echo :AUTOCOMMIT
drop database drop_db;
rollback;
\l+Output:
- In the above example, we have dropped the database and tried to roll back the same, but it will not roll back the drop database transaction.
- We can drop the database using the command line as well as a database shell prompt.
- We are using drop database statements using shell prompt and dropdb command for drop the database from the shell prompt.
- If we have permission to drop the database, we can drop the database using GUI tools like pg_admin.
Examples to Implement PostgreSQL DROP DATABASE
Below are the examples mentioned:
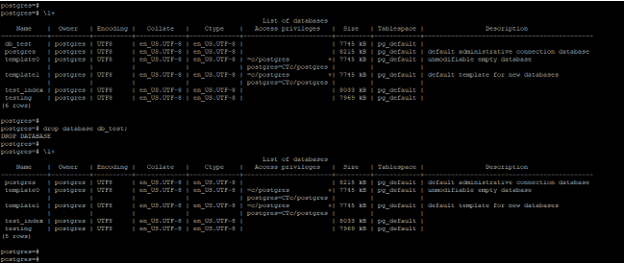
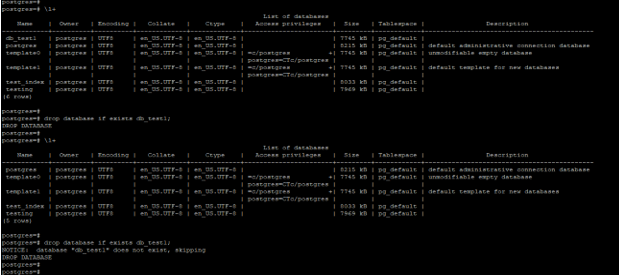
1. Drop the database without using any parameter
- In the below example, we have not used any parameter to drop the database. We have to drop the database from the database prompt.
- We have dropped the database name as a db_test from the user Postgres. Postgres user has admin privileges.
Code:
\l+
drop database db_test;
\l+Output:
2. Drop the database using if exists a parameter
- In the below example, we have used the if exist parameter to drop the database. We have to drop the database from the database prompt in PostgreSQL.
- We have dropped the database name of db_test1 from the user Postgres.
Code:
\l+
drop database if exists db_test1;
\l+
drop database if exists db_test1;Output:
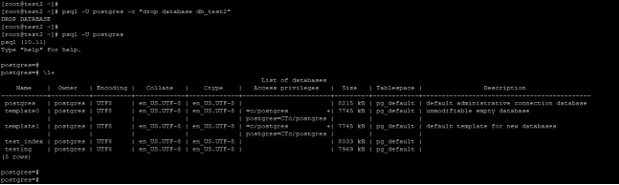
3. Drop the database from the command line prompt
- In the below example, we have dropped the database from the command line prompt. We have dropped the database from the command line prompt in PostgreSQL.
- We have dropped the database name of db_test2 from the user Postgres.
Code:
psql -U postgres -c "drop database db_test2"
psql -U postgres
\l+Output:
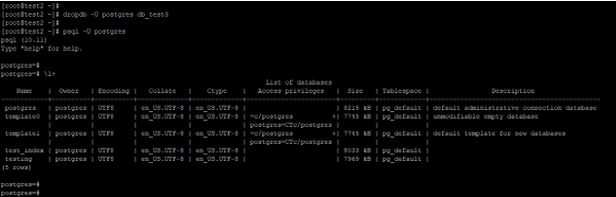
4. Drop the database using the dropdb command
In the below example, we have dropped the database using the dropdb command. We have dropped the database from the command line prompt using the dropdb command.
Code:
dropdb -U postgres db_test3
psql -U postgres
\l+Output:
Conclusion
Drop database statement basically used to drop the existing or unused database from the database server. We can drop the database using the drop database as well as the dropdb command. We cannot rollback the statement of the drop database.
Recommended Articles
We hope that this EDUCBA information on “PostgreSQL DROP DATABASE” was beneficial to you. You can view EDUCBA’s recommended articles for more information.