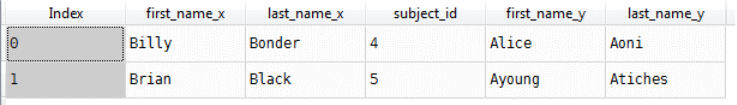Updated April 11, 2023
Difference between Pandas Merge vs Join
Pandas is the most effective and widely used library in python programming because of its dynamic functionality. A Data Frame is a two-dimensional Datatype in pandas where multiple operations are performed. It is a Datatype that is arranged in a Table format with Rows and columns that has index values. Merge and join are two operations that are widely used to perform table merging and combing new tables with desirable data through a common key column or Index. df.merge() and df.join() are the two basic codes that are used to merge and join a Data Frame. There are various other such operations like concat, df.concat(), and append, df.append() also exist in pandas, but here we will discuss Merge and join operation. In this topic, we are going to learn about Pandas Merge vs Join.
Head to Head Comparison Between Pandas Merge vs Join (Infographics)
Below are the top differences between Pandas Merge vs Join
Key Differences of Merge vs Join
Pandas Merge and join operation is an effective in-memory operation that is good in performance when we are working with a large volume of Data. Like the join operation in SQL pandas merge and join operation has different kinds of joins such as “inner”, “outer”, “left”, “right” joins. They are performed with a common column or a key in different Data Frames.
Both Pandas merge and join has similar functionality and scope which is to combine and extract two or more Data Frames but the way both operations is performed is different for both Pandas merge and join. Let’s look at some of the key differences between both.
- The basic difference between merge and join operation comes from the key or a common code which is been used by the two operations. For pandas join whenever we give a command to like df1.join(df2) the joining takes place at the index level of df2. The index will be the key to joining the Data Frames.
- Whereas in Merge when we give a command like pd.merge(df1, df2) it looks for common columns in the df1 and df2 Data Frames and we can join it with one or more columns.
- By default, Pandas join will work on the joining via the index of the Data Frames and we can make it perform a column join by giving
df1.join(df2, on =Key/column name)
- On the other hand, pandas merge on default join via a column of Data Frames and we can make it perform index join by giving
