Updated September 30, 2023
What is Object Oriented Programming in Python?
Python is an object-oriented programming language. t is an interpreted and high-level programming language for general programming requirements. It was designed and developed by Guido van Rossum and was first released in 1991. It has a dynamic type of discipline and is also strong. Its filename extensions are different types, such as .py, .pyc, .pyd, .pyo, .pyw, and .pyz. It is object-oriented, functional, procedural, reflective, and imperative. It is being maintained and developed by the Python Software Foundation. It was mainly influenced by the languages such as Coffee script, JavaScript, Go, Ruby, Swift, and Groovy. It is also a multi-paradigm programming language. The ‘Lisp programming language inspired its’ functional programming features. It also supports aspect-oriented programming.

Table of Contents
- What is Object Oriented Programming in Python?
- Why Python is called an object-oriented language?
- Comparison with other object-oriented programming languages
- Difference between Object Oriented and Non-Object Oriented Programming Languages
- Best Practices and Tips
Why Python is called an object-oriented language?
Python is called an object-oriented programming (OOP) language because it is designed and built around the principles of object-oriented programming. Object-oriented programming uses objects as fundamental building blocks. Python treats everything as an object and provides mechanisms for defining and manipulating these objects. The object-oriented programming model works by interacting and invoking the properties of different objects. It has concepts such as Classes, Objects, Polymorphic, Encapsulation, Inheritance, and Abstraction. The other features of Object Oriented Programming are as follows:
1. Class
This blueprint of the object defines the fields or attributes and methods that contain the real functionality. We refer to these as members, and you can access them based on the access modifiers defined during the declaration of these members.
2. Object
An object becomes an instance of the class when you declare and instantiate it by calling the class’s constructor. An object will have a state containing data that the classes will hold.
3. Inheritance
This is the third step in which the data will be visualized, cleaned, transformed, and exposed by reducing useless information and transforming it into essential sets of information to obtain valuable information from the existing data.
4. Polymorphism
Polymorphism is the process of performing a single task in different possible ways. It can be achieved in two ways: method overloading and method overriding. Method overloading is also called Compile Time Polymorphism, whereas Method Overriding is also called Run Time Polymorphism.
5. Encapsulation
This is the process of encapsulating, which means hiding, binding, or wrapping the code into a single unit or module defined as a Class. Encapsulation in object-oriented programming is achievable through the use of a class. It defines an object as encapsulated when the class’s members are private (using the access modifier), making them accessible solely through the class’s getter and setter methods.
6. Abstraction
Object-oriented feature abstraction involves concealing the implementation of functionalities while revealing only the necessary interfaces or accessing methods for invoking the implementation class’s methods. You can accomplish this abstraction in a programming language by defining either an Interface or an Abstract Class.
Example
Below is an example of object-oriented programming in Python:
Code:
# Define a class
class Dog:
def __init__(self, name):
self.name = name
def bark(self):
print(f"{self.name} says Woof!")
# Create objects (instances) of the class
dog1 = Dog("Kenzo")
dog2 = Dog("Burton")
# Access object attributes and call methods
print(dog1.name)
dog2.bark()Output:
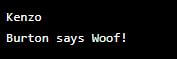
In this example, Dog is a class, and dog1 and dog2 are objects of that class. Structures allow you to encapsulate data (the dog’s behavior (barking) within the Dog class, making it an object-oriented language.
Comparison with other object-oriented programming languages
The other object-oriented programming languages include such as C++, Java, Objective C, Ruby, Smalltalk, Visual Basic.NET, Simula, JavaScript, etc., In Python, self is equivalent to this reference in Java programming language, which is used to refer to the object, whereas this reference will be used in JavaScript programming language also. In Python, a class is used to define the Class, similar to the remaining object-oriented languages, such as JavaScript, to define a class as per ES6 (EcmaScript – A standard for JavaScript programming Language). The initial method that will be called while instantiating the object is __init__ whereas a default or declared Constructor will be called in the case of Java, whereas, in the case of JavaScript, it is a prototype-based mechanism where the root or parent class object mechanism will be called or implemented as it has prototypal inheritance mechanism.
Inheritance mechanism exists in Python, similar to other languages such as C++, Java, etc. Python usually takes more time than Java, which results in slower execution of the Python programs. Writing programs in Python proves easier compared to other Object-Oriented Programming (OOP) languages due to its simpler and more concise syntax. Additionally, Python facilitates seamless integration with other OOP languages like Java, enabling the development of applications that can leverage the functionalities of both languages. You can invoke both programs within each other to execute the application.
