Updated May 24, 2023
Introduction to PostgreSQL Drop Schema
PostgreSQL provides a Drop Schema statement. The schema is described as a series of database objects in the database administration system. Object consists of tables, functions, relations, and operators. The drop schema statement removes a schema from databases that are no longer used. Drop schema statement can perform only the owner of the schema or superuser. In PostgreSQL, it provides the facility to delete multiple schemas at the same time by using a drop schema statement. In PostgreSQL, we use a different drop schema statement. Finally, we can say the Drop schema statement provides flexibility to users.
Syntax:
DROP SCHEMA [IF EXISTS] SPECIFIED SCHEMA NAME
[CASCADE RESTRICT ];Explanation:
- A drop schema statement removes a schema from the database in the above syntax.
- If Exists in the above statement is an optional part of the syntax. It is used to check whether a schema exists or not. When we include this statement in syntax, no error may occur if the specified schema does not exist.
- Cascade is an optional part of syntax when a specific schema is deleted from the database that also deletes tables and functions associated with that specific schema.
- Restrict it is also an optional part of the syntax. It is used to ensure that a schema is deleted if no other object is associated with them. When the schema is empty, then you can restrict the clause.
How to Drop Schema in PostgreSQL using Various Methods?
Before going to see how to Drop schema statement work in PostgreSQL, we need some prerequisites as follows:
- First, you must install PostgreSQL on your system.
- Service PostgreSQL status command to check whether PostgreSQL is working properly or not. If the status is active, that means PostgreSQL is installed successfully.
- You must have basic knowledge about PostgreSQL.
Now we create a new schema to understand how drop statements work using different methods.
Code:
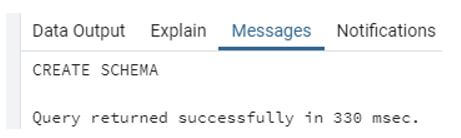
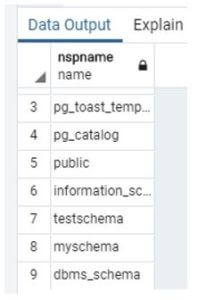
Create schema testschema;Using the above statement, we create testschema. Illustrate the end result of the above declaration by employing the use of the following snapshot.
Output:
After that, we create different tables under testschema using the following statement.
Code:
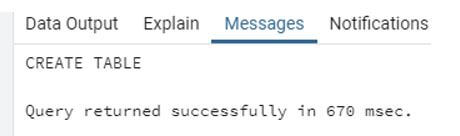
create table testschema.emp ( emp_id INT NOT NULL,
emp_name VARCHAR (30) NOT NULL, emp_age INT NOT NULL,
emp_salary DECIMAL (25, 2), primary key (emp_id) );Illustrate the end result of the above declaration by using the use of the following snapshot.
Output:
Drop Schema Methods:
Given below are the Drop Schema Methods:
1. Drop Schema
This method is used to delete schema from the database.
Syntax:
Drop Schema schema_name;Explanation:
- In the above statement, drop schema is the statement, and schema name is the schema name we need to delete.
Example:
Code:
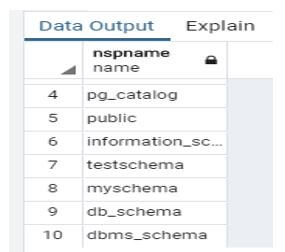
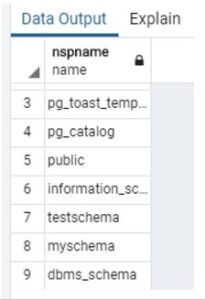
drop schema post_schema;In the above statement, delete test_schema from the database. Illustrate the end result of the above declaration by using the use of the following snapshot.
Output:
Illustrate the end result of the above statement before the execution of the above statement, as shown in the snapshot.
Output:
2. Drop Schema IF Exists
This is the second method in the drop schema. In this method, we delete the schema if and only if the schema is present.
Syntax:
Drop schema IF EXISTS schema name;Explanation:
- In the above syntax, where to drop schema is a drop statement, IF EXISTS clause is used to check whether the schema is present or not, and schema name is the specified schema name we need to delete.
Example:
Code:
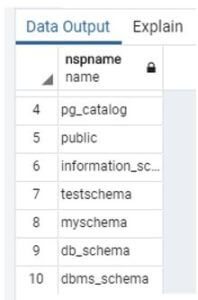
drop schema if exists db_schema;Using the above statement, we deleted the schema name db_schema from the database. Illustrate the end result of the above declaration by using the use of the following snapshot.