Pd.merge (df1, df2, right_index=True)
- Pandas merge on default performs an “inner join”
- Pandas merge on default performs a “left join”
Let’s look at some of the examples of how Pandas Merge and Join function works.
Pandas Merge:
The basic structure of the Pandas merge command is
pd.merge(left, right, how='inner', on=None, left_on=None, right_on=None, left_index=False, right_index=False, sort=True)
Example:
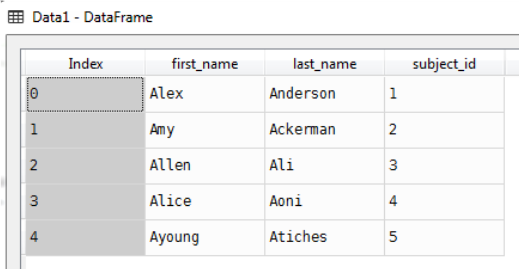
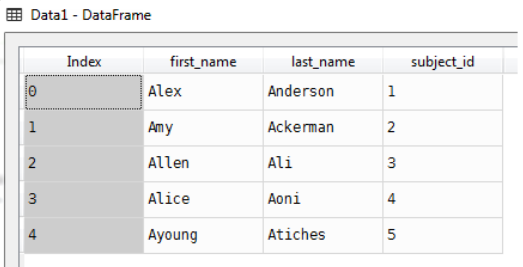
raw_data_1 = {
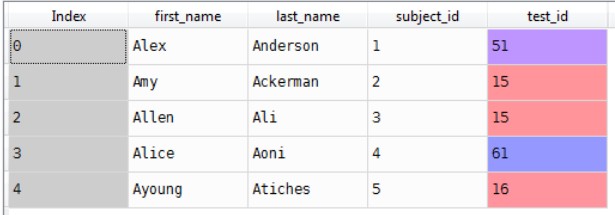
subject_id': ['1', '2', '3', '4', '5'],
'first_name': ['Alex', 'Amy', 'Allen', 'Alice', 'Ayoung'],
'last_name': ['Anderson', 'Ackerman', 'Ali', 'Aoni', 'Atiches']}
Data1=pd.DataFrame(raw_data_1)
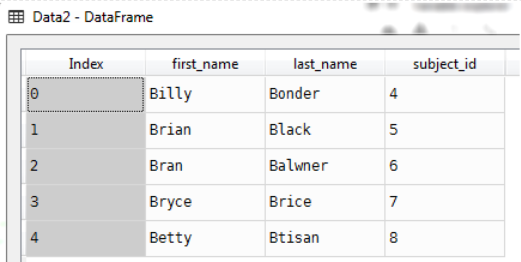
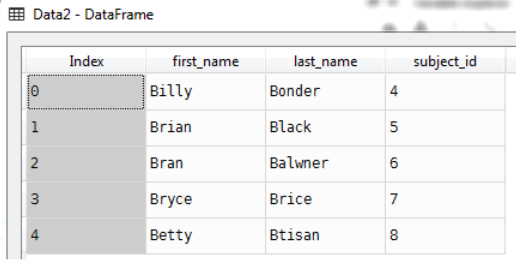
raw_data_2 = {
'subject_id': ['4', '5', '6', '7', '8'],
'first_name': ['Billy', 'Brian', 'Bran', 'Bryce', 'Betty'],
'last_name': ['Bonder', 'Black', 'Balwner', 'Brice', 'Btisan']}
Data2=pd.DataFrame(raw_data_2)
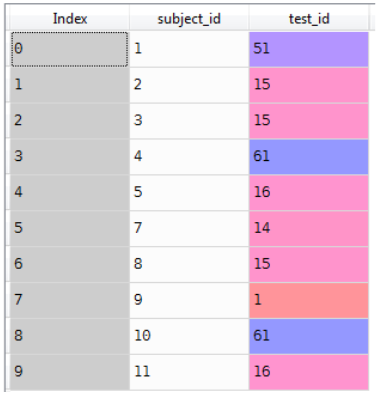
raw_data_3 = {
'subject_id': ['1', '2', '3', '4', '5', '7', '8', '9', '10', '11'],
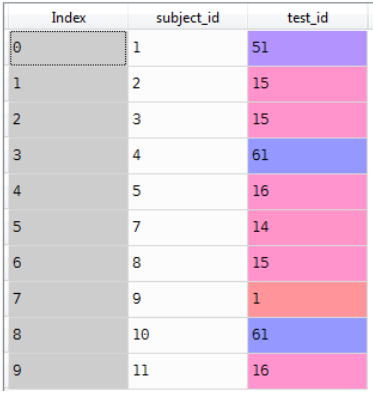
'test_id': [51, 15, 15, 61, 16, 14, 15, 1, 61, 16]}
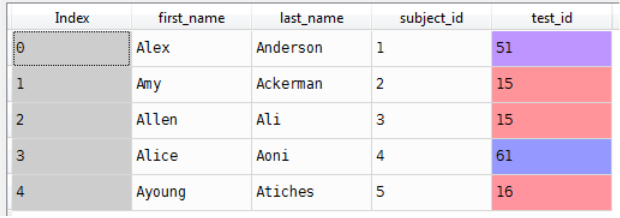
Data3=pd.DataFrame(raw_data_3)
Data1
Data2
Data3
Now let’s perform different merge operation on the three Data Frames,
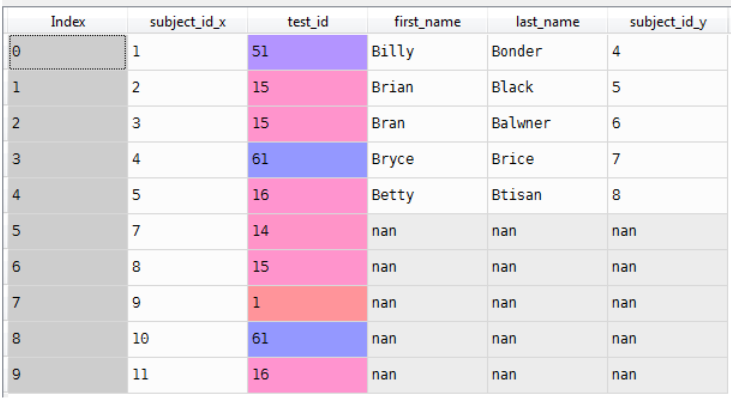
merg_1=pd.merge(Data1,Data3,on='subject_id')
Result:
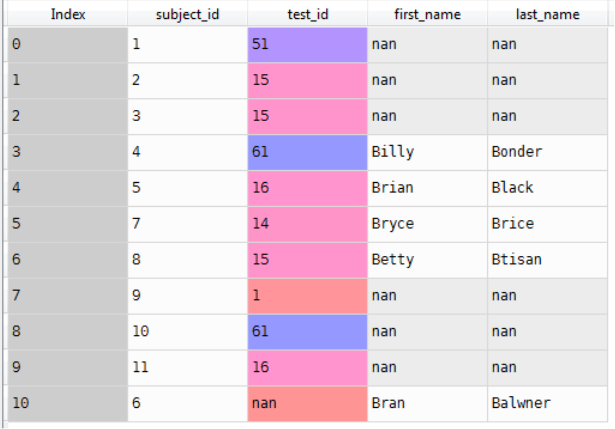
merg_2=pd.merge(Data2,Data1,how='inner',on='subject_id')
Result:
merg_3=pd.merge(Data3,Data2,how='outer',on='subject_id')
Result:
merg_4=pd.merge(Data3,Data2,how='left',right_on=None, left_index=True, right_index=True)
Pandas Join:
Basic Pandas Join command is
DataFrame.join(self, other, on=None, how='left', lsuffix='', rsuffix='', sort=False)
Example:
Data1
Data 2
Data 3
Join Types
1. Index join
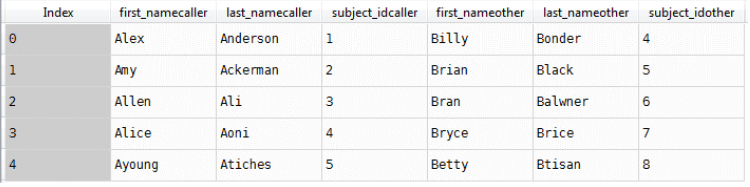
join_1=Data1.join(Data2,lsuffix='caller',rsuffix='other')
Result
2. Column Join
3. On Join
join_2= Data1.join(Data3.set_index('subject_id'), on='subject_id',lsuffix='caller',rsuffix='other')
Result
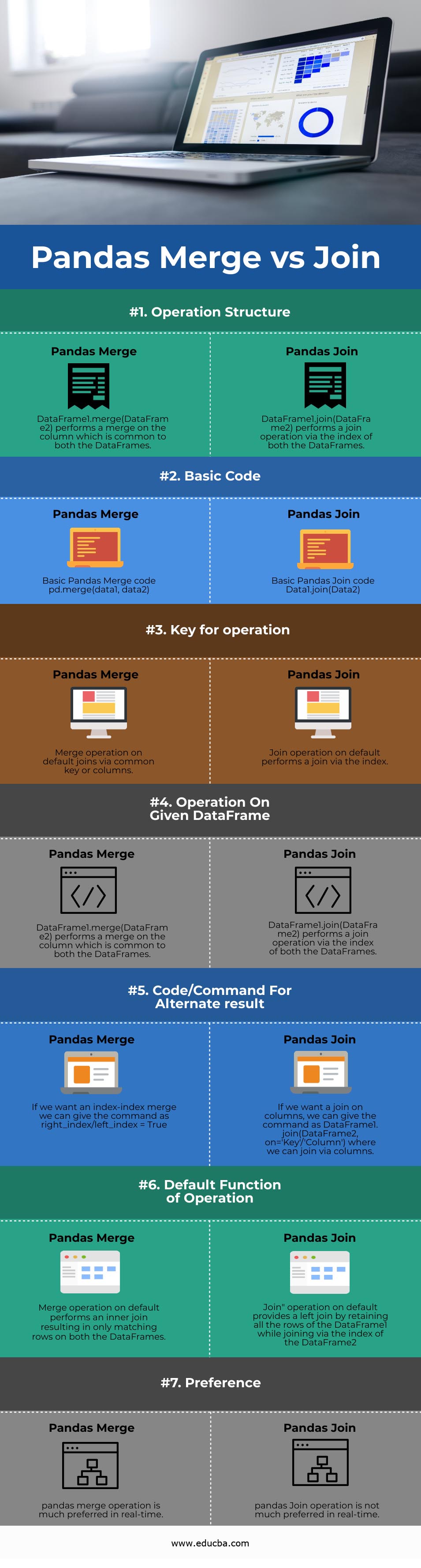
Comparison Table of Pandas Merge vs Join
Now let’s draft the comparison between Pandas Merge vs Join in a table below
| Basis of Comparison | Pandas Merge | Pandas Join |
