Updated March 1, 2023
Differences Between PIG vs MapReduce
Pig is a scripting language used for exploring large data sets. Pig Latin is a Hadoop extension that simplifies Hadoop programming by giving a high-level data processing language. As Pig is scripting we can achieve the functionality by writing very few lines of code. MapReduce is a solution for scaling data processing. MapReduce is not a program, it is a framework to write distributed data processing programs. Programs written using the MapReduce framework have successfully scaled across thousands of machines.
PIG
Pig is a Dataflow and High-Level Language. Pig works with any of the versions in Hadoop.
Components of Pig
- Pig Latin — a language used to express data flows
- Pig Engine — an engine on top of Hadoop
Advantages of PIG
- Removes the need for users to tune Hadoop
- Insulates users from changes in Hadoop interfaces.
- Increases in productivity.
- In one test 10 lines of Pig Latin ≈ 200 lines of Java
- What takes 4 hours to write in Java takes about 15 minutes in Pig Latin
- Open system to non-Java programmers
If we are aware of HIVE and PIG, there is no need to care about code, if the Hadoop version is upgraded to a higher version.
For example: if the Hadoop version is 2.6 now it is upgraded to 2.7. PIG supports in any versions no need to worry whether the code works or not in the Higher Versions.
Features of PIG
Pig Latin is a data flow language
- Provides support for data types – long, float, char array, schemas, and functions
- Is extensible and supports User-Defined Functions
- Metadata not required, but used when available
- Operates on files in HDFS
- Provides common operations like JOIN, GROUP, FILTER, SORT
PIG Usage scenario
- Weblog processing
- Data processing for web search platforms
- Ad hoc queries across large data sets
- Rapid prototyping of algorithms for processing large data sets
Who uses Pig
- Yahoo, one of the heaviest users of Hadoop, runs 40% of all its Hadoop jobs in a pig.
- Twitter is also another well-known user of Pig
MapReduce
- In the past, processing increasingly larger datasets was a problem. All your data and computation had to fit on a single machine. To work on more data, you had to buy a bigger, more expensive machine.
- So, what is the solution to processing a large volume of data when it is no longer technically or financially feasible to do on a single machine?
- MapReduce is a solution for scaling data processing.
MapReduce has 3 stages/Phases
The steps below are executed in sequence.
- Mapper phase
Input from the HDFS file system.
- Shuffle and sort
Input to shuffle and sort is an output of mapper
- Reducer
Input to the reducer is output to shuffle and sort.
MapReduce will understand the data in terms of only Key-value combination.
- The main purpose of the map phase is to read all of the input data and transform or filter it. The transformed or filtered data is further analyzed by business logic in the reduce phase, although a reduce phase not strictly required.
- The main purpose of the reducing phase is to employ business logic to answer a question and solve a problem.
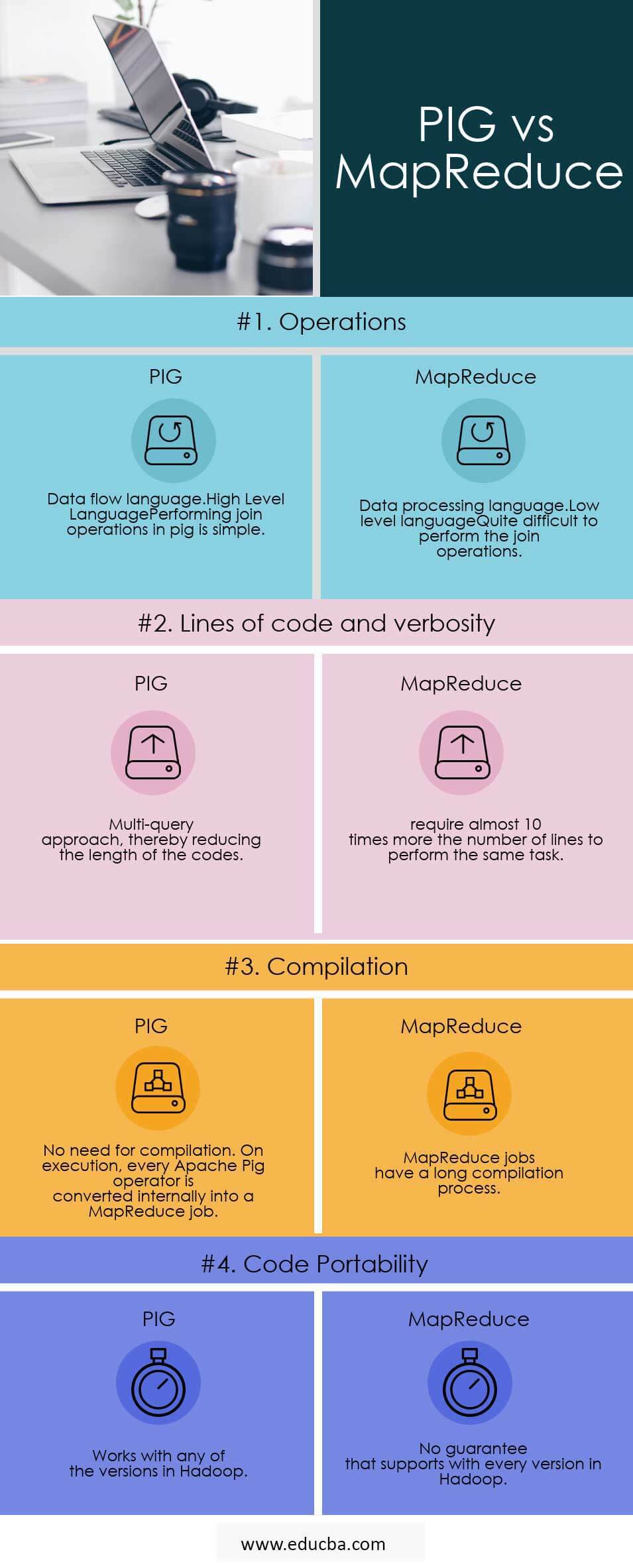
Head to Head Comparison Between PIG and MapReduce (Infographics)
Below are the Top 4 comparisons between PIG and MapReduce:
Key Differences Between PIG and MapReduce
Below are the most important Differences Between PIG and MapReduce:
PIG or MapReduce Faster
Any PIG jobs are rewritten in MapReduce.so, Map Reduce is only faster.
