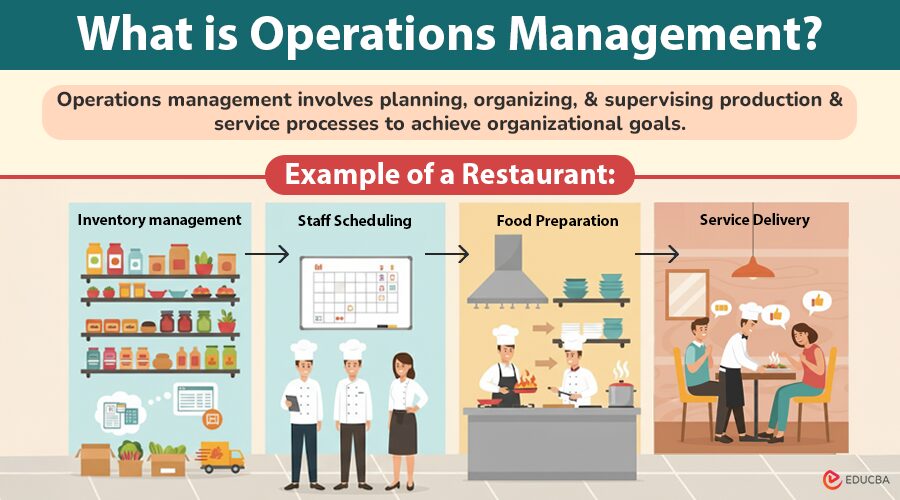
What is Operations Management?
Operations management involves planning, organizing, and supervising production and service processes to achieve organizational goals. It focuses on converting inputs (resources, labor, capital) into outputs (products or services) efficiently, with minimal waste, and while maintaining high quality.
Key Objectives of operations management are:
- Efficiency: Streamline processes to reduce costs and maximize output.
- Quality assurance: Deliver consistent products that meet or exceed standards.
- Customer satisfaction: Ensure timely delivery and responsive service.
- Cost control: Optimize resources to maintain profitability.
- Flexibility: Adapt operations to meet market demands and respond to technological advancements.
For example, a restaurant’s OM includes inventory management, staff scheduling, food preparation, and service delivery, all aimed at providing customers with consistent quality and timely service.
Table of Contents
- Meaning
- Importance
- Types
- Functions
- Key Performance Indicators (KPIs)
- Role of Technology
- Strategies
- Lean vs Agile Organizations
- Models and Frameworks
- Challenges
- Emerging Trends
- Real-World Examples
- Impact on Organizational Success
Importance of Operations Management
Operations management is critical for organizational success because it directly impacts performance, profitability, and competitiveness.
Key Benefits:
-
- Enhanced productivity: Identifies and eliminates bottlenecks to improve workflow efficiency.
- Quality control: Ensures consistency, reduces errors, and minimizes returns or complaints.
- Cost reduction: Optimizes resource allocation, reduces wastage, and controls overheads.
- Strategic alignment: Ensures daily operations contribute to long-term organizational objectives.
- Innovation & adaptation: Encourages adoption of new processes, technologies, and sustainable practices.
For example, Amazon’s operations management uses automation, robotics, and predictive analytics to streamline warehouses, reduce delivery times, and maintain a competitive advantage globally.
Types of Operations Management
Operations management can be categorized based on the nature of operations and industry:
- Manufacturing operations: Focus on producing physical goods. Includes production scheduling, inventory management, and quality control.
- Service operations: Focus on intangible products such as healthcare, hospitality, or banking services. Organizations measure efficiency by tracking service speed, customer satisfaction, and the effectiveness with which they utilize resources.
- Project-based operations: Applied to unique, one-time projects like construction, IT implementation, or event management. Emphasizes deadlines, budget adherence, and resource allocation.
- Retail & logistics operations: Involves inventory management, order fulfillment, and distribution. Example: E-commerce companies like Flipkart or Amazon are optimizing last-mile delivery.
Functions of Operations Management
Operations management encompasses a range of interrelated functions that ensure smooth, efficient, and high-quality business operations. Each function plays a critical role in optimizing resources, reducing costs, and enhancing customer satisfaction.
1. Product Design & Development
Operations managers collaborate with R&D teams to develop products that meet customer needs while striking a balance between cost, quality, and practicality. This function ensures that products are innovative, practical, and aligned with customer expectations.
2. Process Design & Improvement
This function focuses on streamlining workflows to maximize efficiency and reduce waste. Operations managers apply methodologies such as:
- Lean Manufacturing: Eliminates unnecessary steps, reduces waste, and enhances value-added activities.
- Six Sigma: Uses statistical techniques to minimize errors and ensure consistent quality.
3. Capacity Planning
Capacity planning ensures the organization has the right resources at the right time to meet fluctuating demand without overproduction or underutilization. It involves forecasting, analyzing historical trends, and adjusting staffing, equipment, and production schedules accordingly to optimize efficiency.
4. Inventory Management
Operations managers maintain optimal stock levels to meet customer demand while minimizing holding and storage costs. Common techniques include:
- Just-In-Time (JIT): Receives goods only when needed, reducing excess inventory.
- Economic Order Quantity (EOQ): Calculates the ideal order size to minimize costs while meeting demand.
5. Supply Chain Management
This function coordinates the flow of materials, products, and information across suppliers, manufacturers, distributors, and retailers. Effective supply chain management reduces delays, prevents disruptions, and ensures products reach customers on time.
