Updated July 4, 2023
Definition of Oracle SYS_GUID()
SYS_GUID () function in oracle database can be defined as a built-in function in PL/SQL, which is used to generate and return a global unique identifier (GUID) (RAW value) of size 16 bytes for each row of the table, and it does not accept any argument in the function, it generates GUID which is supposed to be unique meaning they should never be repeated twice, and it also consists of a host identifier a process or thread identifier of the process which invoked the function.
Syntax:
In the previous section, we discussed the definition of the function. In this section, we will discuss the syntax of the function. Let us go through the syntax of this function below.
SYS_GUID()
One important point to remember is that this function takes no argument.
How SYS_GUID() Works in Oracle?
In this section, we will discuss the working of sys_guid built-in function in the Oracle database. This function generates unique identifiers that are of type RAW, and it is a 128-bit number or 16 bytes in size. So when we execute the function SYS_GUID it generates a 128-bit number which is unique, which means it is not the same as the previous numbers it generated. It relies on a combination of components to make sure it is unique every time. A UUID consists of a reference to the network address of the host who generated the UUID, a timestamp (the exact time in which it was generated), and the last component is a randomly generated component. The network address and the timestamp of the exact time when the number was generated help in making the number always generated a unique number, and the last component also help in contributing to the uniqueness of the number. The combination of these three components helps the function to generate a unique number every time.
Examples of Oracle SYS_GUID()
In the previous sections, we discussed the working of the sys_guid (), and now in this section, we are going to discuss a few examples.
1. SYS_GUID() with Dual
In the first example, we are going to generate a Unique identification number using this function. So, let us prepare the query for the same.
Query:
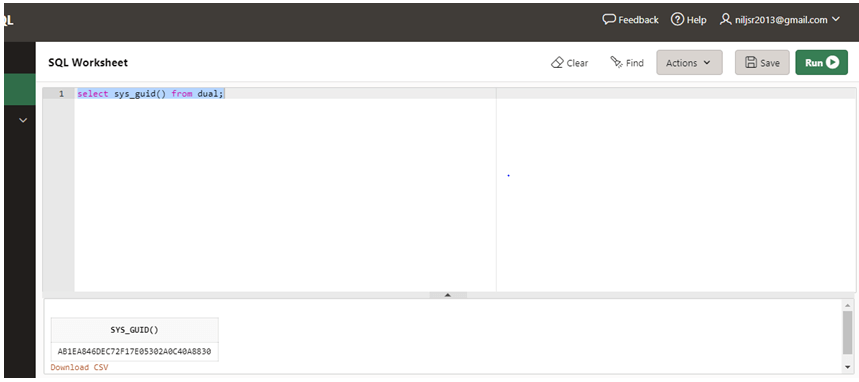
SELECT sys_guid() from DUAL;
In the above query, DUAL is one row and one-column table present by default in the Oracle database. It is accessible to all users by the name DUAL.
Let us now run the query in the SQL worksheet and check the result.
As we can see in the above screenshot, a unique 128-bit or 16-byte number has been generated.
2. Insert a Unique Id in A Column Using SYS_GUID
In the previous example, we created a unique identifier using the function. We can also use this function to insert a unique identification number in columns of a table. In this example, we will insert a random unique number in the employee id column present in the table employee. The employee id column is the primary key of the table. We will use the function SYS_GUID for this purpose. Let us prepare an INSERT query for the same.
Query:
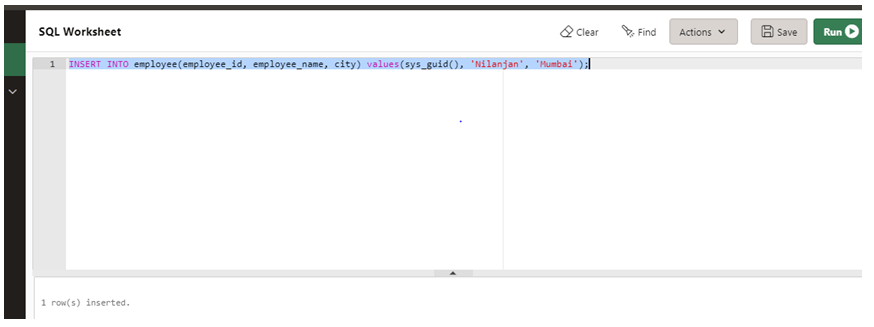
INSERT INTO employee(employee_id, employee_name, city) values(sys_guid(), 'Nilanjan', 'Mumbai');
In the above query, we are using the sys_guid() function for the employee_id column. Let us execute the query in the SQL worksheet and check the result.
As we can see on the screenshot, a row has been inserted successfully.
Let us now check the data in the employee table and verify. Let us prepare a SELECT statement for the same.
