Updated May 26, 2023
Introduction to PostgreSQL group by month
PostgreSQL group by month is used to retrieve the data by using a monthly basis, we have applied group by clause on date_trunc function to retrieve table data as per month basis in PostgreSQL. If we need table data on a per month basis then we have to use PostgreSQL group by month in PostgreSQL. We have used date_trunc, group by, and aggregate functions to retrieve table data on a monthly basis in PostgreSQL, we have used the date_trunc function on a column from which we have retrieved data on a monthly basis.
Syntax:
Below is the syntax of the group by month in PostgreSQL.
Group by month using date_trunc function
Select DATE_TRUNC ('month', name_of_column) count (name_of_column) from name_of_table GROUP BY DATE_TRUNC ('month', name_of_column);Group by month using to_char function
SELECT aggregate_function (name_of_column), TO_CHAR (name_of_column, 'Month') FROM name_of_table GROUP BY TO_CHAR(date, 'Month');Group by month using extract function
SELECT aggregate_function (name_of_column), EXTRACT(MONTH FROM name_of_column) FROM name_of_table GROUP BY EXTRACT (MONTH FROM name_of_column);Below is the parameter description syntax of the group by month in PostgreSQL.
- Select – Select operation is used to select the data from the table and convert it month-wise using the date_trunc, extract, and to_char functions in PostgreSQL. We have a select date column from the table to convert data into month-wise.
- Date_trunc – This function converts the date column data month-wise by using the group by month in PostgreSQL. Date trunc will convert the data into the month.
- Month – This variable was used with the date_trunc function to convert the date into the month format in PostgreSQL. We have used group by clause with the month in PostgreSQL.
- Name of the column – This is defined as the name of the column we used with the date_trunc and to_char functions. We have converted date column data into the month-wise by using the group in PostgreSQL.
- Count – This function is used to count the rows of data using the count function. Count function is an optional parameter of the date_trunc function.
- Name of the table – This is defined as the name of the table we have used with the date_trunc and to_char functions in PostgreSQL. We have to convert date column table data to month-wise by using the group in PostgreSQL.
- Aggregate function – We are using the aggregate function while using the to_char function. All the aggregate functions we are using with the to_char and date_trunc function.
- To_char – We have used the to_char function to retrieve monthly data using an aggregate function in PostgreSQL.Using the to_char function, we have retrieved the month in character format.
How to perform group by month in PostgreSQL?
1. Below is the way to perform the group by month.
2. we have used the date_trunc and to_char functions to perform group by month.
3. We also use an aggregate function with date_trunc and to_char functions to use group by month.
4. We have used the below aggregate function with date_trunc and to_char function to use group by month.
- Avg
- Sum
- Count
- Min
- Max
5. The below example shows that we have used an aggregate function with the group by month.
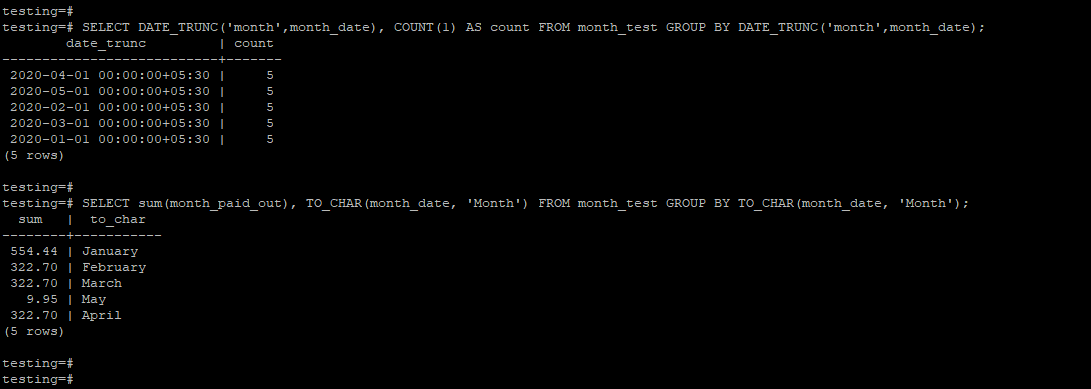
SELECT DATE_TRUNC('month',month_date), COUNT(1) AS count FROM month_test GROUP BY DATE_TRUNC('month',month_date);SELECT sum(month_paid_out), TO_CHAR(month_date, 'Month') FROM month_test GROUP BY TO_CHAR(month_date, 'Month');Output:
6. In the first example, we used the aggregate count function by using the date_trunc function to retrieve group data by month.
