Updated March 4, 2023
Introduction to Oracle XMLTABLE
Oracle XMLTABLE function is a new function added to Oracle since Oracle 10g along with other function like XQuery to its collection of XML handling APIs. Here, the XQuery will let you construct the XML data as well as relational data and query XML using the XQuery language. But the XMLTABLE function in Oracle is responsible for creating the relational tables and its columns from Oracle XQuery command query results. Generally, the XMLTABLE function will return the content of any XML document or maybe any element present in a relational table format structure. XMLTABLE is a SQL/XML function that is implemented in the FROM clause of a SQL but in combination with a driving table that contains the XML data for translating the XML data to a relational form. Hence, using this Oracle XMLTABLE function one can retrieve several information from the XML data.
Syntax
The basic syntax for the XMLTABLE function is explained below:
XMLTABLE(‘<XQuery>’ PASSING <xml Table_column >
COLUMNS <New_Table_Column_Name> <Column Type> PATH <XQuery path>)
The XMLTABLE function comprises one row-generating XQuery expression and in the clause COLUMNS, there exists one or more than one column-generating expression.
Before practicing the Oracle XMLTABLE function, we should know first about the XPath, where XPath implements a path expression for selecting nodes as well as a list of nodes from an xml document. Here, is the list of beneficial paths and expression which can be applied for selecting any node or nodelist from an xml document.
Expression Description
Nodename Picks all nodes having the name ‘nodename’
/ Chooses from the root node
// Picks nodes in the document from the present node which equals the choice no matter where they are
. Picks the present node
.. Picks the parent of the present node
@ Chooses attributes
Table_element Picks all nodes with the name ‘Table_element’
Table_Name/Table_Element Chooses all table elements that are offspring of table
//Table_Element Picks all table elements no matter where they exist in the document
Also, a list of predicates is stated in square brackets [….] which are applied to discover a particular node or a node that covers a definite value.
Path Expression Result
/table_name/table_element[1] Picks the initial table element which is known to be the child of the table element.
/table_name/table_element[last()] Picks the last table element which is known to be the child of the table element.
/table_name/table_element[last()-1] Picks the last but a single table element which is known to be the child of the table element.
//table_element[@type=’admin’] Picks all the table elements which hold an attribute named type having a value of ‘admin’.
How XMLTABLE function works in Oracle?
- The XMLTABLE operator in Oracle permits a user to fragment the XML data ahead into table rows and project table columns on to it. For this, a Cartesian product is effectually created concerning the data table and the XMLTABLE call that permits the XMLTABLE for splitting an XML document in one row into more than one row present in the final result of execution.
- The table column will be recognized as the source of data using the PASSING clause. Here, the table rows are recognized through an XQuery expression separated with a slash symbol. After that, the columns are predictable onto the resulting XML fragments using the table COLUMNS clause that detects the appropriate tags through the path expression and allots the preferred table column names with the respective data types.
- We should be cautious with the column names provided in the clause COLUMNS. If anything is applied other than the upper case, then they may be required to be mentioned for making a straight reference to them. It should be noticed that it is being queried using the alias of the XMLTABLE call somewhat than the consistent table alias.
Examples
Let us illustrate with few instances the Oracle XMLTABLE function using several expressions of XPath for fetching few info from the XML document as below:
XMLTABLE = (XML_namespaces_clause, XQuery_string,XMLTABLE _options)
This describes the XMLTABLE structure where the XML_namespace_clause consists as a set of XML namespace declarations that are referenced by the provided XQuery expression (XQuery_string) further computing the row and with the XPath expression in the clause PATH of the XML_Table_Column, for computing the columns for the whole XMLTABLE function.
Reading Ordernum and Orderdate of all orders
We will query the command below applying the XMLTABLE function for parsing the XML content from the person table as created which also includes few XML data:
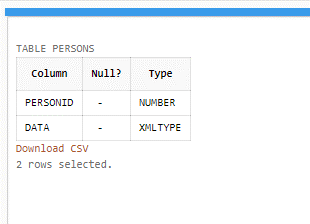
CREATE TABLE Persons (PersonID NUMBER, data XMLTYPE);
After running the query, the table will be ready to be operated.
Output:
So, firstly let us enter few records into it using the INSERT statement and a record with XML data type in it as:
INSERT INTO Persons VALUES(1, xmltype(‘<Persons>
<Person pcode=”111” type =”admin”>
<personname>Nikhil</personname>
<profile>Engineer</profile>
<age>30</age>
<mailid>[email protected]</mailid>
</Person>
<Person pcode=”112” type =”admin”>
<personname>Sahil</personname>
<profile>Teacher</profile>
<age>31</age>
<mailid>[email protected]</mailid>
</Person>
<Person pcode=”113” type =”user”>
<personname>Divya</personname>
<profile>Executive</profile>
<age>28</age>
<mailid>[email protected]</mailid>
</Person>
</Persons>’));
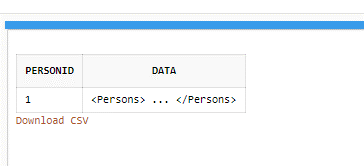
We can view the contents of table Persons as;
SELECT * FROM Persons;
Output:
The XML includes the person-related data thus, now we will apply the Oracle XMLTABLE function for retrieving any information from this created XML document using the XPath and XQuery string expressions as follows:
SELECT t.PersonID, x.* FROM Persons t, XMLTABLE ('/Persons/Person' PASSING t.data COLUMNS Personname VARCHAR2 (30) PATH ‘text()’ ) x WHERE y.PersonID =1;
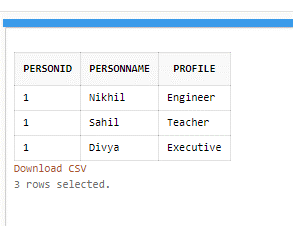
Here, the server reads the content of node Personname/age/profile/mailid where also sometimes we need to fetch the text value of the presently selected node item. So, in the above query, we have chosen the path as /Persons/Person/personname, and with the use of expression text() we will receive the value of this node. Therefore, the result will read the names of personname and related profiles of entire persons in the table using the XMLTABLE function in Oracle.
SELECT t.PersonID, x.* FROM Persons t, XMLTABLE ('/Persons/Person' PASSING t.data COLUMNS Personname VARCHAR2 (30) PATH 'personname',Profile VARCHAR2(30) PATH 'profile' ) x WHERE t.PersonID =1;
Output:
Conclusion
- Oracle XMLTABLE function and operator functions actually well with small XML documents or database tables along with several rows where each one includes an insignificant XML document.
- Again, whenever the XML documents get superior then the performance of the server becomes worse as equated to the manual parse technique. But when dealing with these big XML documents, the user might have to relinquish the accessibility for the XMLTable operator in favor of a labor-intensive resolution.
Recommended Articles
This is a guide to Oracle XMLTABLE. Here we discuss How the XMLTABLE function works in Oracle along with the examples and outputs. You may also have a look at the following articles to learn more –