Updated May 12, 2023
Definition of PostgreSQL CTE
PostgreSQL CTE is an abbreviation for common table expressions used to simplify complex queries. The common table expression result is temporary, which we can include in the SELECT, INSERT, UPDATE, and DELETE, etc. SQL statements. The Common Table Expressions result is temporary, which means that the common table expression exists while executing the SQL statement only. We can use the common table expressions to increase the readability of the complex JOINs and SQL statements; we can also organize the complex JOINs and SQL statements in a human-readable and organized manner.
Syntax:
Consider the following syntax of the PostgreSQL CTE:
WITH CTE_name (column_name_list) AS (
CTE_SQL_statement_definition
)
statement;Explanation:
- CTE_name: We define the name to be given to the common table expression. The names of the columns follow the common table expression. The column name list is optional.
- CTE_SQL_statement_definition: We define the SQL statement, which returns the result set inside the body of the WITH clause. The CTE_SQL_statement_definition becomes the names of the column list of the common table expression if we have not defined the column names after the names of the common table expression.
- statement: This can be used as a view or table in the statement, which can be a SELECT, INSERT, UPDATE, or deletes SQL statements.
How CTE Works in PostgreSQL?
- To define a WITH clause, follow the syntax section by specifying the name of the common table expression and then list the column names.
- The WITH clause contains a body; if we have not defined the column name, it takes all columns from the SQL statement defined in the body of the WITH clause.
- The Common Table Expressions result is temporary, which means that the common table expression exists while executing the SQL statement only.
Examples:
We will create two tables of the name ‘student’ and ‘teacher’ by using the PostgreSQL CREATE TABLE statement as follows to understand the examples:
create table student
(
stud_id serial PRIMARY KEY,
stud_fname VARCHAR(80) NOT NULL,
stud_lname VARCHAR(80) NOT NULL,
stud_marks INT NOT NULL,
teach_id INT NOT NULL
);
create table teacher
(
teach_id serial PRIMARY KEY,
teach_fname VARCHAR(80) NOT NULL,
teach_lname VARCHAR(80) NOT NULL
);We will insert some data into the ‘teacher’ table by using the PostgreSQL INSERT INTO statement as follows:
INSERT INTO teacher(teach_fname, teach_lname)
VALUES
('William','Joe'),
('Oliver','John'),
('Jack','Richard'),
('Harry','Joseph'),
('George','Thomas'),
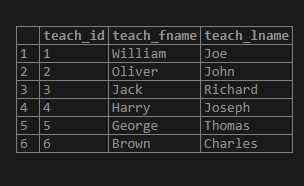
('Brown','Charles');Illustrate the result of the above INSERT INTO statement by using the following SQL statement and snapshot.
select * from teacher;Now, we will insert some data into the student’ table by using the PostgreSQL INSERT INTO statement as follows:
INSERT INTO student(stud_fname, stud_lname, stud_marks, teach_id)
VALUES
('Smith','Johnson',67,1),
('Williams','Jones',42,1),
('Harper','James',54,2),
('Jack','Liam',58,2),
('Harry','Mason',62,3),
('Jacob','Oscar',69,3),
('Michael','Charlie',75,4),
('William','Joe',44,4),
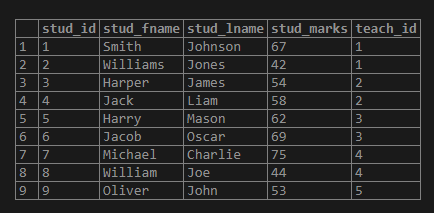
('Oliver','John',53,5);Illustrate the result of the above INSERT INTO statement by using the following SQL statement and snapshot.
select * from student;1. Consider the following basic example, which will be used to retrieve all the records from the student table by using common table expression:
With CTE_student AS
(
select
stud_id,
stud_fname,
stud_lname,
stud_marks,
teach_id
FROM
student
)
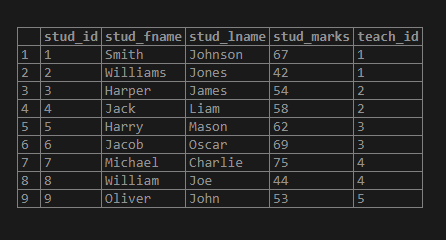
select * from CTE_student;Illustrate the result of the above SQL statement by using the following snapshot.
2. Consider another example; here, we will first define a cte_student as a common table expression by using the WITH clause as defined below:
WITH cte_student AS (
SELECT
stud_id,
stud_fname,
stud_lname,
(CASE
WHEN stud_marks <= 40
THEN 'Fail'
WHEN stud_marks > 40 AND stud_marks <= 55
THEN 'Third'
WHEN stud_marks > 55 AND stud_marks <= 60
THEN 'Second'
WHEN stud_marks > 60 AND stud_marks <= 65
THEN 'First'
WHEN stud_marks > 65
THEN 'Distinction'
END) Grade
FROM
student
)
SELECT
stud_id,
stud_fname,
stud_lname,
Grade
FROM
cte_student
WHERE
Grade = 'Distinction'
ORDER BY
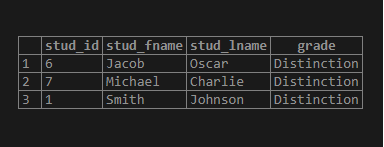
stud_fname;Illustrate the result of the above SQL statement by using the following snapshot.
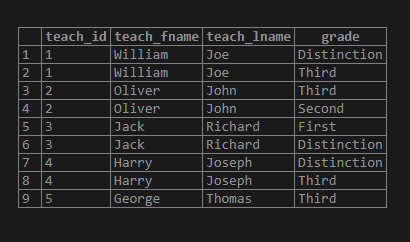
3. Consider one more example; we can use the JOIN with the column table expression as follows:
WITH cte_student AS (
SELECT
stud_id,
stud_fname,
stud_lname,
teach_id,
(CASE
WHEN stud_marks <= 40
THEN 'Fail'
WHEN stud_marks > 40 AND stud_marks <= 55
THEN 'Third'
WHEN stud_marks > 55 AND stud_marks <= 60
THEN 'Second'
WHEN stud_marks > 60 AND stud_marks <= 65
THEN 'First'
WHEN stud_marks > 65<
THEN 'Distinction'
END) Grade
FROM
student
)
SELECT t.teach_id,
teach_fname,
teach_lname,
Grade
FROM teacher t
INNER JOIN cte_student USING (teach_id);Illustrate the result of the above SQL statement by using the following snapshot.
Conclusion
From the above article, we hope you understand how to use the PostgreSQL common table expression and how the PostgreSQL common table expression works. Also, we have added several examples of PostgreSQL common table expression to understand them in detail.
Recommended Articles
We hope that this EDUCBA information on “PostgreSQL CTE” was beneficial to you. You can view EDUCBA’s recommended articles for more information.