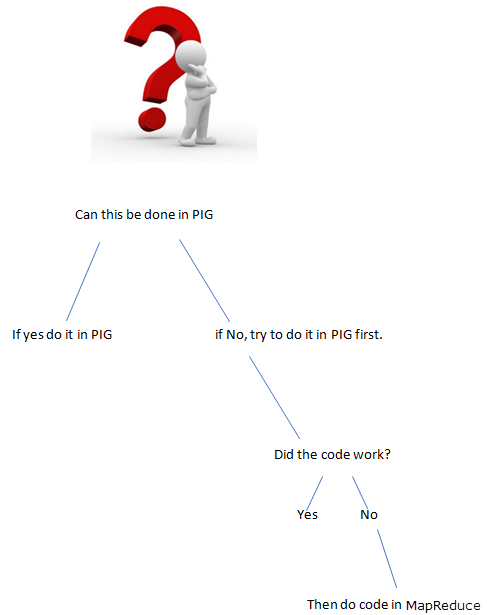
Things that can’t be in PIG
When something is hard to express in Pig, you are going to end up with a performance i.e., building something up of several primitives
Some examples:
- Complex groupings or joins
- Combining lots of data sets
- Complex usage of the distributed cache (replicated join)
- Complex cross products
- Doing crazy stuff in nested FOREACH
In these cases, Pig is going to slow down a bunch of MapReduce jobs, which could have been done with less.
Usage of MapReduce Scenarios
- When there is tricky stuff to achieve use MapReduce.
Development is much faster in PIG?
- Fewer lines of code i.e. smaller the code save the time of the developer.
- Fewer java level bugs to work out but these bugs are harder to find out.
In addition to the above differences PIG supports
- It allows developers to store data anywhere in the pipeline.
- Declares execution plans.
- It provides operators to perform ETL (Extract, Transform, and Load) functions.
Head to Head Comparison Between PIG and MapReduce
Below are the lists of points, describe the comparisons between PIG and MapReduce:
| Basis for comparison |
PIG |
MapReduce |
| Operations |
|
|
| Lines of code and verbosity | Multi-query approach, thereby reducing the length of the codes. | require almost 10 times more the number of lines to perform the same task. |
| Compilation | No need for compilation. On execution, every Apache Pig operator is converted internally into a MapReduce job. | MapReduce jobs have a long compilation process. |
| Code portability | Works with any of the versions in Hadoop | No guarantee that supports with every version in Hadoop |
Conclusion
Example: we need to count the reoccurrence of words present in the sentence.
What is the better way to do the program?
PIG or MapReduce
Writing the program in pig
input_lines = LOAD ‘/tmp/word.txt’ AS (line:chararray);
words = FOREACH input_lines GENERATE FLATTEN(TOKENIZE(line)) AS word;
filtered_words = FILTER words BY word MATCHES ‘\\w+’;
word_groups = GROUP filtered_words BY word;
word_count = FOREACH word_groups GENERATE COUNT(filtered_words) AS count, group AS word;
ordered_word_count = ORDER word_count BY count DESC;
STORE ordered_word_count INTO ‘/tmp/results.txt’;
Writing the program in MapReduce.
import org.apache.hadoop.fs.Path;
import org.apache.hadoop.io.IntWritable;
import org.apache.hadoop.io.Text;
import org.apache.hadoop.mapreduce.lib.input.FileInputFormat;
import org.apache.hadoop.mapreduce.lib.output.FileOutputFormat;
import org.apache.hadoop.mapreduce.Job;
public class WordCount {
public static void main(String[] args) throws Exception {
if (args.length != 2) {
System.out.printf(
“Usage: WordCount <input dir> <output dir>\n”);
System.exit(-1);
}
@SuppressWarnings(“deprecation”)
Job job = new Job();
job.setJarByClass(WordCount.class);
job.setJobName(“Word Count”);
FileInputFormat.setInputPaths(job, new Path(args[0]));
FileOutputFormat.setOutputPath(job, new Path(args[1]));
job.setMapperClass(WordMapper.class);
job.setReducerClass(SumReducer.class);
job.setOutputKeyClass(Text.class);
job.setOutputValueClass(IntWritable.class);
boolean success = job.waitForCompletion(true);
System.exit(success ? 0 : 1);
}
}
If the functionality can be achieved by PIG, what is use of writing functionality in MapReduce(Lengthy codes).
Always Use the right tool for the Job, get the job faster and better.
Recommended Articles
This has been a useful guide to PIG vs MapReduce.Here we have discussed head to head comparison, key differences along with infographics and comparison table respectively. You may also look at the following articles to learn more –