Difference between Object Oriented and Non-Object Oriented Programming Languages
Below are the differences:
| Aspect | Object-Oriented Programming (OOP) | Non-Object Oriented Programming |
| Basic Programming Unit | Objects | Procedures or Functions |
| Data Encapsulation | Supported (Private, Public, etc.) | Limited (e.g., via scoping) |
| Inheritance | Supported (Class hierarchies) | Not a core concept |
| Polymorphism | Supported (Method overriding) | Limited (e.g., function overloading) |
| Code Reusability | High (through inheritance) | Lower |
| Complexity Management | Better for complex systems | Suitable for simpler programs |
| Code Organization | Classes and Objects | Procedures and Functions |
| Examples of Languages | Java, Python, C++, C# | C, Pascal, Fortran |
| Modularity | Supported through classes/modules | It can be implemented through functions |
| Abstraction | Supported (Abstract classes, interfaces) | Limited |
| Code Flexibility | Generally more flexible | May have less flexibility |
| Code Readability | Typically more readable | Can vary |
| Use Cases | Complex software systems, GUI applications, simulations | System-level programming, scripting,
algorithms |
Best Practices and Tips
Here are some best practices and tips for Object-Oriented Programming (OOP) in Python, explained concisely:
- Follow the PEP 8 Style Guide: Use Python’s style guide to write clean and readable code, including proper naming conventions for classes, methods, and variables.
- Use Descriptive Class and Method Names: Choose meaningful and self-explanatory names for classes and methods to improve code clarity.
- Avoid Large Classes: Keep classes focused on a single responsibility (Single Responsibility Principle) and avoid creating monolithic classes.
- Favor Composition over Inheritance: Use composition to build complex objects by combining simpler ones instead of relying heavily on Inheritance to prevent complex inheritance hierarchies.
- Use Docstrings: Document your classes and methods using docstrings to provide clear explanations and enable automatic documentation generation.
- Keep Methods Short and Cohesive: Aim for concise methods that perform a single, well-defined task (Single Responsibility Principle).
- Avoid Using Global Variables: Minimize using global variables within your classes, as they can lead to unexpected side effects.
- Leverage Inheritance Carefully: Ensure derived classes can substitute base classes using the Liskov Substitution Principle when utilizing Inheritance.
- Prefer Duck Typing: Python uses duck typing, so instead of checking an object’s type, focus on whether it can perform a specific task.
- Encapsulate Data: Use private attributes (prefix with an underscore) and provide getter and setter methods for controlled access to object data.
- Handle Exceptions Gracefully: Use try-except blocks to handle exceptions gracefully within your classes.
- Test Your Classes: Write unit tests to ensure they work as expected, following the Arrange-Act-Assert (AAA) pattern.
- Avoid Mutating Immutable Objects: Immutable objects like strings and tuples should not be modified in place. Instead, create new objects.
- Use Abstract Base Classes (ABCs): When defining interfaces, consider using ABCs to ensure that derived classes implement the required methods.
- Follow the Dependency Inversion Principle: Depend on abstractions, not concrete implementations, to make your code more flexible and extensible.
- Document Your Code Clearly: Write clear and concise comments and docstrings to help others understand your code’s purpose and usage.
- Avoid Global State: Minimize reliance on global variables or global states within your classes to make them more modular and easier to test.
- Optimize for Readability: Strive for code that is easy to read, understand, and maintain, even if it means sacrificing a small amount of performance.
- Use Version Control: Employ a version control system like Git to track changes to your codebase, enabling collaboration and easy rollback.
- Continuously Refactor: Regularly review and refactor your code to improve its design, readability, and maintainability.
These best practices and tips will help you write more robust, maintainable, and scalable Python code when applying Object-Oriented Programming principles.
Conclusion
The object-oriented features of a programming language give a rich set of features for developing larger and more complex applications to enable and run larger businesses in the current digital world with increasing data and customers. Developers can use Python to create web applications with the help of the Django framework, which simplifies web development by providing most of the necessary implementations. In various scenarios, developers can pair Python with other frameworks to create various types of applications to fulfill specific requirements. Python also has other features, such as Functional, procedural, reflective, imperative, etc., other than Object Oriented. Besides OOP, Python provides other functionalities such as Networking, Web frameworks, Graphical User Interfaces, Databases, Automation, etc.
Recommended Articles
We hope this EDUCBA information on “Object-oriented Programming In Python” benefited you. You can view EDUCBA’s articles for more information.


