Updated March 17, 2023

Introduction to Palindrome in C++
A palindrome is a number, sequence or a word that reads the same backward as forwards. Madam In Eden, I’m Adam is one of the best examples of palindrome words that sounds the same after reversing. This is where palindrome makes things interesting they act as mirrors. The name ‘palindrome’ actually means running back again according to Greek etymology. In C++ palindrome number is a number that remains the same after reverse. But how is this possible? How will we check if a number is too big and complex? Always keep in mind this small algorithm to check if a number is a palindrome or not.
- Get the input number from the user.
- Hold it in a temporary variable.
- Reverse the number.
- After reversing compare it with a temporary variable.
- If same then the number is a palindrome.
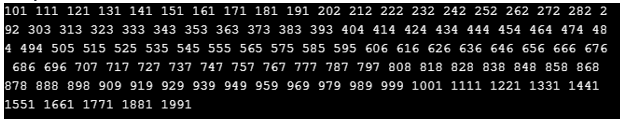
Don’t worry here is an example suppose we have to print palindromes between the given range of numbers. For example range is {10,122} then output should be {11, 22, 33, 44, 55, 66, 77, 88, 99, 101, 111, 121}
How to Implement palindrome in C++?
Below are the different examples to implement palindrome in c++.
Example #1
Code:
#include<iostream>
using namespace std;
// Function to check if a number is a palindrome or not.
int Palindrome(int n)
{
// Find reverse of n
int reverse = 0;
for (int i = n; i > 0; i /= 10)
reverse = reverse*10 + i%10;
// To check if they are same
return (n==reverse);
}
//function to prints palindrome between a minimum and maximum number
void countPalindrome(int minimum, int maximum)
{
for (int i = minimum ; i <= maximum; i++)
if (Palindrome(i))
cout << i << " ";
}
// program to test above functionality
int main()
{
countPalindrome(100,2000);
return 0;
}Output:
Let’s take one more example specifically using a while loop that will also explain the algorithm we discussed in the introduction. We will take a number as an input from the user and check if it is a palindrome or not.
Example #2
Let us check if a number is a palindrome or not by using the C++ program.
Code:
#include <iostream>
using namespace std;
int main()
{
int n,sum=0,temp,reverse;
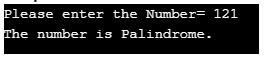
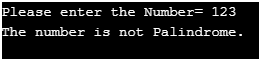
cout<<"Please enter the Number=";
cin>>n;
temp=n;
while(n>0)
{
reverse=n%10;
sum=(sum*10)+reverse;
n=n/10;
}
if(temp==sum)
cout<<"The number is Palindrome.";
else
cout<<"The number is not Palindrome.";
return 0;
}Output:
The above code will take a number as an input from the user and put it into a temporary variable as you can see that sum is already 0 it will use a while loop until the number becomes 0 and as the code is written it will perform the operation as written after while loop. If the number becomes 0 then it will check if the temporary variable is equal to the sum or not. If the condition satisfies then it will print that the number is palindrome otherwise if the condition fails it will go to else part and will print that the number is not a palindrome.
One more example using a do-while loop will also explain the algorithm we discussed in the introduction. We will take a number as an input from the user and check if it is a palindrome or not.
Example #3
Let us check if a number is a palindrome or not by using C++ program.
Code:
#include <iostream>
using namespace std;
int main()
{
int x, number, reverse = 0, temp ;
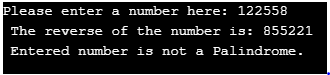
cout << "Please enter a number here: ";
cin >> number;
x = number;
do
{
temp = number % 10;
reverse = (reverse * 10) + temp;
number = number / 10;
} while (number != 0);
cout << " The reverse of the number is: " << reverse << endl;
if (x == reverse)
cout << " Entered number is a Palindrome.";
else
cout << " Entered number is not a Palindrome.";
return 0;
}Output:

Advantages
Following are the advantages mentioned.
- Suppose that in your project you want to match the first string/element with the last one then the second element/string to the second last one and so on and the string will be palindrome if you reach to the middle. By just using for loop you can perform all the operations and it saves a large amount of time and space when it comes to programming because in this case, you neither have to modify the existing string nor write another variable to memory. Also, the matches required in completely equal to half of the string length.
- If you are working on a programming language where string reversal is easy but it will require an extra amount of space to store that reverse string in another way such as recursion require more stack frame. There is one more way rather than recursion and that is writing a loop in the middle of the string to check if the corresponding letter at each end is the same or not. If unequal then break the pair early and declare the string as not a palindrome.
- The above approach has the advantage of not wasting any computational resources such as recursion, without needing extra stack frames, but it’s also not simple as just reversing the string and checking the equality between them. It does take effort but it will always be less than other algorithms because that is the simplest way to find a palindrome.
- Each technique has its benefits in programming and there are thousands of other ways of doing the same task but in an efficient way. It completely depends upon the current project you are working on. You only have to decide according to your situation that which technique will help you give the best benefits irrespective of the drawbacks.
- In a real project, you need to perform n number of palindrome checks on a frequent basis in a short span of time then you should implement the above algorithm in the first place until and unless you require a more optimistic solution for current technical constraints.
Conclusion
By using a palindrome algorithm you can make your search more efficient and faster in finding palindromes irrespective of data types such as string character or integer. For projects that have multiple data in the different systems, these algorithms can be used to make overall performance much faster.
Recommended Articles
This is a guide to Palindrome in C++. Here we discuss the basic concept, C++ program to check and implement the Palindrome with advantages in detail. You may also look at the following article to learn more –


