Difference Between Packet Switching and Circuit Switching
Packet switching is a channel addressed with packets for data transmission. Packet switching is a routing method and grouping the data as packets to transfer in a channel, where the packet channel can be made available for the next transfer in network traffic. It basically occupies the channel in traffic so that the packets containing can be transferred to the network’s routed address. To deliver the data correctly, Packets are structured with header and payload in it. Header – Used for directing the data packets to destination and Payload – Used for data extraction, and it’s the core data. Packet switching is referred to as message switching. In the data transmission, any messages exceeding the maximum limit will be broken into smaller units, and that smaller unit is considered as packets.
Circuit switching is entirely different from packet switching. Because the path is very dedicated to the entire data transmission. Though the data is transmitted or not, it ensures that the establishment is made in advance for communicating. This results in bandwidth wastage, and switches are not released until the source ensures the network that communication is complete. The example for circuit switching is a telephone conversation; the established connection gets over only when the caller and receiver end the call line.
Head to Head Comparison between Packet Switching and Circuit Switching (Infographics)
Below are the top 13 comparisons between Packet Switching vs Circuit Switching:
Key differences between Packet Switching and Circuit Switching
Let us discuss some key differences between Packet Switching vs Circuit Switching in the following points:
1. Circuit switching is dedicated during connection and keeps unavailable for other users until the linkage ends. Packet switching follows such a tradition that the communication type between the senders and receiver is connectionless. When the data are transmitted, the communication is broken down into packets, and it shares the same data path with various users in the same network is called connectionless.
2. Originally, circuit switching is designed for voice communicating purpose and packet switching is designed for data communication.
3. In packet switching, the packet has the intelligence to find its destination path using routers when a linkage is broken or the packets are lost. So this is resilient that packets can transfer efficiently in traffic where circuit switching cannot track when the packet gets lost.
4. Packet switching is network efficient as each packet identifies its own path to reach the destination, and it does not require any dedicated connection for transmission. Where circuit switching requires and sets specific path and path won’t be changed till the session ends.
5. Packet switching is cost-effective and scalable as the packets efficiently use the data transmission path and links are managed efficiently, and bandwidth is not wasted where circuit switching wastes the bandwidth irrelevant to data transmission.
6. In packet switching, it is so reliable in networking where the packets are not lost in transmission. Because the packets are numbered, it can reassemble at the receiver end, though it travels in the different communications paths. Where circuit switching is sent in the order in a path; packets cannot be arranged if it gets lost in the communication path.
7. Packet switching is a connectionless protocol that is used when the transmission doesn’t require any prior setup for packet transfer. Circuit switching is a connection-oriented protocol that is used for complex data transactions. Prior setup is made and routed from source to destination. The delay time is the same as the data transfer time in connectionless switching.
Comparison Table of Packet Switching vs Circuit Switching
The table below summarizes the comparisons between Packet Switching vs Circuit Switching:
| Basis of Comparison between Packet Switching vs Circuit Switching | Packet Switching | Circuit Switching |
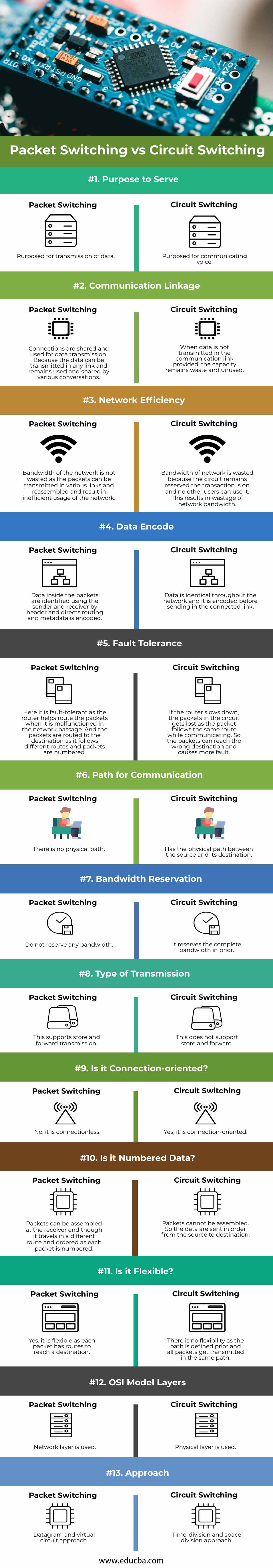
| Purpose to Serve | Purposed for transmission of data. | Purposed for communicating voice. |
| Communication Linkage | Connections are shared and used for data transmission. Because the data can be transmitted in any link and remains used and shared by various conversations. | When data is not transmitted in the communication link provided, the capacity remains waste and unused. |
| Network Efficiency | The bandwidth of the network is not wasted as the packets can be transmitted in various links and reassembled and resulted in inefficient usage of the network. | The bandwidth of the network is wasted because the circuit remains reserved; the transaction is on, and no other users can use it. This results in wastage of network bandwidth. |
| Data Encode | Data inside the packets are identified using the sender and receiver by header and directs routing, and metadata is encoded. | Data is identical throughout the network, and it is encoded before sending in the connected link. |
| Fault Tolerance | Here it is fault-tolerant as the router helps route the packets when it malfunctions in the network passage. And the packets are routed to the destination as it follows different routes and packets are numbered. | If the router slows down, the packets in the circuit get lost as the packet follows the same route while communicating. So the packets can reach the wrong destination and causes more fault. |
| Path for Communication | There is no physical path. | Has the physical path between the source and its destination. |
| Bandwidth Reservation | Do not reserve any bandwidth. | It reserves the complete bandwidth in prior. |
| Type of Transmission | This supports store and forward transmission. | This does not support the store and forward. |
| Is it Connection-oriented? | No, it is connectionless. | Yes, it is connection-oriented. |
| Is it Numbered Data? | Packets can be assembled at the receiver end though it travels in a different route and ordered as each packet is numbered. | Packets cannot be assembled. So the data are sent in order from the source to destination. |
| Is it Flexible? | Yes, it is flexible as each packet has routes to reach a destination. | There is no flexibility as the path is defined prior, and all packets get transmitted in the same path. |
| OSI Model Layers | The network layer is used. | The physical layer is used. |
| Approach | Datagram and virtual circuit approach. | Time-division and space division approach. |
Conclusion
Both Packet Switching and Circuit Switching are very essential and used as converged technologies in wider networks. And it has evolved over a period and optimized for greater efficiency. It is also checked whether the network can handle the connections and suits up for infrastructure or not. It is also essential that quality is maintained over the communication in the network. With all criteria in a row, packet switching stands higher than circuit switching.
Recommended Articles
This is a guide to the top differences between Packet Switching vs Circuit Switching. Here we also discuss the key differences with infographics and comparison table. You may also have a look at the following articles to learn more –