| Operation Structure | DataFrame1.merge(DataFrame2) performs a merge on the column which is common to both the DataFrames.
|
DataFrame1.join(DataFrame2) performs a join operation via the index of both the DataFrames.
|
| Basic Code | Basic Pandas Merge code
pd.merge(data1, data2) |
Basic Pandas Join code
Data1.join(Data2) |
| Key for operation | Merge operation on default joins via common key or columns | Join operation on default performs a join via the index |
| Operation
On Given DataFrame |
DataFrame1.merge(DataFrame2) performs a merge on the column which is common to both the DataFrames.
|
DataFrame1.join(DataFrame2) performs a join operation via the index of both the DataFrames.
|
| Code/Command
For Alternate result |
If we want an index-index merge we can give the command as
right_index/left_index = True
|
If we want a join on columns, we can give the command as DataFrame1.join(DataFrame2, on=’Key’/’Column’) where we can join via columns.
|
| Default Function of Operation | Merge operation on default performs an inner join resulting in only matching rows on both the DataFrames. | Join” operation on default provides a left join by retaining all the rows of the DataFrame1 while joining via the index of the DataFrame2 |
| Preference | pandas merge operation is much preferred in real-time. | pandas Join operation is not much preferred in real-time. |
Conclusion
As we discussed both the operation as a dynamic functionality and provides easier operation when working with DataFrame datatypes. DataFrames are the most widely used data types in the Data Science world. Both the operation provides greater value and highly optimized operations. Although similar to SQL join operation pandas merge and join operation is much faster and very compatible and handles large data. On the whole both Merge and Join operations are mostly similar in their capabilities.
In the real-world Scenario, pandas merge operation is much preferred to join because of the basic and simple query structure and can perform direct column-wise joining of the table. In cases where we want to exclude the columns and if we want to join only on the index of the DataFrames we can go with the merge join operation since it has slightly lesser code to type.
Recommended Articles
This is a guide to Pandas Merge vs Join. Here we discuss the Pandas Merge and Join key differences with infographics and comparison table. You may also have a look at the following articles to learn more –