Updated May 6, 2023
Introduction to PostgreSQL CONCAT()
In order to concatenate more than two strings, we can use either the string concatenation operator (||) or CONCAT() function provided by PostgreSQL. The CONCAT() function is a built-in function provided by PostgreSQL since version 9.1. We can pass an array of string elements to the PostgreSQL CONCAT() function as it is a VARIADIC function and takes a list of elements as input. The PostgreSQL CONCAT() function ignores the NULL input if passed, which means we can concatenate the strings even if one of the input strings from a list of arguments provided is NULL.
Syntax:
Consider the following syntax of the CONCAT() function:
CONCAT(string_1, string_2, ...)Explanation: The PostgreSQL CONCAT() function inputs an argument list.
How does PostgreSQL CONCAT() Function Work?
- The PostgreSQL CONCAT() considers each list element as an argument, as this function is a VARIADIC function that can take any number of elements as input.
- The input argument provided to the function should be string type or convertible to the string type.
- The string type means the input argument should be of any of the following data types:
- Varchar
- Char
- text
Examples
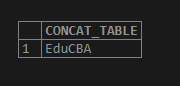
Consider the following example, which concatenates the two strings by using the PostgreSQL CONCAT() function. Illustrate the CONCAT function by using the following SELECT statement and a snapshot.
SELECT CONCAT ('Edu', 'CBA') as CONCAT_TABLE;Output:
We will create a table named ‘student’ by using the CREATE TABLE statement as follows:
create table student
(
stud_id serial PRIMARY KEY,
stud_fname VARCHAR(80) NOT NULL,
stud_lname VARCHAR(80) NOT NULL
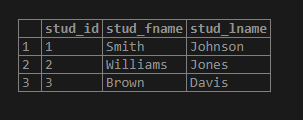
);We will insert some data into the student table using the following INSERT INTO statement.
INSERT INTO student(stud_fname,stud_lname)
VALUES
('Smith','Johnson'),
('Williams','Jones'),
('Brown','Davis');Illustrate the above INSERT statement’s result using the following SQL statement and snapshot.
select * from student;Output:
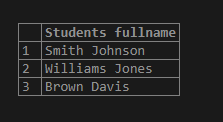
Using the following SQL statement and snapshot, we will concatenate the values of the stud_fname and stud_lname columns of the student table.
SELECT
CONCAT (stud_fname, ' ', stud_lname) AS "Students fullname"
FROM
Student;Output:
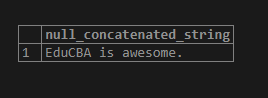
We can concatenate the NULL values with strings using the CONCAT() function using the following SQL statement and snapshot.
SELECT CONCAT('EduCBA is', NULL, ' awesome.') AS NULL_concatenated_string;Output:
We can see that the PostgreSQL CONCAT() function ignored the NULL string while joining the input arguments. At the same time, we will see the following SQL statement result, which uses the string concatenation operator (||) to concatenate the strings.
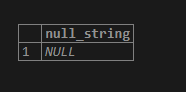
SELECT 'EduCBA is'|| NULL || 'awesome' AS NULL_string;Output:
We can see the returned result is a NULL string, whereas the CONCAT function worked properly to ignore the NULL string.
We can use the PostgreSQL CONCAT() function for various operations like we need to build a statement that will give us the resultant string by combining the following strings:
- ‘Student name is of.’
- Length if the student’s first name.
- ‘Characters.
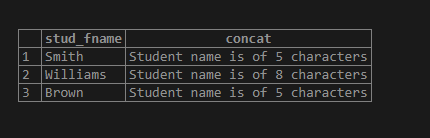
SELECT
stud_fname,
CONCAT('Student name is of ', LENGTH (stud_fname), ' characters' )
FROM
student;Output:
The PostgreSQL also provides the function named CONCAT_WS, which means concatenate with separator.
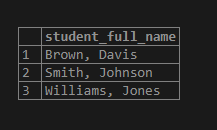
We will concatenate the stud_fname and stud_lname of the student table by using the following statement, which a single comma and space will separate.
SELECT
concat_ws (', ', stud_fname, stud_lname) AS student_full_name
FROM
student
ORDER BY
stud_fname;Output:
Advantages
- We can concatenate two or more strings using the string concatenation operator (||), which fails with NULL arguments where the CONCAT() function ignores NULL arguments concatenate them.
- The CONCAT() function is a variadic function that can take a list of the argument as input.
- We can build the required output string by concatenating more than one strings.
- The CONCAT() function operates on string type input only.
Recommended Articles
We hope that this EDUCBA information on “PostgreSQL CONCAT()” was beneficial to you. You can view EDUCBA’s recommended articles for more information.