Updated March 4, 2023
Introduction to Permute Matlab
‘Permute’ command in Permute Matlab is used to rearrange the elements within a multidimensional array. To access this command we just need to pass the order of the multi-dimensional matrix. It has various features like dimension, size, circshift, and reshape. Permute command can be implemented for a reverse condition which is specified by ‘ipermute’. permute and permute are two conditions of the transpose. The output of permuting is always transposed of the output of permute and output of permuting is always transposed of the output of ipermute.
Syntax
Below is the syntax for Permute Matlab:
Output = permute( input, [ 2 1 ] )
Output variable name = permute ( input variable name, order of dimension )
Output = ipermute ( input, [ 1 2 3 ] )
Output variable name = ipermute ( input variable name, order of dimension )
Why we use Permute Matlab?
The main principle of permuting is to rearrange the elements of multi-dimensional matrix .so while solving matrix or multidimensional problems but if we face size overfitting or underfitting issues then we can use permute and ipermute commands. It reduces the complexity of the system and helps to understand the problem in a better way.
Examples to Implement Permute Matlab
Below are the examples mentioned :
Example #1
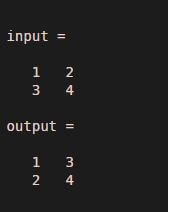
Let us assume one matrix input with two rows and two columns. Row 1 elements are 1 and 2 and row 2 elements are 3 and 4. And let us give the order as 2 and 1.
Code:
clc ;
clear all ;
input = [ 1 2 ; 3 4 ]
output = permute ( input, [ 2 1 ] )
Output:
Example #2
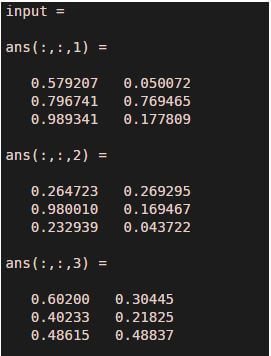
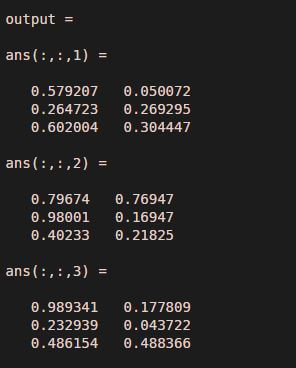
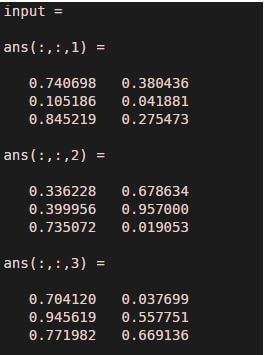
In this example, we randomly created an input matrix with three rows and two columns and there are three such matrices. Along with the input we have pass order as [ 3 2 1]. Implementation of example 2 (a) shows permute command and example 2 (b) shows ipermute command. If we observe both the outputs then the output of example 2(b) is the transpose of the output of Example 2 (a) and vice versa.
a. permute command
Code:
clc ;
clear all ;
rng default
input = rand ( 3 , 2 , 3 )
output = permute ( input, [ 3 2 1 ] )
Output:
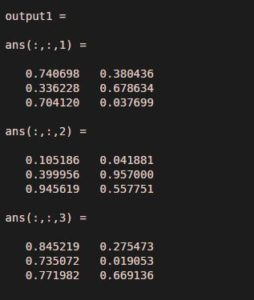
b. ipermute command:
Code:
clc ;
clear all ;
rng default
input = rand(3,2,3)
output1 = ipermute ( input , [ 3 2 1 ] )
Output:
Example #3
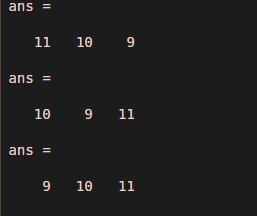
In this example, we will use one feature of the permuted matrix that is size. Here we consider one random input of parameters ( 9, 1 0, 1 1) which represents a total eleven matrix, nine rows, and 10 columns. here we have changes order three times to check the size of the output matrix. Assume three orders as [ 3 2 1 ] , [ 2 1 3 ] and [ 1 2 3 ]. If we observe the output of three matrix and sizes of three matrices then all the dimensions are different.
Code:
clc ;
clear all ;
rng default
input = rand ( 9, 10, 11) ;
output = permute ( input, [ 3 2 1 ] ) ;
output1 = permute ( input , [ 2 1 3 ] ) ;
output2 = permute ( input, [ 1 2 3 ] ) ;
size ( output)
size ( output1)
size ( output2)
Output:
Conclusion
In this article, we have seen how to use permute and ipermute command and how to arrange elements in matrix or multidimensional array or vector. By using permute command we can handle large data and n number of elements.
Recommended Articles
This is a guide to Permute Matlab. Here we discuss an introduction to Permute Matlab, syntax, and implementation with programming examples. You can also go through our other related articles to learn more –