Updated March 24, 2023

Introduction to Pig Architecture
Let’s look into the Apache pig architecture which is built on top of the Hadoop ecosystem and uses a high-level data processing platform. Pig uses pig Latin data flow language which consists of relations and statements. Pig has a rich set of operators and data types to execute data flow in parallel in Hadoop. A pig can execute in a job in MapReduce, Apache Tez, or Apache Spark. Pig programs can either be written in an interactive shell or in the script which is converted to Hadoop jobs using Pig frameworks so that Hadoop can process big data in a distributed and parallel manner. Pig uses UDFs (user-defined functions) to expand its applications and these UDFs can be written in Java, Python, JavaScript, Ruby or Groovy which can be called directly. Now we will look into the brief introduction of pig architecture in the Hadoop ecosystem.
Pig Architecture With its Components
The following is the explanation for the Pig Architecture and its components:
Hadoop stores raw data coming from various sources like IOT, websites, mobile phones, etc. and preprocessing is done in Map-reduce. Pig framework converts any pig job into Map-reduce hence we can use the pig to do the ETL (Extract Transform and Load) process on the raw data. Apache pig can handle large data stored in Hadoop to perform data analysis and its support file formats like text, CSV, Excel, RC, etc.
Apache pig is used because of its properties like
- Ease of Programming: To make programming easy to write and understand most of the complex tasks are encoded as data flow sequences to achieve parallel execution.
- Optimization Opportunities: Pig gives permission to the system to optimize tasks automatically so that the programmer can achieve semantic efficiency.
- Extensibility: It provides UDFs so that the programmer can create their own function and for processing.
Apache Pig Framework
Apache pig framework has below major components as part of its Architecture:
- Parser
- Optimizer
- Compiler
- Execution Engine
The Architecture of Apache Pig
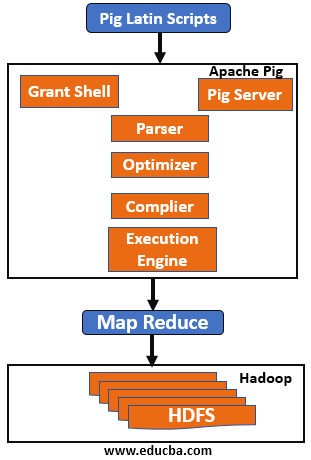
Let’s Look Into the Above Component in a Brief One by One:
1. Parser: Any pig scripts or commands in the grunt shell are handled by the parser. Parse will perform checks on the scripts like the syntax of the scripts, do type checking and perform various other checks. These checks will give output in a Directed Acyclic Graph (DAG) form, which has a pig Latin statements and logical operators. The DAG will have nodes that are connected to different edges, here our logical operator of the scripts are nodes and data flows are edges.
2. Optimizer: As soon as parsing is completed and DAG is generated, It is then passed to the logical optimizer to perform logical optimization like projection and pushdown. Projection and pushdown are done to improve query performance by omitting unnecessary columns or data and prune the loader to only load the necessary column.
3. Compiler: The optimized logical plan generated above is compiled by the compiler and generates a series of Map-Reduce jobs. Basically compiler will convert pig job automatically into MapReduce jobs and exploit optimizations opportunities in scripts, due this programmer doesn’t have to tune the program manually. As pig is a data-flow language its compiler can reorder the execution sequence to optimize performance if the execution plan remains the same as the original program.
4. Execution Engine: Finally, all the MapReduce jobs generated via compiler are submitted to Hadoop in sorted order. In the end, MapReduce’s job is executed on Hadoop to produce the desired output.
5. Execution Mode: Pig works in two types of execution modes depend on where the script is running and data availability :
- Local Mode: Local mode is best suited for small data sets. Pig is implemented here on single JVM as all files are installed and run on localhost due to this parallel mapper execution is not possible. Also while loading data pig will always look into the local file system.
Command to invoke grunt shell in local mode:
pig -x local
To run pig in tez local modes (Internally invoke tez runtime) use below:
pig -x tez_local
- MapReduce Mode (MR Mode): In MapReduce, the mode programmer needs access and setup of the Hadoop cluster and HDFS installation. In this mode data on which processing is done is exists in the HDFS system. After execution of pig script in MR mode, pig Latin statement is converted into Map Reduce jobs in the back-end to perform the operations on the data. By default pig uses Map Reduce mode, hence we don’t need to specify it using the -x flag.
Command to invoke grunt shell in MR mode:
pig -x mapreduce OR pig
Apart from execution mode there three different ways of execution mechanism in Apache pig:
- Interactive Mode Or Grunt Shell: Enter the pig statement and get the output in the command shell.
- Batch Mode or Script Mode: This is the non-interactive way of executing where programmer write a pig Latin script with ‘.pig’ extension and execute the same.
- Embedded Mode: Use programming languages like java in our script with the help of UDFs.
Pig Job Execution Flow
Below we explain the job execution flow in the pig:
- The programmer creates a Pig Latin script which is in the local file system as a function.
- Once the pig script is submitted it connect with a compiler which generates a series of MapReduce jobs
- Pig compiler gets raw data from HDFS perform operations.
- The result files are again placed in the Hadoop File System (HDFS) after the MapReduce job is completed.
Conclusion
We have seen here Pig architecture, its working and different execution model in the pig. based on the above architecture we can see Apache Pig is one of the essential parts of the Hadoop ecosystem which can be used by non-programmer with SQL knowledge for Data analysis and business intelligence. A pig is a data-flow language it is useful in ETL processes where we have to get large volume data to perform transformation and load data back to HDFS knowing the working of pig architecture helps the organization to maintain and manage user data.
Recommended Articles
This is a guide to Pig Architecture. Here we discuss the basic concept, Pig Architecture, its components, along with Apache pig framework and execution flow. You can also go through our other related articles to learn more –


