Updated May 8, 2023
Definition of PostgreSQL SPLIT_PART()
PostgreSQL split_part function is used to split a string into nth substring by using a specified delimiter; the string’s splitting is based on a specified delimiter that we have used. Splitting the string using the split_part function starts from left to right; it will always split the string from left to right. This function requires three arguments as string, delimiter, and position. The string argument states that the string has been used to split, and a delimiter is used to split the string into the nth part. The position states which position string we want to return.
Syntax:
Below is the syntax of the split_part function in PostgreSQL.
Split_part (String, delimiter, Position)Select split_part (String (In this position column name as we have defined a string.), delimiter, Position), split_part (String (In this position column name as we have defined a string.), delimiter, Position), Column_nameN from table_name;Parameter:
Below is the parameter description of the above syntax.
- String: String states that which string we have used to split using a split_part function in PostgreSQL. We can use any of the strings to split it; we can also use a column name as a substring to split the data from the column.
- Split_part (): PostgreSQL split_part function is used to split a string into a specified delimiter and return into result as an nth substring, the splitting of the string is based on a specified delimiter which we have used.
- Delimiter: Delimiter splits the string into sub-parts using a split_part function in PostgreSQL. We can split the string into a number of parts using a delimiter.
- Position: Position in the split part function states which position string we want to return using the split_part function in PostgreSQL. The position will start from 1 and should not be negative; it is always a positive integer.
- Select: Select is used to select a table column using the split_part function in PostgreSQL. We can select a column using the split_part function and split column string.
- Column 1 to Column N: Column name used to get the information from the table. We can split the column data rows using the split_part function in PostgreSQL.
- Table name: In PostgreSQL, you can use the split_part function along with the table name to retrieve data from a specific column.
How PostgreSQL SPLIT_PART() Function Works?
Below is the working of the function.
- The split part function is very important and useful in PostgreSQL to split a string into nth parts.
- We must define a position value as a positive number; a negative value is not allowed in the position argument.
- We need to define a greater than zero value at the time using the split_part function in PostgreSQL.
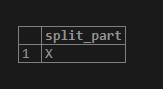
- In the below first example, we have used a position of 1; after using position 1, it will display the string’s value as X.
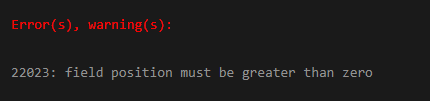
- Using values 0 and -1 will display the error as “ERROR: field position must be greater than zero”.
SELECT SPLIT_PART('X,Y,Z', ',', 1);SELECT SPLIT_PART('X,Y,Z', ',', -1);
SELECT SPLIT_PART('X,Y,Z', ',', 0);
- This function splits a string using a specified delimiter and returns the nth substring. The splitting of the string is based on the specified delimiter.
- The string argument states which string we have used to split using a split_part function in PostgreSQL. We can use any of the string to split it; we can also use a column name as a substring to split the data from the column.
- PostgreSQL uses the delimiter argument with the split_part function to split a string into sub-parts. We can split the string into a number of parts using a delimiter.
- The position argument in the split_part function specifies which part of the string we want to retrieve. The position will start from 1 and should not be negative; it is always a positive integer.
- Splitting the string using the split_part function starts from left to right; it will always split the string from left to right.
- It requires three arguments as string, delimiter, and position.
Example
- Below is an example of the split_part function in PostgreSQL as follows.
- We have used the example of the employee table to describe the example.
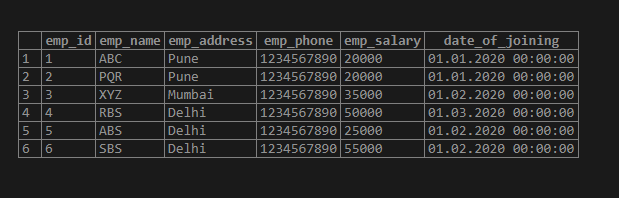
- Below is the employee table as follows.
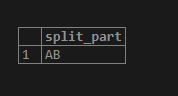
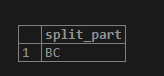
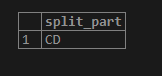
select * from employee;1. In the below example, we have split the ABBCCD string into three parts using a delimiter. In the first part, we have split the string as AB. The second part split it as BC, and in the third part, we split it as CD.
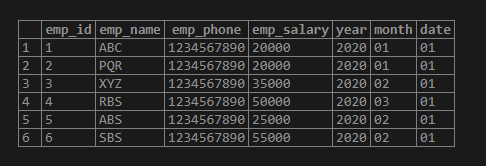
SELECT SPLIT_PART('AB,BC,CD', ',', 1);SELECT SPLIT_PART('AB,BC,CD', ',', 2);SELECT SPLIT_PART('AB,BC,CD', ',', 3);2. In the below example, we have split the date of joining column as year, month, and date wise into three columns.
SELECT emp_id, emp_name, emp_phone, emp_salary, split_part(date_of_joining::TEXT,'-',
1) AS Year, split_part(date_of_joining::TEXT,'-', 2) AS Month, split_part(date_of_joining::TEXT,'-', 3) AS Date FROM employee;In the above example, we have split the joining column’s date into three substrings: date, year, and month.
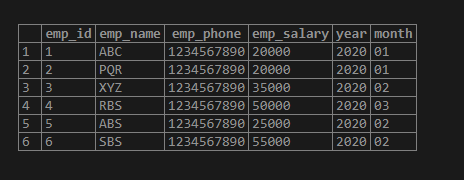
3. The example below shows only the month and year of the employee joining from the employee table.
SELECT emp_id, emp_name, emp_phone, emp_salary, split_part(date_of_joining::TEXT,'-',
1) AS Year, split_part(date_of_joining::TEXT,'-', 2) AS Month FROM employee;Advantages of Using SPLIT_PART() Functions in PostgreSQL
- In PostgreSQL, you can use the split_part function to split a string into its nth part.
- Using a split_part function, we can identify common data from the table column.
- We can increase data quality by using the split_part function in PostgreSQL.
- We can extract multiple substrings from one string in PostgreSQL.
- This function is essential and useful in PostgreSQL.
Conclusion
This function splits a string using a specified delimiter and returns the nth substring. The function uses the delimiter to determine the splitting point of the string. The split_part function requires three arguments as string, delimiter, and position.
Recommended Articles
We hope that this EDUCBA information on “PostgreSQL SPLIT_PART()” was beneficial to you. You can view EDUCBA’s recommended articles for more information.