What is Overloading in C++?
To achieve compile-time polymorphism, the C++ programming language provides an overloading feature that allows for an overload of the two or more methods with the same name but different parameters. It can be performed by using function overloading and operator overloading. Function overloading overloads the two or more functions with the same name but different parameters, whereas operator overloading overload operators provide special meaning to the user-defined data types.
This feature allows using built-in operators on user-defined types. Operator overloading simplifies the code by redefining the functionality as per the user requirements. This article will focus on both the function overloading and the operator overloading; we will see the details of it and how it is used in C++.
C++ allows writing flexible and easy to understand code using the concept know as Overloading. It allows achieving different functionality within the existing code with very minimal changes, thus reducing the duplicate code. Basically, there are mainly two primary types of overloading that C++ supports.
C++ allows us to write functions with the same name but with the difference in datatypes or in the number of arguments passed to it; this feature is known as Function Overloading in C++. This feature allows developers to define the functions with the same name within the same scope. With the same name, the functions represent the same functionality, thus allowing to achieve compile-time polymorphism. The function overloading has one advantage that it improves the readability of the code.
Types of Overloading in C++
Below are the types mentioned:
- Function Overloading: It allows us to define the function with the same name, but it distinguishes the functions depending upon the type of parameters passed to them, or the number of parameters passed to them. So, all the functions will have the same name but will have either a different data type or a different number of parameters passed to it. When the function is called, the compiler will choose the function with the matching type of parameter and matching the number of arguments. Now its developers can choose which function to call according to the requirements. They can choose the appropriate function by passing the parameters following the rules.
- Operator Overloading: It allows operators to work for user-defined data types, i.e. classes. The existing operators are overloaded and given the power to operate on the user-defined class and objects. Operator overloading is achieved by defining the function with the special name. The function will have the name ‘operator’ followed by the operator symbol. We can use the operator symbol directly on the user-defined data type and perform the operation. The necessary action or operation is defined in that special function by us. By means of operator overloading, we can perform operations of different types on the same type of data type.
How does Overloading work in C++?
Function Overloading can be achieved in anyways in terms of usage of parameters. When we say usage of parameters, it refers to a type of parameters or count of parameters or sequence of parameters. So, function calc (int x, float y) having parameters (int x, float y) is different from a function defined as calc (float x, int y), which have different parameters with the different datatype.
There can be a number of types in which function overloading can be achieved; let’s see the simple example of function overloading in C++.
#include <iostream>
using namespace std;
class Display {
public:
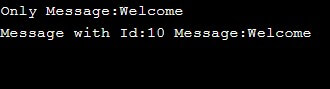
static void show (char message[] ) {
cout<< "Only Message:" << message << endl;
}
static void show (int messageId, char message[]) {
cout<< "Message with Id:";
cout << messageId << " Message:" << message << endl;
}
};
int main (void) {
Display obj;
char message[] = "Welcome";
int messageId = 10;
obj.show(message); //calling overloaded function with 1 parameter
obj.show(messageId, message);//calling overloaded function with 2 parameters
return 0;
}Here, we have class Display which has an overloaded method show. The show method will be called depending upon the arguments passed to it.
Output:
Operator overloading can be achieved on almost all the built-in data types available in C++. There is no such different types of operator overloading, but the approaches can be different to achieve operator overloading. Operators such as Unary, Binary, Relational, Assignment, etc., can be overloaded in C++.
Let’s see the simple example of overloading of ++ operator. In this example, instead of primitive data type, we will use the ++ operator on the user-defined class object.
#include <iostream>
using namespace std;
class Bike {
private:
int height;
public:
Bike (): height (80) {} //constructor which initializes the height variable
void operator ++() {
height = height + 5;
}
void Specs () {
cout << "The height of the bike is: " <<height <<endl;
}
};
int main(void)
{
Bike bike;
bike.Specs();
++bike; //calling overloaded operator
bike.Specs();
return 0;
}So, we have an object whose initial height will be set at 80 and will be increased by 5 when we call ++ operator over it.
Output:
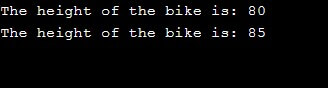
Rules of Overloading in C++
Below are the different C++ overloading rules as follows:
Rules for the function overloading
- In function overloading, the function must differ in terms of data type, number or sequence of parameters. It cannot differ simply on the basis of the return type of function.
Rules for the operator overloading
- Only built-in operators can be overloaded; the new operators cannot be overloaded.
- There are four operators which cannot be overloaded, these are . (member selection), :: (scope resolution), .* (member selection using pointer to function) and ?: (ternary operator).
- The overloaded operator will contain at least one operand of the user-defined data type.
- There are certain operators that cannot be overloaded by using the friend function, but they can be overloaded as a member function.
Conclusion
So, the overloading in C++ is a unique feature that provides multiple advantages to us. There are mainly two types of overloading, i.e. function overloading and operator overloading. Function overloading improves the code readability, thus keeping the same name for the same action. Operator overloading allows redefining the existing functionality of operators, thus by giving special meaning to them. Both are very useful in programming in C++.
Recommended Articles
This is a guide to Overloading in C++. Here we discuss its working rules and two types of overloading in c++, i.e. function overloading and operator overloading. You may also look at the following article to learn more –


