What are Non-Operating Expenses?
Non-operating expenses are costs businesses incur to fulfill their financial obligations separate from their day-to-day operations. Some examples include loss due to failed investments, natural disasters, currency exchange, asset disposal, etc.
They can significantly affect a company’s overall financial performance as they can cause an increase or decrease in its net income. As a result, high non-operating expenses can negatively impact a company’s profitability. Thus, investors and analysts review a company’s non-operating costs when evaluating its financial performance.
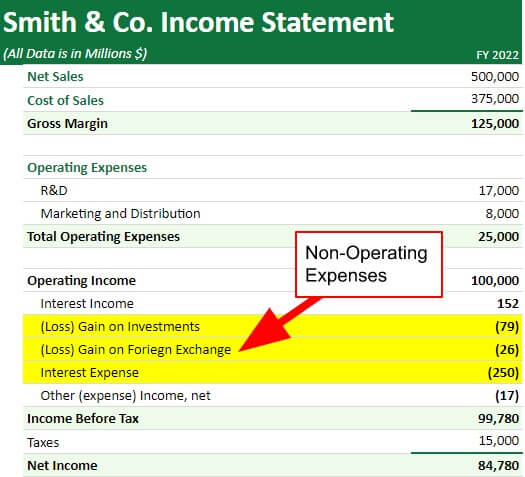
For example, Company XYZ spends $120 on interest expense of loans, $300 on losses from the sale of assets, and $200 on post-retirement plans of senior employees. These expenses do not affect the company’s day-to-day activities and do not directly generate revenue. Therefore, the total non-operating costs of Company XYZ sum up to $620.
Non-Operating Expenses List
Some of the most common examples of non-operating expenses include:
Interest expense:
- It includes the cost of borrowing money, such as loans or bonds. The lender charges this amount from the borrower.
- For instance, a company takes out a loan to purchase new equipment and incurs an interest expense of $50,000 for the year.
- It is non-operating because it is not directly related to the company’s primary operations.
Expense toward lawsuit settlement:
- Costs like settlement expenditures and payments to the attorney belong to this category.
- They are non-operating costs as they fulfill legal and social formalities and do not impact the business’s core operations.
Loss from abandonment of long-lived assets:
- It is the loss a company incurs when it discontinues using an asset and decides to dispose of it.
- Businesses derive this expense amount by determining the present market value of the asset.
Expenses incurred due to relocation of business:
- Relocation of any business includes costs of hiring a moving company, new marketing setups, the employees’ individual relocating costs, etc.
- Loss of productivity for a significant period is also a notable factor in the relocation of a business.
- When relocating your business, utilizing a moving cost calculator becomes essential in managing expenses and ensuring a smooth transition to a new location, allowing for efficient budgeting and planning.
Foreign currency exchange losses:
- They occur due to changes in exchange rates when a company exports goods to a foreign country and receives payment in a foreign currency.
- If the value of the foreign currency decreases compared to the domestic currency, the company will record a loss.
Loss from the sale of investments or assets:
- Businesses sell or buy assets or invest in other companies to gain a strong market by creating internal diversity.
- However, sometimes these investments lead to losses called capital losses.
- Companies determine them by calculating the difference between the cost and selling price of assets or investments.
Loss from natural disasters or accidents:
- It includes expenses related to damages from natural disasters such as floods, hurricanes, earthquakes, etc. Such incidents are unavoidable, and the related costs are not in the control of the business.
- For example, a company incurs an expense of $50,000 due to damages from a flood. As this is a one-time expense due to an unavoidable natural disaster, this is a non-operating expense.
Pension and post-retirement benefit costs:
- It includes expenses related to retiree welfare, such as pension plans or healthcare benefits.
- The total expenditure for the pension of all its employees is a company’s net periodic benefit cost.
How Do Non-Operating Expenses Work?
A business’s daily operations do not include non-operating expenses. Businesses subtract these costs and taxes from gross income to find their net income. These costs are not under the company’s control and are, therefore, unavoidable.
Businesses record these expenses separately on their income statements on annual reports. It helps professionals to analyze and predict the financial health of businesses. For example, a company incurs a profit throughout but faces a sudden loss more significant than the profit due to a storehouse fire. That does not mean that it is not running well. By recording this damage expense separately, they can easily track the progress and profit.
Non-Operating Expenses Examples
#1 Foreign Currency Exchange:
An American company exports goods to a European country and receives payment in euros (1 Euro= $1.09). If the exchange rate changes from $1.09 to $2, the company will record a loss as the value of Euros increases in terms of Dollars. Since this fluctuation is not under the company’s control and the amount does not come from any of its direct activities, this loss is a non-operating expense.
#2 Investment:
A mutual fund investment company incurs expenses for hiring personnel for investment activities. The company also invests in mutual funds, so the investment activities qualify as the company’s core operations. In this case, the expenses incurred for carrying out the investment activities is non-operating.
#3 Interest Expense:
All businesses require funds for fuelling growth, so companies resort to a mix of equity and debt to finance their business growth. Consequently, the companies bear the interest expense and pay at regular intervals. Now, although debt financing facilitates business growth, it is not part of the core operations of any company. As such, the interest payment is a non-operating expense.