Query:
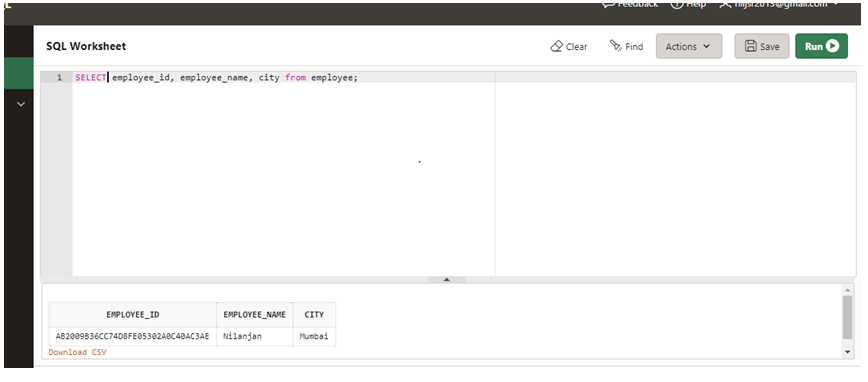
SELECT employee_id, employee_name, city from employee;
As we can see in the above screenshot, the employee id consists of a 16-byte or 128-bit Unique Identification Number. Hence, we can use this function to generate primary numbers.
3. Update a Unique Id in A Column Using SYS_GUID
In the previous example, we discussed that we can insert a primary key using the SYS_GUID function. In this example, we will check how to update the value of an existing column using this function. Just as we used in the previous example to INSERT a unique Identification Number, Similarly we will use the same function to update the value of a column with a unique number. Let us prepare an UPDATE statement for the same.
Query:
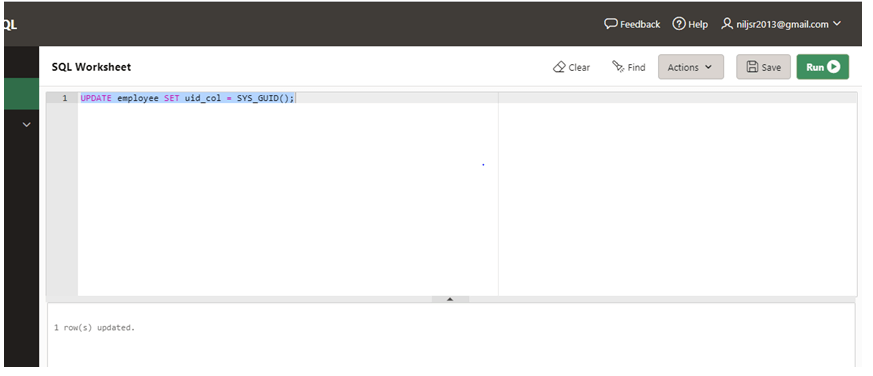
UPDATE employee SET uid_col = SYS_GUID();
Let us execute the query in the SQL worksheet and check the result.
As we can see in the screenshot above, the row has been updated. Let us now check the data in the employee table and verify. Let us prepare a SELECT statement for the same.
Query:
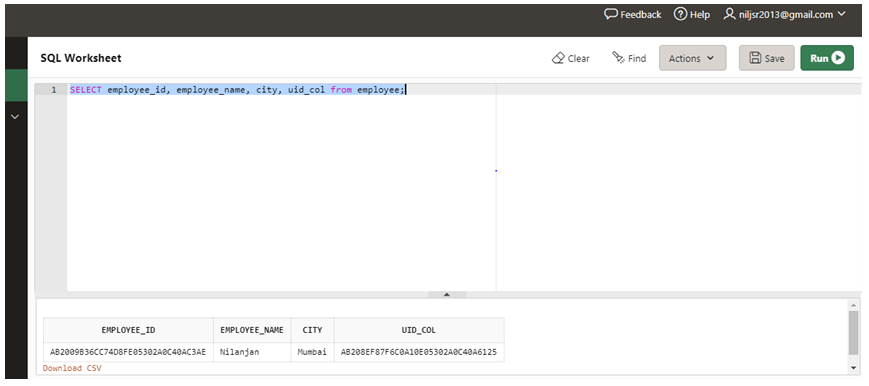
SELECT employee_id, employee_name, city, uid_col from employee;
Let us now execute the above query in the SQL worksheet and verify the result.
As we can see in the above screenshot, the UID_COL shows a unique number generated from the function SYS_GUID ().
Advantages
In the above section, we discussed a few examples to get a better understanding of using this function. Now, we will discuss the advantages of using this function. This function can be used as a default value for a primary key. This function can be used as an alternative instead of a sequence which we generally use. The numbers generated are always unique because the number generated from this function consists of three parts: a reference to the network address of the host who generated the UUID, a timestamp, and the last component is a randomly generated component which means that it will always be unique. One important point to note is that the numbers generated are not sequential but generally random, and it also reduces contention for hot blocks, and we cannot perform arithmetical operations.
Conclusion
In this article, we discussed the definition of the topic SYS_GUID() at the beginning of the article. Later we discussed the syntax of the function and the working of the function. We discussed a few examples and ended the article with the advantages of this function.
Recommended Articles
This is a guide to Oracle SYS_GUID(). Here we also discuss the definition and how sys_guid() works in Oracle? along with different examples and code implementation. You may also have a look at the following articles to learn more –