Output:
Illustrate the end result of the above statement before the execution of the above statement, as shown in the snapshot.
Output:
Now see what happens when we execute the same statement.
Code:
drop schema if exists db_schema;Illustrate the end result of the above declaration by using the use of the following snapshot.
Output:
In the above snapshot, the error message shows.
3. Drop Schema Cascade
This is the third method of drop schema. In this method, it automatically deletes the table function, etc.
Syntax:
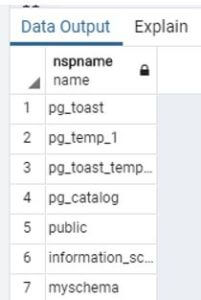
Drop schema testschema, dbms_schema;In the above statement, we deleted the schema name as testschema and dbms_schema, but when we execute the above statement, it returns an error message as we cannot delete the specified object because another object depends on it. Illustrate the end result of the above declaration by using the use of the following snapshot.
Output:
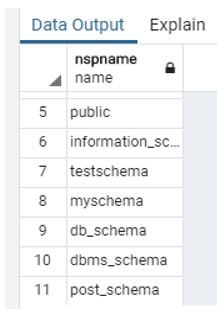
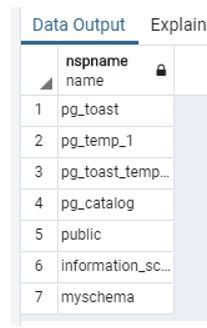
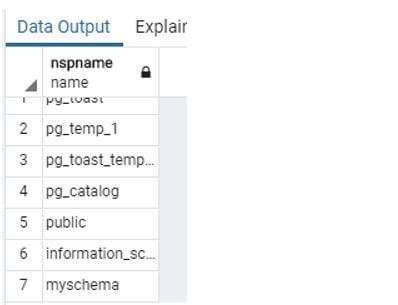
Now we need to delete schemas consisting of tables and functions and add cascade clauses.
See the below snapshot both schema testschema and dbms_schema shows in the list.
Output:
Now we execute the same statement. Just add the cascade clause at the end of the statement.
Code:
DROP SCHEMA testschema, dbms_schema cascade;Illustrate the end result of the above declaration by using the use of the following snapshot.
Output:
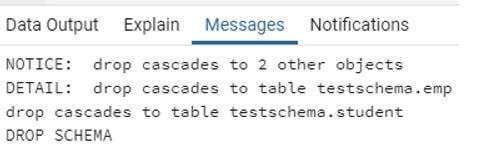
When we perform drop schema using cascade clause, notice that it delete testschema and dbms_schema as well as two other objects or table such as emp and student. Illustrate the end result of the above declaration by using the use of the following snapshot.
Output:
4. Drop Multiple Schema
In this method, we can delete multiple schemas at the same time by using below two syntaxes as follows:
Syntax:
drop schema if exists schema name1, schema name 2;Explanation:
- In the above syntax, if exists a clause with two schema names, if both schema names are present in the database, then it can be deleted otherwise, it shows an error message.
Example:
Code:
drop schema if exists demo, demo1;Both schema are present in the database in the above statement, so the drop schema statement deletes both schemas. Illustrate the end result of the above declaration by using the use of the following snapshot.
Output:
Syntax:
drop schema schema_1, schema_2;Explanation:
- We execute a drop schema statement with if it exists in the above syntax.
Example:
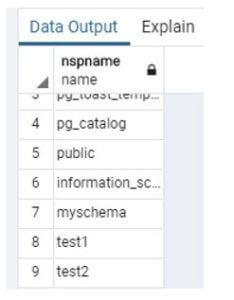
Code:
drop schema test1, test2;Illustrate the end result of the above declaration by using the use of the following snapshot.
Output:
Illustrate the end result of the above statement before the execution of the above statement, as shown in the snapshot.
Output:
Conclusion
From the above article, we saw how we can drop schema from the database along with different methods of drop schema like drop schema, drop schema if it exists and how we can drop multiple schemas and drop schema cascade with different examples. From this article, we saw how we can handle operation correctly because drop schema is permanent.
Recommended Articles
We hope that this EDUCBA information on “PostgreSQL Drop Schema” was beneficial to you. You can view EDUCBA’s recommended articles for more information.