Updated May 17, 2023
Introduction to PostgreSQL TEXT
PostgreSQL text defines the text data type for the column, varchar, and the text data type is the character data type in PostgreSQL. Basically, it is used to stored character value in the table. The text data type is basically used to store the variable’s unlimited length; we can store unlimited variable length into the column field using text data type in PostgreSQL. Using text datatype, we do not need to define a length specifier in PostgreSQL.
Syntax
Below is the syntax of the text data type in PostgreSQL:
TextOR
Create table table_name (column_name1 data_type, column_name2 data_type,column_name3 text,column_nameN data_type)Parameter
Below is the parameter description syntax of text data type in PostgreSQL:
Text: This is the data type used in PostgreSQL to store the character string’s unlimited length. We have used text datatype on the column the same as other data types in PostgreSQL.
Create: This operation is used to create a table with data type as text. We can define text data type on multiple columns in a single table.
Table name: Table name is an essential parameter while defining text data type on the column. The table name is defined as one in which we have defining text data type on the table column. We have used any table to define text data type on the column.
Column name: This is defined as the column’s name on which we have defining the text data type. The column name is also an essential parameter while using text data type in PostgreSQL.
Data type: This is defined as we have to define another data type on the table column. We have used data types in PostgreSQL such as int, char, and varchar.
How does TEXT data type work in PostgreSQL
PostgreSQL provides the data type name as text; basically, it stores the string of any length into the column field. In PostgreSQL, we store character string using the char, varchar, and text data type. There are key differences in each data type in PostgreSQL. Varchar and text data types function similarly, but the difference lies in the fact that the varchar data type requires specifying the length of the character that can be stored in the table.
The below example shows that the varchar and text data type works the same, but we have to define a length specifier to store character value in the varchar data type.
Code:
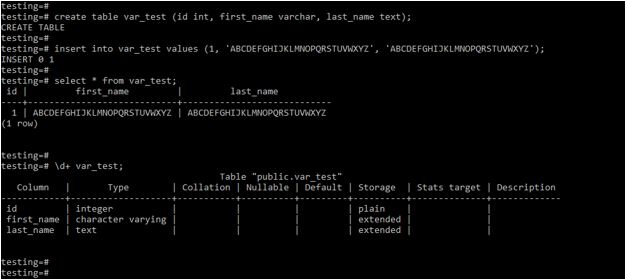
create table var_test (id int, first_name varchar, last_name text);
insert into var_test values (1, 'ABCDEFGHIJKLMNOPQRSTUVWXYZ', 'ABCDEFGHIJKLMNOPQRSTUVWXYZ');
select * from var_test;
\d+ var_test;Output:
Explanation: In the above example, we have created a table name as var_test; at the time of table creation, we have defined varchar and text data type on the column. After creating a table, we have to insert records into the table. We have inserted the same string of varchar and text data types. The above example shows that if we do not specify the varchar data type column’s length specifier, it works the same as a text data type in PostgreSQL.
While specifying the varchar data type column’s length specifier, it will not work the same as the text data type. Using text data type in PostgreSQL, we can store the unlimited length of the string. The text data type can store data up to 1 GB in a column field. Varchar and text data type performance is the same in PostgreSQL. But varchar allows only to store 255 characters into the column. We can easily convert the text data type into the other data type; also, we have to convert other data types into text easily.
Examples
Below is the example of text data type:
1. Define text data type to the column at the time of table creation
The below example shows that define data type as text at the time of table creation. We have created a table name as a stud_test table and define the text data type on the column.
Code:
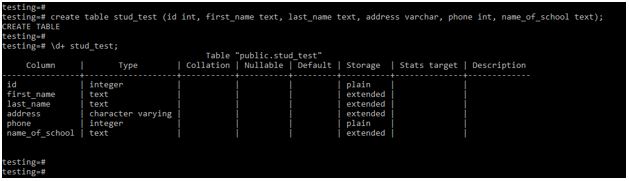
create table stud_test (id int, first_name text, last_name text, address varchar, phone int, name_of_school text);
\d+ stud_test;Output:
Explanation: In the above example, we have to define text data type on the first_name, last_name, and name_of_school column. Also, we have defined the varchar data type on the address column; when defining it, we have not declared any length specifier, so it is working as a text data type in PostgreSQL. We have defined the int data type on the id and phone column at the time of table creation.
2. Insert value into text data type column
The below example shows that insert a value into the text data type column. We have inserted a value into the stud_test table.
Code:
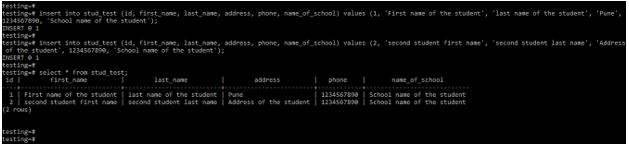
insert into stud_test (id, first_name, last_name, address, phone, name_of_school) values (1, 'First name of the student', 'last name of the student', 'Pune', 1234567890, 'School name of the student');
insert into stud_test (id, first_name, last_name, address, phone, name_of_school) values (2, 'second student first name', 'second student last name', 'Address of the student', 1234567890, 'School name of the student');
select * from stud_test;Output:
Explanation: In the above first example, we have insert values as text column; we have specified length specifier in the varchar data type column. We have not specified the length specifier in the varchar data type column in the second example.
3. Alter the column to change the data type of the column
The below example shows that change data type as text from another data type. We have to change the data type of the id and phone column.
Code:
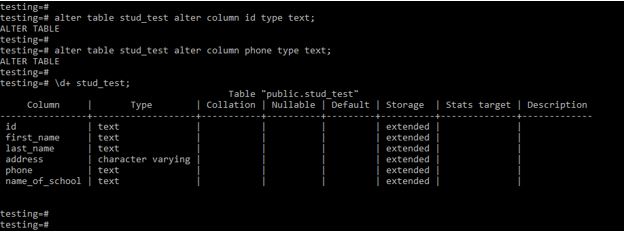
alter table stud_test alter column id type text;
alter table stud_test alter column phone type text;
\d+ stud_test;Output:
Recommended Articles
We hope that this EDUCBA information on “PostgreSQL TEXT” was beneficial to you. You can view EDUCBA’s recommended articles for more information.