7. In the second example, we used the sum aggregate function by the to_char function to retrieve group data by month.
8. Basically date_trunc function is used to retrieve date and time with specific precision.
9. We have used two arguments with the date_trunc function: the date precision and the name of the column.
10. To use group by month, we need to define the month with the date parameter.
11. To_char is used to convert the integer into the sting using to_char, we have defining month in character format.
Examples of PostgreSQL group by month
Below is an example of the group by month. We have used the month_test table to describe the example of the group by month.
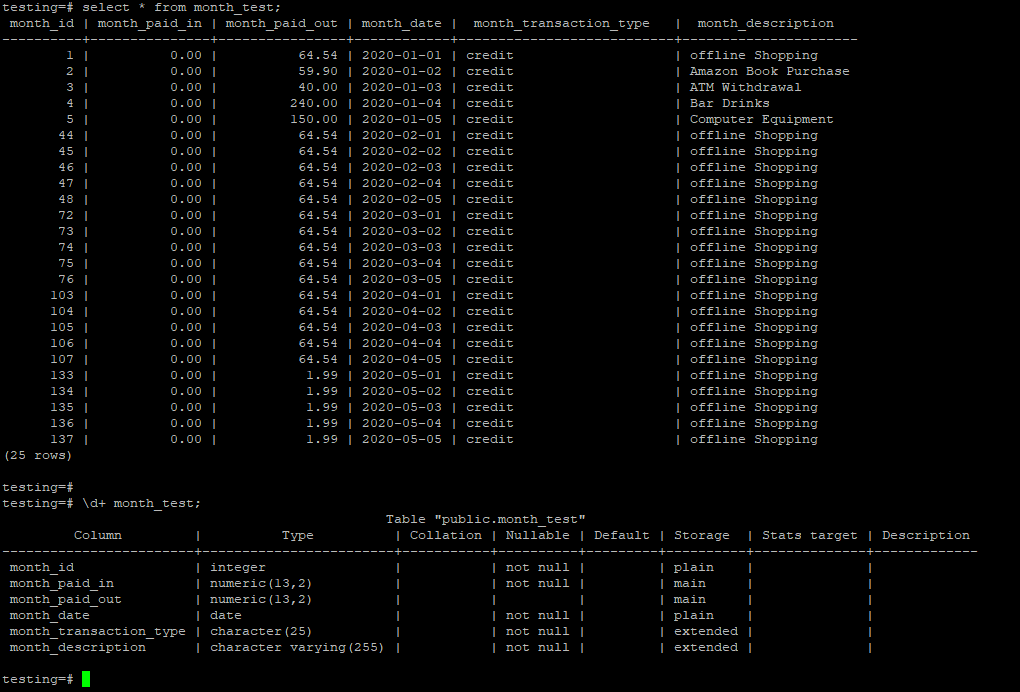
Below is the table and data description of the table month_test.
select * from month_test;
\d+ month_test;Output:
Example #1 – by using the date_trunc function
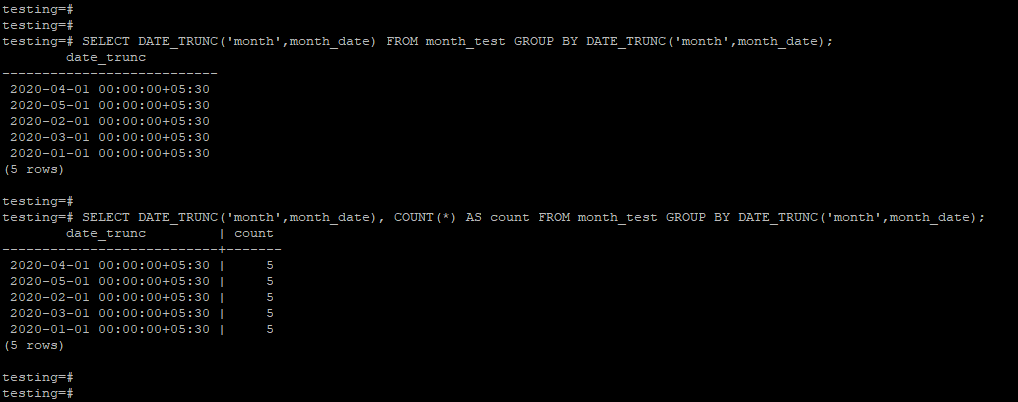
The below example shows the group by month by using the date_trunc function.
In the first example, we have not used the aggregate function, in the second example, we have used the aggregate function.
SELECT DATE_TRUNC('month',month_date) FROM month_test GROUP BY DATE_TRUNC('month',month_date);SELECT DATE_TRUNC('month',month_date), COUNT(*) AS count FROM month_test GROUP BY DATE_TRUNC('month',month_date);Output:
Example #2 – by using the to_char function
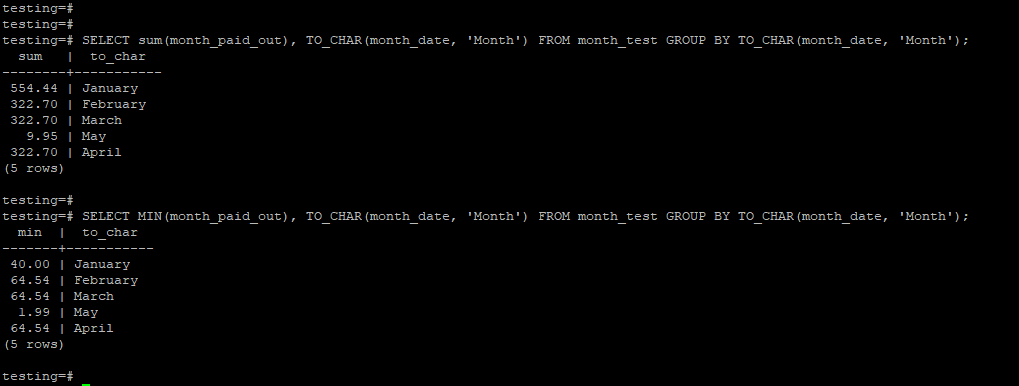
The below example shows that group by month by using to_char function.
In the first example, we have used the sum aggregate function, in the second example, we have used the min aggregate function.
SELECT sum(month_paid_out), TO_CHAR(month_date, 'Month') FROM month_test GROUP BY TO_CHAR(month_date, 'Month');SELECT MIN(month_paid_out), TO_CHAR(month_date, 'Month') FROM month_test GROUP BY TO_CHAR(month_date, 'Month');Output:
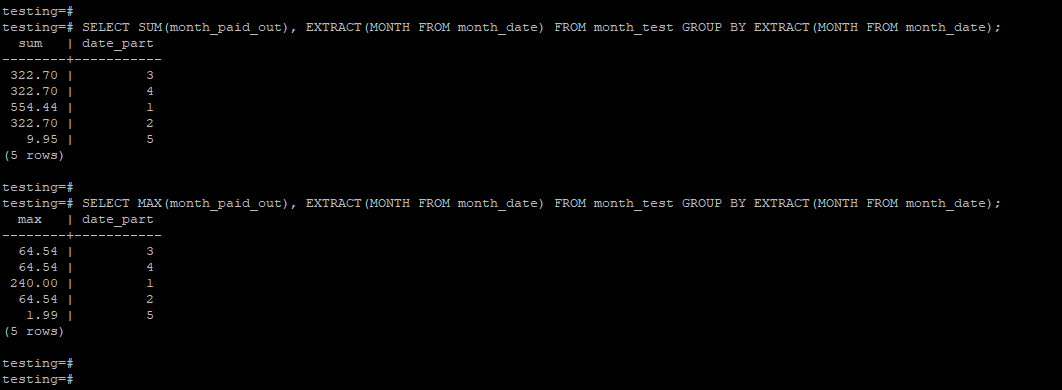
Example #3 – by using the extract function
The below example shows the group by month by using the extract function.
In the first example, we have used the sum aggregate function, in the second example, we have used the max aggregate function.
SELECT SUM(month_paid_out), EXTRACT(MONTH FROM month_date) FROM month_test GROUP BY EXTRACT(MONTH FROM month_date);SELECT MAX(month_paid_out), EXTRACT(MONTH FROM month_date) FROM month_test GROUP BY EXTRACT(MONTH FROM month_date);Output:
Conclusion
We have used group by month using date_trunc, to_char, and extract function. PostgreSQL group by month is important to display the records of the specified month. Using the to_char function, month displays the character format, and extract and date_trunc function month will be displayed in an integer format.
Recommended Articles
We hope that this EDUCBA information on “PostgreSQL group by month” was beneficial to you. You can view EDUCBA’s recommended articles for more information.