Updated May 19, 2023
Introduction to Oracle GRANT
An Oracle GRANT clause is a Data Control language statement. It is employed to grant certain rights to users. By using the Grant command, more users can access the database. For database security, it is employed. Data Control Language (DDL) is what it is. By establishing and specifying distinct Schema Objects and granting them the necessary Privileges, databases are made secure. The Oracle Grant command can be used to grant the privileges. When the database needs to be shared with additional users, the grant command is used. Other users receive a particular set of rights. On Oracle Table objects, Views, Synonyms, Indexes, Sequences, etc., Grant instructions can be issued. A user may receive several privileges in a single Grant command. The database owner or the object’s owner can issue a Grant command on the object. A user with the ADMIN Option or the Grant Any Privilege role has the ability to issue a Grant command on an object.
Syntax
Below is the syntax for Oracle GRANT:
GRANT<PrivilegeName_1>, <PrivilegeName_2>ON<ObjectName>TO<UserName / Role>;
Explanation:
PrivilegeName_1/ _2/ _N: It can be a privilege name.
ObjectName: Object name can be an Oracle object i.e. Table, Views, Synonyms, Indexes, Sequence, etc.
Username: User that will receive the privilege.
Role: It’s not a user, but it’s a group of privileges that can be assigned to a User or another Role.
How does GRANT command work in Oracle?
The GRANT clause is used to prevent performing any unnecessary operation of the object by other users. Grant command allows that specific user to perform that specific or granted operation on that specific Oracle object so that an unknown user cannot access any object or data.
List of Some Commonly used Privileges:
below is the list of used privileges:
| Type of Privilege | Description |
| SELECT | It allows users to perform SELECT statements on that object. |
| INSERT | It allows users to perform INSERT records on that object. |
| UPDATE | It allows users to perform UPDATE records on that object. |
| DELETE | It allows users to perform DELETE records on that object. |
| REFERENCES | It allows users to create a constraint that refers to that object. |
| ALTER | It allows users to perform ALTER TABLE statements to change that object definition. |
| EXECUTE | It allows users to compile or execute Function / Procedure directly. |
| INDEX | It allows users to create an index on that object with the create index statement. |
| ALL | It provides all access to users. |
Examples to Implement Oracle GRANT
Implementations of GRANT command with Examples:
In this section, we’ll see the implementation of Oracle GRANT Command and its behavior. For that, we will create a user to understand the Oracle GRANT command behavior.
1. Oracle CREATE privilege
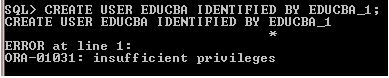
Step 1: The current session logged on as a SCOTT user and tried to create a new user.
Code:
CREATE USER EDUCBA IDENTIFIED BY EDUCBA_1;
Output:
Explanation: In the above example, a Scott user tried to create a new user, but it returned an error “insufficient privileges”. Because the user (Scott) doesn’t have the privilege to create a new user for the DB.
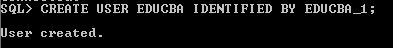
Step 2: Now connected to the current session as an SYSDBA. It’s like an admin role to the DB. Now will try to create a user in this session.
Code:
CREATE USER EDUCBA IDENTIFIED BY EDUCBA_1;
Output:
Explanation: Now user (EDUCBA) is created successfully. So privileges are essential for the users to perform any operation on DB. But the user EDUCBA doesn’t have any privilege, even if it does not have to create session privilege, and because of that user is unable to log on to the DB.
Step 3: To log on to the DB, the user needs to create session privileges.
Code:
GRANT CREATE SESSION TO EDUCBA;
Output:
Explanation: In the above query, SYSDBA provided a Create session privilege to EDUCBA. Now user “EDUCBA” is successfully created a session and logged into DB.
TIP: In the same way, object owners can GRANT privileges to users.
2. How to Check Received Privileges
All the privileges received by the user ‘EDUCBA’ or any other user can be checked. For that, the user needs to log on and run the below SQL query.
Code:
SELECT * FROM USER_SYS_PRIVS;
Output:
Explanation: In the above example, the user “EDUCBA” has only created session privileges. So EDUCBA cannot access or perform any operation except create a session.
Code:
SELECT * FROM Employee;
Output:
Explanation: In the above example, user “EDUCBA” tries to access an object ‘Employee’ and returns an error because the user does not have any privilege except create a session. To access objects or perform any operation, it requires respective privileges.
TIPS: Instead of providing privileges to users, better to create a Role, assign PRIVILEGES to that Role, and then Grant that Role to multiple Users and Roles.
Roles reduce the effort to provide privileges one at a time to users. The syntax for Role creation is below:
CREATE ROLE<RoleName>IDENTIFIED BY<Password>;
Revoke is used to remove the privileges from users or Roles.
Conclusion
Oracle GRANT command is a very useful command to allow users to perform specific operations on the specific object. This is also very useful for security purposes. Without the privilege, users are not authorized to operate on the DB objects.
Recommended Articles
We hope that this EDUCBA information on “Oracle GRANT” was beneficial to you. You can view EDUCBA’s recommended articles for more information.