Updated May 24, 2023
Introduction to PostgreSQL FORMAT
The PostgreSQL provides the FORMAT() function, which gives the formatted output based on the format string. The PostgreSQL FORMAT function is the same as the sprintf() function provided in the C programming language. PostgreSQL FORMAT is an extension of the built-in function provided by PostgreSQL for formatting. The PostgreSQL FORMAT() functions help us to build the dynamic SQL statements or get the formatted result which contains various operations provided on string input like concatenation etc. The input array values are considered ordinary FORMAT() function arguments.
Syntax of PostgreSQL FORMAT
FORMAT(format_string [, format_arg [, ...] ])Explanation:
The PostgreSQL FORMAT() function takes multiple numbers of arguments termed variadic functions. We can pass the arguments to the PostgreSQL FORMAT() function by using the VARIADIC keyword.
1. format_string
This string defines the required format of the resultant string. It consists of format and text specifiers. The format acts as a placeholder for the input arguments we insert into the output string, and the text is placed as it is in the output string.
Understand the format specifier syntax by using the following statement:
%[position][flags][width]typeExplanation:
The percentage(%) character is the starting character of the format specifier.
The format specifier consists of the following optional components:
- Position:
Using the position defined, we can decide the argument to be added to the output string. We use the n$ form to determine the position.
n: index of the argument. The first index of the argument is 1.
We can skip the position as PostgreSQL considers the following argument by default.
- flags:
This can instruct the format specifier to treat the output as left-justified when the flag is minus(-).
It is required to define the width to use the flags component.
- width:
The width field is optional and defines the minimum characters required to display the format specifier’s result. To fill the width, the output string can get padded with the space characters on the left or right sides. The output is shown by skipping truncation if the width is too small.
The width can have any one of the following values:
- Non-negative integer value.
- To use the width as the next function argument, it will be an asterisk (*).
- To use the width as an nth function argument, it will be in the form *n$.
- Type:
The optional component type can be converting an argument value as:
s: For formatting as a string.
I: For treating an SQL identifier.
L: For quoting an SQL literal.
To build dynamic SQL statements, we generally use I and L. Also, we need to use double percentages %% if we want % to be in the output string.
2. Format_arg argument
We have multiple arguments, as we have seen PostgreSQL FORMAT() function.
Output value :
We get the formatted string as a result of The PostgreSQL FORMAT() function.
How does PostgreSQL FORMAT function work?
Consider the following example to understand the working of the PostgreSQL format function. We will create a student table by using the CREATE TABLE statement as follows:
CREATE TABLE student
(
stud_id serial PRIMARY KEY,
stud_fname varchar(80),
stud_lname varchar(80)
);Now we will insert some data in the ‘student’ table by using the INSERT INTO statement as follows:
INSERT INTO student (stud_fname, stud_lname)
values
('Oliver','Jake'),
('Jack','Connor'),
('Harry','Callum'),
('Jacob','John'),
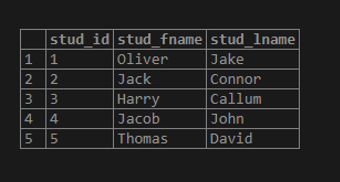
('Thomas','David');Illustrate the result of the above statement by using the following snapshot and SQL statement.
select * from student;Now we will use the FORMAT() function for building the full names of the student from the stud_lname and stud_fname columns:
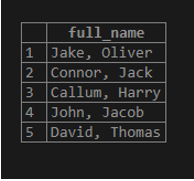
SELECT FORMAT('%s, %s',stud_lname, stud_fname) AS full_name
FROM Student;Illustrate the result of the above statement by using the following snapshot
In the above example, we have used %s %s, which gets replaced by values in the stud_lname and stud_fname columns.
Examples to Implement FORMAT Function in PostgreSQL
We will use the following example to understand the PostgreSQL FORMAT() function.
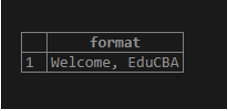
1. Simple format
SELECT FORMAT('Welcome, %s','EduCBA');Illustrate the result of the above statement by using the following snapshot :
In the above example, the %s is replaced by the ‘EduCBA’ string argument.
2. Component – flags
Let’s see the statement defined below to understand the flag’s usage.
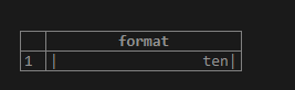
SELECT FORMAT('|%20s|', 'ten');Since we have defined the flag with no sign, the resultant string will right-align and left-pad with white spaces.
Illustrate the result of the above statement by using the following snapshot
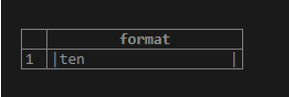
To make the result left-aligned, we will use the minus sign( – ) in the flag:
SELECT FORMAT('|%-20s|', 'ten');Illustrate the result of the above statement by using the following snapshot
3. Component – position
Let’s see the statement defined below to understand the usage of the position.
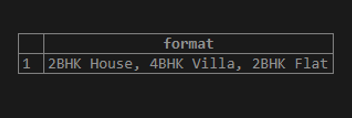
SELECT FORMAT('%1$s House, %2$s Villa, %1$s Flat', '2BHK', '4BHK');Illustrate the result of the above statement by using the following snapshot.
In the above example, we have defined arguments 2BHK and 4BHK strings. 1$ and 2$ are the positions that instruct the FORMAT() function to use the (2BHK ) and (4BHK ) as first and second arguments, respectively, and place them into the respective location.
Placing the position 1$ twice in the format string causes the insertion of the first argument, “2BHK”, twice.
Advantages of using FORMAT Function in PostgreSQL
- We use the PostgreSQL format function to construct dynamic SQL statements.
- Use the optional parameter in the SQL statement by using the FORMAT function.
- We can Format the result by using the FORMAT function.
- Combine column values of the table using the FORMAT statement.
Conclusion
We hope from the above article, you have understood how to use the PostgreSQL FORMAT() function and how the PostgreSQL FORMAT() function works. Also, we have added some examples of the PostgreSQL FORMAT() function to understand it in detail.
Recommended Articles
We hope that this EDUCBA information on “PostgreSQL FORMAT” was beneficial to you. You can view EDUCBA’s recommended articles for more information.