Updated April 15, 2023

Introduction to PL/SQL Add Column
PL/ SQL add column statement is used the process of adding one or more new columns to the existing tables in PL/ SQL. We can make use of ALTER TABLE ADD COLUMN statement in PL/ SQL to add the new column or columns in a particular table. Note that the columns which we will be adding will get added at the end of the other columns present in the table. There is no manual method which will allow us to specify the position of the column that we want to add in the table when working with PL/ SQL in oracle unlike that of SQL.
In this article, we will learn about the syntax of adding single or multiple columns to an existing table in PL/ SQL and also study how we can confirm if the columns are added or not. Along with this, we will also study the implementation with the help of certain examples.
Syntax:
The syntax of adding a new column to an existing table in PL SQL with the help of ALTER TABLE command is as shown below –
ALTER TABLE name of table
ADD "name of column" "datatype of the column" "constraints if any"Alternatively, if you want to add more than one column using a single query statement then you can make the use of the following syntax –
ALTER TABLE name of table
ADD
("Name of column1" "datatype of the column" "constraints if any",
"Name of column2" "datatype of the column" "constraints if any",
…..
);In both of the above-mentioned syntaxes, the terminologies used are as explained here one by one –
name of table – This should be the name of the existing table in which you wish to add a new column in PL/ SQL. If the table with the specified name does not exist the command will throw an error saying No Table with such name exists in the database.
- Name of column – When you are trying to add a single column this should be specified for the name of the column that you wish to add to the table.
- Name of column1, Name of column2, … – While adding multiple columns to the existing table, you should specify the column names which are unique and which do not already exist in the table in which you are trying to add them.
- datatype of the column – This will be the datatype of the corresponding column of the table specifying the type of value that will be stored in the respective column. Most common datatypes used in PL/ SQL areVARCHAR2, NUMBER, TIMESTAMP, DATE, etc.
- constraints if any – You can specify any kind of restrictions that you want to apply on the column you are adding. For example, you can specify the NOT NULL constraint so that the column will never accept NULLL values for storing inside it or you can specify constraint as GENERATED BY DEFAULT AS IDENTITY for the column whose value will be auto-generated internally one by one which is mostly done for columns behaving as primary keys.
Note: If you will try to insert a column that already exists in the table then the query statement of adding the column will issue an error.
Examples of PL/SQL Add Column
Let us try to create one table named customer_details for storing customer data and demonstrating the use of ALTER TABLE ADD COLUMN command using the below query statement –
CREATE TABLE customer_details
( customer_id NUMBER(6)
, f_name VARCHAR2(20)
, l_name VARCHAR2(25)
, email_id VARCHAR2(100)
, mobile_number VARCHAR2(20)
, purchase_date DATE
, store_id VARCHAR2(20)
, bill_amount NUMBER(8,2)
, salesman_id NUMBER(6)
, department_id NUMBER(4)
);The execution of the above query statement gives the following output –
Suppose that we want to add the columns named birth_date and anniversary_date having the DATE datatype and NOT NULL constraint over them so that the column will not store NULL value in it. For this, we can make the use of the following query statement to add these two columns to our existing table customer_details –
ALTER TABLE customer_details
ADD
(birth_date DATE NOT NULL,
anniversary_date DATE NOT NULL);The execution of the above query statement gives the following output –
We can even add a single column by making the use of first syntax. Consider that we want to add the column named last purchased on with TIMESTAMP datatype. For this, we can make the use of the following query statement that follows the first syntax –
ALTER TABLE customer_details
ADD COLUMN last_purchased_at TIMESTAMP WITH TIME ZONE NOT NULL;The execution of the above query statement gives the following output:
Checking the addition of column –
In order to confirm if the table contains the column that you added, you can make use of the table user_tab_cols which contains the list of all the columns belonging to all the tables in our database. Suppose, you want to check if the column with the name last_purchased_at exist in you table or not. Then you can make the use of below query statement –
SELECT
COUNT(*)
FROM
user_tab_cols
WHERE
column_name = last_purchased_at'
AND table_name = 'customer_details';The output of the above query statement is as shown below retrieving 1 which means that there is one column with the specified name in our table –
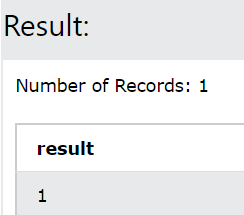
This functionality proves to be very helpful when you have to first check if the column exists or not and if doesn’t exit then add the column as shown in the below example –
SET SERVEROUTPUT ON SIZE 1000000
DECLARE
count_for_column NUMBER
BEGIN
SELECT count(*) INTO count_for_column
FROM user_tab_cols
WHERE column_name = 'expected_date_of_next_purchase'
AND table_name = 'customer_details';
IF (count_for_column = 0) THEN
EXECUTE IMMEDIATE 'ALTER TABLE customer_details ADD expected_date_of_next_purchase DATE';
ELSE
DBMS_OUTPUT.PUT_LINE('The column named expected_date_of_next_purchase already exists');
END IF;
END;When executed first time the program will give the following output –

But when we are trying to execute it again then the output will be as shown below saying that the column we are trying to add already exists.
Conclusion
The new column or columns can be added in PL/SQL Add Column with the help of ALTER TABLE ADD COLUMN command statement. We can even check if the column is added or not by retrieving the values from the table user_tab_cols.
Recommended Articles
We hope that this EDUCBA information on “PL/SQL Add Column” was beneficial to you. You can view EDUCBA’s recommended articles for more information.


