Updated February 28, 2023
Introduction to Oracle REGEXP
The following article provides an outline for Oracle REGEXP. Oracle Regular Expression is a technique which is used to represent a group of strings according to a particular format / pattern. Regular Expression is a declarative mechanism to represent a group of string. Regular Expression allows to specify complex patterns of character sequence.
Points of Concentration:
- All four functions can be used on any data type that consists character data. These are CHAR, NCHAR, CLOB, NCLOB, NVARCHAR2, and VARCHAR2.
- For better readability of the code, Regular expression must be enclosed between single quote.
- Oracle provides four sets of SQL functions for using regular expressions that allow us to manipulate or search strings.
Syntax of SQL Functions:
Oracle provides four SQL functions that are being used for Regular Expressions.
REGEXP_LIKE (Expression, Pattern, Match_Pattern)
REGEXP_REPLACE(string, pattern[, replacement_string[, start_position[, nth_appearance [, Match_Pattern]]]])
REGEXP_SUBSTR(string, pattern[, start_position[, nth_appearance[, match_parameter[, sub_expression]]]])
REGEXP_INSTR(string, pattern[, start_position[, nth_appearance[, return_option[, match_parameter[, sub_expression]]]]])
Description:
- Expression: It can user provided expression or column name.
- Pattern: It is a searching pattern.
- Replacement_String: It’s optional. It replaces match pattern. If this parameter is omitted, function will remove the match pattern.
- start_position: It’s optional. Search begins at given position. If it’s omitted, starts from the first position. By default value 1.
- nth_Appearance: It’s optional. It indicates number of occurrence of given pattern. If omitted, default value is 1.
Operators used for Oracle Regular Expression
There are various types of operators available:
- Pre-Defined Character Classes
- Quantifiers Operators
- Character Classes
- Others
1. Pre-Defined Character Classes
| \s | Space Character. |
| \S | Any Character Except Space Character. |
| \d | Any Digit From 0 to 9. |
| \D | Any Character Except Digit. |
| \w | Any Word Character [a-z A-Z 0-9]. |
| \W | Any Character Except Word Character (Special Character). |
| . | Any Character Including Special Character. |
| \A | Matches at the Beginning or at the ending of a string. |
| \Z | Matches at the End of a String. |
2. Quantifier Operators
Quantifier operators are used to quantify the number(s) of character.
| a | Exactly one a. |
| a+ | At least one a. |
| a* | Any number of a’s including ZERO number. |
| a? | At most ONE a i.e. either ZERO number or ONE number. |
| a{m} | Exactly m number of a’s. |
| a{m, n} | Minimum m number of a’s and Maximum n number of a’s. |
3. Character Classes
Character class operators can be used to search a group of characters.
| [abc] | Either a or b or c. |
| [^abc] | Except a, b and c. |
| [a – z] | Any lower case alphabet. |
| [A – Z] | Any upper case alphabet. |
| [a – z A – Z] | Any alphabet. |
| [0 – 9] | Any digit from 0 to 9. |
| [a – z A – Z 0 – 9] | Any alpha numeric character. |
| [^a – z A – Z 0 – 9] | Except alpha numeric character (Special character). |
4. Others
| ^a | It will check whether target string starts with a or not. |
| a$ | It will check whether target string ends with a or not. |
| | | Nature is ‘OR’, allows to specify more than one alternative |
| ( ) | Used to group expressions as a subexpression |
| ‘c’ | Perform case sensitive. |
| ‘i’ | Perform case insensitive. |
| ‘n’ | Allows period character to match new line character. |
| ‘m’ | Indicates to have multiple lines. |
| ‘x’ | Indicates to ignore whitespace character. |
Examples of Oracle REGEXP
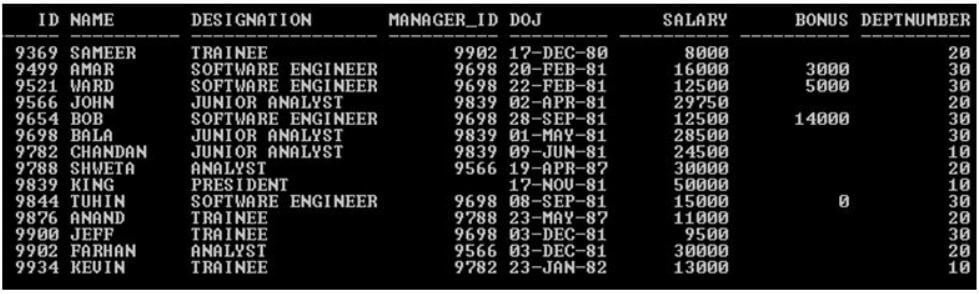
Here we will use the below sample table (Employee) with 14 records for the Oracle Regular Expression behavior.
Code:
SELECT * Employee;
Output:
Example #1
REGEXP_LIKE (Expression, Pattern, Match_Pattern)
This Regular Expression can be applied in WHERE clause to perform string matching.
It can be applied in SELECT, INSERT, UPDATE, or DELETE statement.
It is very similar to Oracle LIKE operator, LIKE operator performs for simple search and REGEXP_LIKE function is used for complex search.
Code:
SELECT Name FROM Employee WHERE REGEXP_LIKE (Name, '^A(*)');
Output:
The above statement returns two rows out of 14 because in the Regular expression condition ^A checks the name which starts with ‘A’ and (*) check any number of ‘A’ occurrences. And it finds two rows.
Example #2
REGEXP_REPLACE (string,pattern[,replacement_string[,start_position[,nth_appearance [,Match_Pattern]]]])
This Regular Expression helps us to replace complex matching string.
Code:
SELECT REGEXP_REPLACE ('EDUCBA is a great platform to learn', '^(\S*)','
https: //www.educba.com/') EDUCBA_Link FROM dual;
Output:
In the above output ‘EDUCBA’ replaced with’https: //www.educba.com/’ because condition ^ (\S*) checks the first word should be character with any number of occurrences.
Example #3
REGEXP_ SUBSTR (string, pattern[, start_position[, nth_appearance[, match_parameter[, sub_expression]]]])
- The REGEXP_ SUBSTR () function is an extension of Oracle SUBSTR function.
- It allows to extract a substring using Regular Expression Operators.
- sub_expression: It’s an optional. If pattern has sub expression then it can be used to target the pattern sub expression.
- It returns string value.
- Returns NULL if pattern does not find.
Code:
SELECT REGEXP_SUBSTR ('EDUCBA is a great learning platform', '(\S*)(\s)') Substring FROM DUAL;
Output:
The above example returns ‘EDUCBA’ because (\S*) it specifies to extract all non-space characters and (\s) it specifies to extract first space characters. So result includes first character as well as first space after the word.
Example #4
REGEXP_INSTR (string, pattern[, start_position[, nth_appearance[, return_option[, match_parameter[, sub_expression]]]]])
- The REGEXP_ INSTR () function is an extension of Oracle INSTR function.
- It returns ZERO ‘0’ if pattern does not find.
- It returns string value.
- sub_expression: It’s an optional. If pattern has sub expression then it can be used to target the pattern sub expression.
Code:
SELECT REGEXP_INSTR('EDUCBA is a great learning platform',’t’, 1, 1, 0, 'i')FROM DUAL;
Output:
The above example returns numeric value ‘17’ because ‘t’ exist at 17th position because of the parameters start_position is 1, an nth_appearance is 1, a return_option is 0, and a match_parameter of ‘i’. Here ‘i’ checks for upper or lower case of t in short it indicates to ignore case based search.
Conclusion
Oracle Regular Expression is a standardized syntax convention technique that allows us to pattern search for in string data. Oracle Regular Expressions are a very powerful text processing functions. Oracle Regular Expression is very useful while searching for complex pattern string.
Recommended Articles
This is a guide to Oracle REGEXP. Here we discuss the introduction to Oracle REGEXP with operators used for regular expression and examples. You may also have a look at the following articles to learn more –