Updated July 3, 2023

Introduction to Perl bless function
In Perl, bless function is a built-in function that can be defined as a function for marking any variable in the program as an object of a particular class using this function which takes a class name and reference to which this object refers to which class and internally informs the Perl compiler as the variable that is passed to this bless function is marked variable as an object of any particular class.
Working of bless() function in Perl with examples
In this article, we will discuss a built-in function where to make the program understand that the variable can be made an object of a particular class in Perl, where this function is known as the bless() function. Unlike in other programming languages, Perl creates an object similar to creating or declaring variables. Therefore the Perl programming language provides a built-in function called bless() function, which makes the variable look like an object of the particular class that it belongs to.
Now let us see the syntax and examples of how the bless() function works in the below example.
Syntax:
bless var_ref, class_name;Parameters:
- var_ref: this parameter refers to the variable as an object of the class whose class name is specified.
- class_name: This parameter specifies the class name to which the object is created by marking the variable reference as an object of this class specified in this parameter.
This function can take only var_ref as an argument also, and this function returns the reference of the marked variable as a reference to an object blessed into a particular or specified class name as specified in the arguments passed to the function.
Examples
Now let us see a simple example of demonstrating the bless() function in the below section.
Example #1
Code:
use strict;
use warnings;
print "Demonstration of bless() function in Perl.";
print "\n";
print "\n";
package student_data;
sub stud
{
my $class_name = shift;
my $var_ref = {
'stud_first_name' => shift,
'stud_course_name' => shift,
'stud_age' => shift,
};
print "The bless() function is now implemented:";
print "\n";
bless $var_ref, $class_name;
return $var_ref;
}
print "Object creation";
print "\n";
print "\n";
my $info = stud student_data("Alen","Python",32);
print "The student's name is :";
print "\n";
print "$info->{'stud_first_name'}\n";
print "\n";
print "The course name student taken is:";
print "\n";
print "$info->{'stud_course_name'}\n";
print "\n";
print "The student's age is :";
print "\n";
print "$info->{'stud_age'}\n";
print "\n";Output:
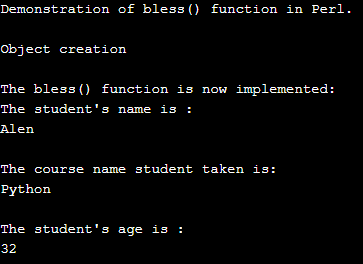
In the above program, we can see we have defined class “stud” using a keyword package in Perl. Then we created a subroutine to print the student’s details. In this variable, we are referring each variable to the class name using the variable reference to object creation and class name as arguments in the bless() function in the above program. Then we are printing each value of the objects created.
Now we will see bless function taking only one argument and two arguments in the example below.
Example #2
Code:
use strict;
use warnings;
print "Demonstration of bless() function in Perl.";
print "\n";
print "\n";
package student_data;
sub stud
{
my $class_name = shift;
my $var_ref = {
'stud_first_name' => shift,
'stud_course_name' => shift,
'stud_age' => shift,
};
print "The bless() function is now implemented:";
print "\n";
bless $var_ref;
return $var_ref;
}
package Employee;
sub emp {
my $class2 = shift;
my $var_ref2 = {
'emp_firstName' => shift,
'emp_lastName' => shift,
'emp_epn' => shift,
};
bless $var_ref2, $class2;
return $var_ref2;
}
print "Object creation";
print "\n";
print "\n";
print "Bless function takes only one argument:";
print "\n";
print "\n";
my $info = stud student_data("Alen","Python",32);
print "The student's name is :";
print "\n";
print "$info->{'stud_first_name'}\n";
print "\n";
print "The course name student taken is:";
print "\n";
print "$info->{'stud_course_name'}\n";
print "\n";
print "The student's age is :";
print "\n";
print "$info->{'stud_age'}\n";
print "\n";
print "Bless() function takes two argument:";
print "\n";
print "\n";
my $per_info = emp Employee("Ram", "Shukla", 343);
print "The employee's name is :";
print "\n";
print "$per_info->{'emp_firstName'}\n";
print "\n";
print "The employee's second name student taken is:";
print "\n";
print "$per_info->{'emp_lastName'}\n";
print "\n";
print "The employee's employee number is :";
print "\n";
print "$per_info->{'emp_epn'}\n";
print "\n";Output:
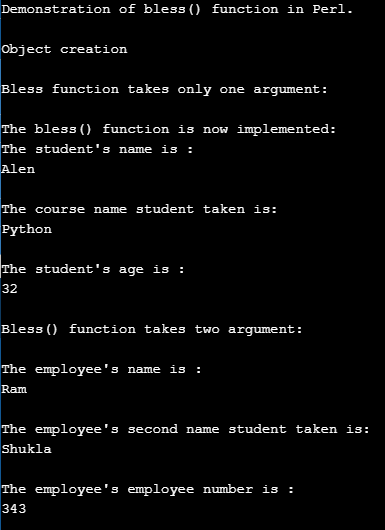
In the above program, we can see we have declared two classes “student_data” and “Employee” wherein the class “Student_data” we have defined function bless() with the single argument so when the variables reference is only passed, it will by default, take only the values of its current class but not of the “employee” class.
Conclusion
In this article, we conclude that the bless() function is a built-in function in Perl for marking the variables reference to object creation which belongs to the particular class with its class name specified as an argument in the bless() function. In this article, we have seen examples of bless() function taking two arguments and what happens if there are two classes and the class name is not specified as an argument in the function, which will, by default, take the current class name.
Recommended Articles
This is a guide to Perl bless. Here we discuss the introduction and Working of bless() function in Perl with examples for better understanding. You may also have a look at the following articles to learn more –