Real World Examples
#1. Amazon
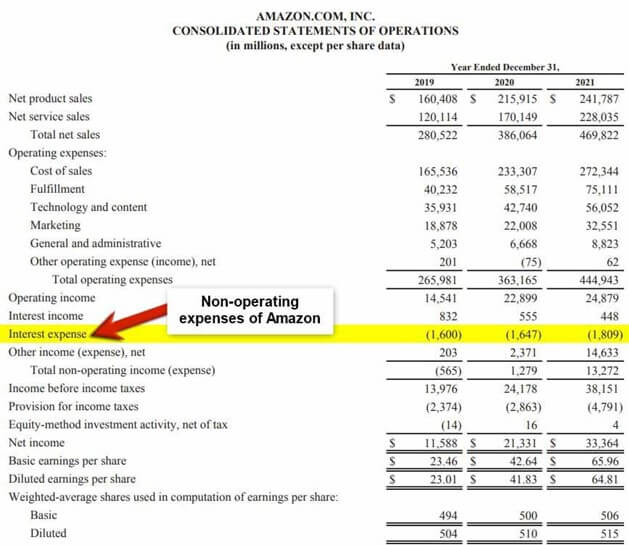
The 2021 annual report of Amazon is where we find the non-operating expenses (Interest expense) in the Consolidated Statement of Operations Interest Expenses.
(Image source: Amazon Annual Report 2021)
In 2019 the interest expense of Amazon was $1,600 million. It increased to $1,647 million in 2020. The expenditure rose to $1,809 million in 2021, with an increase of $162 million. Generally, a company incurs increasing non-operating expenses from the inconsistency in its core operations.
#2. Tesla
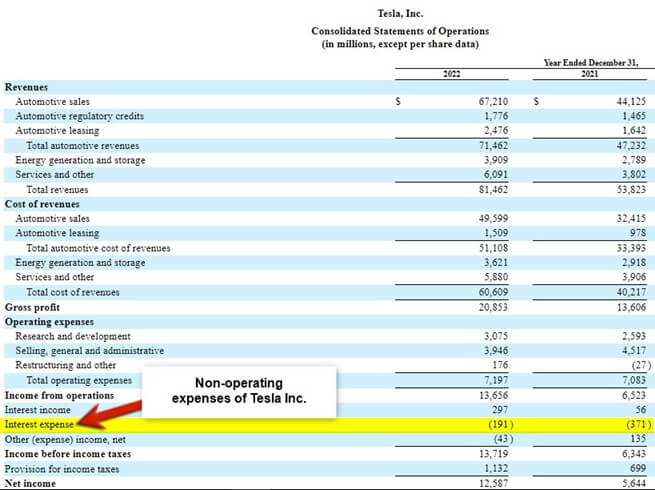
It is Tesla’s 2022 Annual Report. In the Consolidated Statement of Operations, they have recorded the non-operating expenses as Interest Expenses.
(Image Source: Tesla Annual Report 2022)
Tesla had an interest expense of $748 million in 2020. It decreased to $371 million in 2021. The cost further came down to $191 million in 2022. Such a consistent decrease implies a sound performance of the company’s core operations over the years.
Non-Operating Vs. Operating Expenses
|
Non-Operating Expenses |
Operating Expenses |
| They are not directly related to the primary operations of a business. | A company incurs these costs as a part of its normal business operations. |
| Examples include interest expense, foreign currency exchange losses, gains or losses from the sale of investments or assets, etc. | Examples include wages, rent, utilities, and supplies. |
| These expenses do not directly generate revenue but significantly impact a company’s overall financial performance. | Companies incur these expenses in generating revenue, and they help keep the business running.
|
Advantages and Disadvantages of Non-Operating Expenses
|
Advantages |
Disadvantages |
| Subtracting a company’s operating expenses from its operating income gives a proper net earnings estimate. | It varies widely among companies and fluctuates yearly, making its predictability difficult. |
| Companies present it on their income statement so the stakeholders can know the company’s financial performance. | Including non-operating costs in the financial statements can be challenging to evaluate the efficiency and profitability of a company’s operations. |
| Some non-operating costs, such as losses from natural disasters, may be tax-deductible. It can help to reduce a company’s overall tax liability.
|
It is uncontrollable and can negatively impact a company’s profitability, making it difficult to generate positive returns for its shareholders. |
Final Thoughts
Non-operating expenses can significantly impact a company’s overall financial performance, but they can also be challenging to predict and control. Companies should be aware of these limitations and carefully evaluate and manage their non-operating expenditure to achieve the best overall financial performance.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
Q.1. What are non-operating expenses?
Answer: Expenses not directly related to the primary operations of a business are non-operating expenses. These expenses do not contribute to any crucial aspect of business operations.
Q.2. What types of expenses are considered non-operating expenses?
Answer: We consider interest expense, gains or losses from foreign currency exchange, gains or losses from the sale of investments or assets, losses from natural disasters or other events, losses from the abandonment of long-lived assets, and pension and post-retirement benefit costs as non-operating expenses.
Q.3. Why do companies separate non-operating expenses on financial statements?
Answer: Companies separate non-operating expenses on financial statements to accurately record their financial performance. Investors and analysts study these expenses to compare the performance of various companies.
Q.4. What are direct and indirect expenses?
Answer: When a company fixes a cost for any particular product or service, it is a direct expense. On the other hand, the expenditure incurred by the company for its overall functioning year after year is indirect. Non-operating costs fall under the indirect expenses of the company.
Recommended Articles
This was an EDUCBA guide for understanding non-operating expenses. For further studies, please refer to EDUCBA’s Recommended Articles.