Updated May 22, 2023
Introduction to PostgreSQL blob
PostgreSQL blob data type is defined as binary large object, basically blob data type is not available in PostgreSQL instead of blob we have using bytea data type. Blob data type in PostgreSQL is basically used to store the binary data such as content of file in PostgreSQL. The storage size of blob data type in PostgreSQL is 1 to 4 bytes plus the string of actual binary, input format of blob data type is different in PostgreSQL.
Syntax
Below is the syntax :
Create table name_of_table (name_of_column1 data_type, name_of_column2 data_type, name_of_column3 data_type, …, name_of_columnN bytea);Name_of_variable or name_of_column bytea;Alter table name_of_tableadd columnname_of_column bytea;Below is the parameter description syntax of blob/bytea data type in PostgreSQL:
- Create table: We create a table in PostgreSQL by using the “CREATE TABLE” statement and define the column with the data type “BYTEA”. We can create any table and defining data type as bytea to the column.
- Name of table: When creating a table in PostgreSQL, we define the name of the table and assign the “BYTEA” data type to the column. We can define bytea data type to the column at the time of table creation. Also, we are defining the data type as bytea after table creation using alter command.
- Name of column 1 to name of column N: This is defined as create a column on the table and defined bytea data type for the same.
- Data type: When creating a table in PostgreSQL, we assign the data type to the table column. We can define data type as per which data we are storing into the table.
- blob/bytea: The data type “BLOB”/”BYTEA” is specified when creating the column in the table. We store the binary data or file into the table using the blob data type.
- Name of variable: This is nothing but the column name which we used at the time of table creation.
- Alter table: We use the ALTER TABLE command in PostgreSQL to modify a table. With the ALTER command, we can change the data type of a column from one type to another.
- Add column: We use the ADD COLUMN command in PostgreSQL to add a new column to a table. In this case, we are adding a new column and defining its data type as BLOB/BYTEA.
How blob Data Type works in PostgreSQL?
- From PostgreSQL 7.2 version, we can store binary type of data into a table by using the bytea data type.
- The blob data type’s storage size is 1 to 4 bytes, but it depends on the string used at the time of insertion.
- For inserting data into the blob column, we need to create a function first. After creating the function, we call the same and restore data into the table.
- PostgreSQL supports the binary data type, but we need to be careful while using the same.
- At the time of insertion SQL statement in the blob data type column, we need to have a binary string with the values. Also, we have to escape some characters from the binary string as per the rules provided in PostgreSQL.
- In PostgreSQL, binary strings can be divided into character strings in two ways. PostgreSQL bytea supports two external format for output and input.
- Output format of bytea data type depends on the configuration parameter, the default value of bytea data type parameter is hex in PostgreSQL.
- There is no specific data type of blob available in PostgreSQL; instead of a blob, we are using a bytea data type.
Example:
Below example shows that we are using bytea data type instead of blob data type in PostgreSQL.
Code:
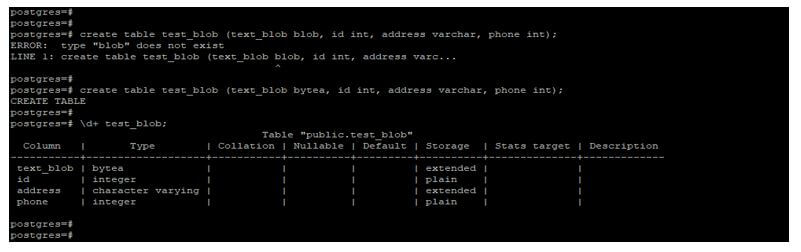
create table test_blob (text_blob blob, id int, address varchar, phone int);
create table test_blob (text_blob bytea, id int, address varchar, phone int);
\d+ test_blob;Output:
- In the above example, we have used the blob data type at the time of table creation, but it will issue an error that the blob data type does not exist.
- In the second example, instead of a blob, we have used bytea data type, using bytea data type, we have created a table. Using bytea data type, we can restore binary type data in PostgreSQL.
Examples
Given below are the examples mentioned :
Example #1
Create a table by using blob/bytea data type.
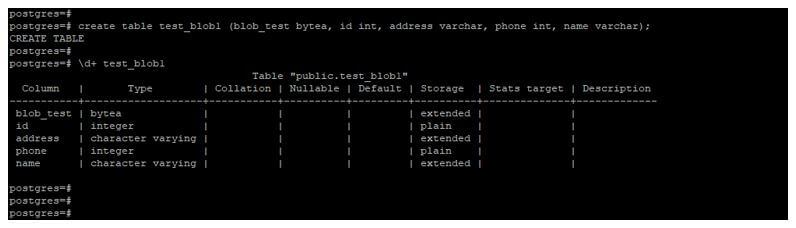
- Below example shows that create a table using blob/bytea data type.
- We have defined bytea data type to blob_test column.
Code:
create table test_blob1 (blob_test bytea, id int, address varchar, phone int, name varchar);
\d+ test_blob1Output:
Example #2
Create a table by defining blob/bytea data type on multiple column.
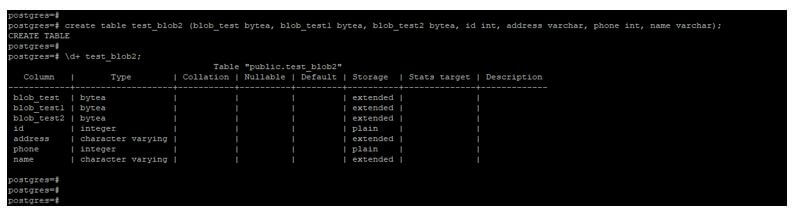
- Below example shows that create a table by using blob/bytea data type on multiple column.
- We have defined bytea data type to blob_test, blob_test1, and blob_test2 column.
Code:
create table test_blob2 (blob_test bytea, blob_test1 bytea, blob_test2 bytea,id int, address varchar, phone int, name varchar);
\d+ test_blob2Output:
Example #3
Add a new column and define the data type as blob/bytea.
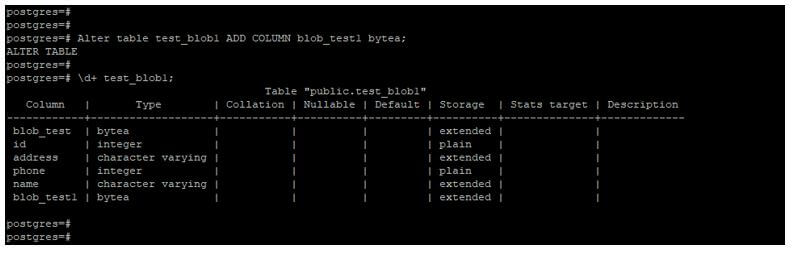
- Below example shows that add a new column and define the data type as blob/bytea.
- In the below example, we are adding the column name as blob_test1 and defining the data type as blob/bytea for the same.
Code:
Alter table test_blob1 ADD COLUMN blob_test1 bytea;
\d+ test_blob1;Output:
Recommended Articles
We hope that this EDUCBA information on “PostgreSQL blob” was beneficial to you. You can view EDUCBA’s recommended articles for more information.