6. Quality Management
Quality management ensures that products and services meet or exceed standards. Approaches include:
- Total Quality Management (TQM): Fosters continuous improvement in all processes.
- ISO Certifications: Verifies compliance with international quality standards and regulatory requirements.
7. Maintenance Management
Maintenance management ensures that equipment, machinery, and infrastructure are in optimal working condition, thereby minimizing downtime and maximizing productivity. Scheduled maintenance helps prevent unexpected breakdowns, reduces repair costs, and ensures operational continuity.
Key Performance Indicators (KPIs) in Operations Management
| KPI | Purpose | Example |
| Production Efficiency | Measures output relative to input | Units produced per labor hour |
| Order Fulfillment Rate | Measures on-time delivery | 95% of orders shipped on time |
| Inventory Turnover | Measures how quickly inventory is sold/used | Annual turnover ratio 8x |
| Overall Equipment Effectiveness (OEE) | Measures machine productivity | 85% OEE indicates high efficiency |
| Customer Satisfaction Index | Measures operational alignment with expectations | 4.7/5 average customer rating |
Role of Technology in Operations Management
Technology has revolutionized operations management by enhancing efficiency and accuracy:
- ERP Systems (Enterprise Resource Planning): Integrates finance, inventory, HR, and production into a unified platform.
- Automation & Robotics: Speeds up repetitive tasks and reduces human error.
- AI & Data Analytics: Predicts trends, optimizes inventory, and informs strategic decisions.
- IoT (Internet of Things): Monitors machinery, tracks supply chains, and ensures real-time visibility.
Strategies in Operations Management
- Lean Management: Aims to reduce waste and boost efficiency.
- Six Sigma: A data-driven method to improve quality and reduce defects.
- Just-In-Time (JIT): Maintains minimal inventory to reduce costs.
- Total Quality Management (TQM): Ensures continuous improvement and customer satisfaction.
- Outsourcing & Automation: Delegates non-core tasks and utilizes advanced technology.
Operations Management in Lean vs Agile Organizations
| Aspect | Lean | Agile |
| Focus | Waste reduction | Flexibility and rapid response |
| Approach | Process efficiency | Quick adaptation to market changes |
| Example | Toyota | Spotify |
| Key Benefit | Cost reduction | Faster innovation |
Lean emphasizes efficiency, while agile prioritizes adaptability, making both approaches suitable for different operational goals.
Operations Management Models and Frameworks
- PDCA Cycle (Plan-Do-Check-Act): Continuous improvement methodology.
- SCOR Model (Supply Chain Operations Reference): Standardizes supply chain processes.
- Kaizen: Small, continuous process improvements to enhance efficiency.
- Balanced Scorecard: Aligns operations with strategic business objectives.
Challenges in Operations Management
- Demand forecasting: Difficulty in predicting market needs.
- Supply chain disruptions: Delays due to logistics, shortages, or geopolitical factors.
- Technology integration: High cost and complexity of adopting new systems.
- Cost management: Balancing quality, efficiency, and expenses.
- Regulatory compliance: Adhering to standards, safety, and legal requirements.
Emerging Trends in Operations Management
- Sustainable & green operations: Reducing carbon footprint and waste.
- Digital twins: Simulate operations to predict outcomes and optimize performance.
- Cloud-based platforms: Facilitate real-time collaboration and monitoring.
- Predictive analytics: Uses historical data to anticipate demand and maintenance needs.
- Robotics & AI-driven automation: Increases productivity and operational accuracy.
Real-World Examples
- Toyota: Leader in Lean Manufacturing and continuous improvement.
- Amazon: World-class supply chain optimization and automation.
- Zara: Agile operations for fast fashion, rapid production, and inventory rotation.
- Tesla: Advanced automation and IoT-enabled production.
Impact on Organizational Success
Effective operations management:
- Boosts revenue growth and profitability
- Ensures high customer satisfaction and loyalty
- Promotes innovation and product development
- Provides a competitive advantage in dynamic markets.
Final Thoughts
Operations management is key to running a business efficiently and supporting growth. By managing processes, resources, and supply chains effectively, companies can reduce costs, enhance quality, and better serve their customers. Utilizing modern technologies, trends, and best practices enables businesses to remain competitive, innovative, and sustainable.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
Q1. What is the difference between operations management and production management?
Answer: Production management focuses only on manufacturing products, whereas operations management covers all processes that produce goods and services, including supply chain, quality, and service delivery.
Q2. How does operations management impact customer satisfaction?
Answer: Efficient operations ensure timely delivery, consistent quality, and responsiveness, all of which directly enhance customer satisfaction and loyalty.
Q3. Which skills does an operations manager need?
Answer: Key skills include leadership, analytical thinking, problem-solving, process optimization, supply chain knowledge, and familiarity with technology like ERP and data analytics.
Q4. How does operations management support business growth?
Answer: By streamlining processes, optimizing resource use, and improving product/service quality, operations management enables scalability, reduces costs, and enhances competitive advantage.
Q5. How is technology changing operations management?
Answer: Technologies like AI, robotics, IoT, cloud-based ERP systems, and predictive analytics improve efficiency, reduce errors, optimize supply chains, and allow real-time decision-making.
Recommended Articles
We hope this guide on Operations Management helped you understand how businesses can streamline processes and improve efficiency. Explore our related articles on:
