Updated March 27, 2023
Introduction to Oracle Constraints
Oracle Constraints clause provides data integrity to the data that is being used by the application from the database by applying certain rules or conditions on a column of a database table which will define a very basic behavioral layer on the column of that particular table to check the sanctity of the data flowing into it like NOT NULL constraint on the column will not allow any data of that column to be NULL as it will not allow users to insert NULL data into the column.
Types of Oracle Constraints
Oracle has multiple types of constraints for multiple purposes. In this section, we are going to go through the different types of constraints in Oracle.
1. NOT NULL
If we just add a column, by default the column is allowed to hold NULL values but in case there is a requirement that the column should not hold any NULL values. We can use NOT NULL constraint on that particular column. This will enforce the column to always have a value and it will not allow any NULL record to be added in the column. We will add NOT NULL constraint using both CREATE TABLE and ALTER TABLE constraint. We will create a table STUDENT with student_id, LastName and zfirstName columns having NOT NULL constraint.
Let us look at the query.
Query:
CREATE TABLE STUDENT (
student_id int NOT NULL,
FirstName varchar(255) NOT NULL,
LastName varchar(255) NOT NULL,
Age int
);
Let us now the query in SQL Developer and look at the result.
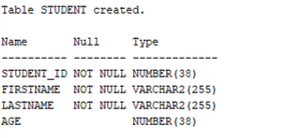
Output:
As you can see from the above screenshot we have successfully created the table with NOT NULL constraints. Let us now look at the ALTER statement query to add NOT NULL constraint to the age column of STUDENT TABLE.
Query:
ALTER TABLE STUDENT MODIFY AGE int NOT NULL;
desc STUDENT;
Let us now run the query in the SQL developer.
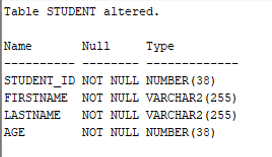
Output:
As we can see from the output the column AGE has now NOT NULL constraint added to it.
2. UNIQUE
This constraint in Oracle ensures that all the values of the column are different from each other and there are no duplicates. We will again use two examples to understand. First using the CREATE statement and then using ALTER statement. We will create a table STUDENT with student_id having UNIQUE constraint.
Let us look at the query using the CREATE TABLE statement.
Query:
CREATE TABLE student (
student_id int NOT NULL UNIQUE,
FirstName varchar(25) NOT NULL,
LastName varchar(25),
Age int
);
Let us now run the above query in SQL developer.
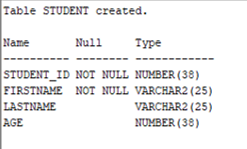
Output:
As we can see UNIQUE constraint has been added to the columns of the table. Now let add a UNIQUE constraint to age column using ALTER TABLE statement.
Query:
ALTER TABLE STUDENT ADD UNIQUE(age);
Let us run this query in SQL developer.
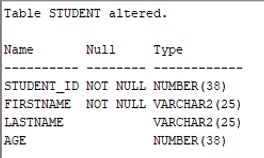
Output:
As we can see the table student has been successfully altered.
3. PRIMARY KEY
Primary key constraint uniquely describes each value of a column. No duplicates or NULL value is allowed. One important point is that a table can have only one primary key which in itself can be a combination of single or multiple fields.
We will first create a table ‘student’ with student_id as the primary key using the CREATE TABLE statement.
Query:
CREATE TABLE STUDENT (
student_id int PRIMARY KEY,
FirstName varchar(255) NOT NULL,
LastName varchar(255),
Age int
);
Now, let us run the query in SQL Developer and check the result.
Output:
As we can see the Table STUDENT has been successfully created. Let us now add primary Key using the ALTER TABLE statement to student_id column after the STUDENT table has been created.
Query:
ALTER TABLE STUDENT
ADD PRIMARY KEY (student_id);
Let us now run the query in SQL developer and check the result.
Output:
As we can see the table STUDENT has been successfully altered.
4. FOREIGN KEY Constraints
A foreign key is a field which refers to the PRIMARY KEY of another table and the table which actually has the foreign key is called child table. Let us now create a table order which we has student_id column as a foreign key refrencing student_id column of student table using CREATE TABLE statement.
Query:
CREATE TABLE Orders(
OrderID int PRIMARY KEY,
OrderNumber int NOT NULL,
student_id int REFERENCES student(student_id)
);
Let us now run the query in SQL developer and look at the result.
Output:
As we can see the orders table has been successfully created. Now we will use the ALTER TABLE statement to add a foreign key to the student_id column of orders table.
Query:
ALTER TABLE Orders
ADD FOREIGN KEY (student_id) REFERENCES student(student_id);
Let us run the query in SQL developer and look at the result.
Output:
As we can see the table orders has been successfully altered.
5. CHECK Constraint
The CHECK constraint is used to limit the value of the range that can be placed in a column. In case we want to restrict certain values in a column or a table we introduce the check constraint. We will introduce the CHECK constraint using both CREATE TABLE and ALTER TABLE statement.
We are going to create a table student with age column having a check constraint.
Query:
CREATE TABLE student (
student_id int NOT NULL,
FirstName varchar(25) NOT NULL,
LastName varchar(25),
Age int CHECK (Age>=18)
);
Let us run the query in SQL developer and look at the result.
Output:
As we can see the table has been successfully created with the CHECK constraint. Let us now add CHECK constraint on the same column after the table student has been created using ALTER TABLE statement.
Query:
ALTER TABLE student ADD CHECK (Age>=19);
Let us now run the query in SQL developer and see the result.
Output:
As we can see the CHECK constraint has been added to the table.
Recommended Articles
This is a guide to Oracle Constraints. Here we discuss the definition of Constraints in Oracle database. We also discussed the various types that can be used in Oracle database along with examples. You can also go through our suggested articles to learn more –