Updated June 14, 2023
Introduction to Nodejs Architecture
Node.js architecture is based on the Single-Threaded Event Loop Model will provide us a better understanding of the advantages that Node.js provide, the way it can handle concurrent client’s requests without creating multiple threads, and how Node.js uses fewer threads; only to utilize fewer resources. We will look after the Single-threaded nature and how Node.js handles a particular request. How the concepts of event queue and thread pool help better process a request in Node.js with high scalability and performance.
Benefits of Single-Threaded nature
- We can easily handle concurrent client requests.
- JS uses fewer threads so that it can use fewer resources. When a Node.JS web server receives concurrent requests, it need not create multiple threads because of the Event loop.
Architecture of Nodejs
Node.JS is based on Single Threaded Event Loop Model. Its processing is mainly based on the JavaScript Event Loop Model.
Let us go through the following two scenarios which will help us understand the architecture of Node.js:
Scenario #1
- The client sends a request to the server.

- The request is registered in the Event Loop.
- The Single Thread Event Loop allows the node to execute non-blocking input-output operations.
- The system examines the incoming request to determine if it includes any database interaction or heavy computations.

- Since the above request doesn’t involve complex operations, the system prepares the request and returns the response to the client.
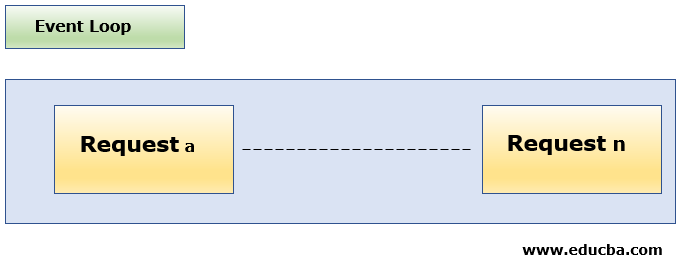
Diagram Explanation for Scenario #1
- In Scenario 1, the client sends the request(a) to the server.
- Request(a) is registered in the Event Loop.
- The Event Loop then checks if the request(a) contains complex operations or interactions with the database.
- As the incoming request(a) does not contain heavy computations, the Node js starts processing the request(a), prepares the response, and sends it back to the client.
Scenario #2

- As seen above, the client sends the request to the server.
- The incoming request is registered in the Event Loop.
- The Event Loop then checks if the incoming request contains complex operations, database queries, or any interaction with the file system.

- If the incoming request contains interaction with the database, the Event Loop checks with the Internal Thread Pool in Nodejs Server.
- The Internal thread pool of the Nodejs Server consists of threads responsible for executing the kind of request that contains interaction with the database or file system.
- A thread, known as a lightweight process, is a path of execution within a process.
- The Event Loop checks if the thread can execute the request in the Internal Thread Pool.
- If the thread is available, the request is assigned to that thread.
- The assigned thread is then responsible for executing the request, preparing its response, and giving it to the Event Loop.
- The Event Loop then finally returns the response back to the client.
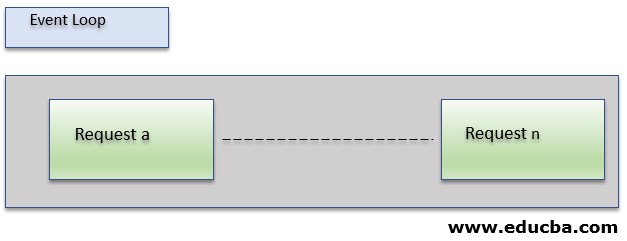
Diagram Explanation for Scenario #2
- In Scenario 2, the client sends the request(b) to the server.
- Request(b) is registered in the Event Loop.
- The Event Loop checks whether the request(b) involves any interaction with a database or any complex operations.
- As the incoming request(b) does contain heavy computations, that is, interaction with the database, the Node js checks for the availability of threads in the Internal thread Pool.
- As the thread is available to process the request(b), the request(b) is assigned to the thread.
- The thread is then responsible for processing that request, preparing its response, and sending it back to the client.
js Platform
Node.js is a JavaScript runtime environment. Node.js helps us build web applications. It is based on Google Chrome’s V8 engine. Node.js runs on various platforms, such as Windows, Mac, Linux, etc.
By default, Node.js follows the mechanism of asynchronous programming. Because of its single-threaded nature, we use Node.js for event-driven servers. NPM stands for Node Package Manager, which is a package manager for the Node JavaScript runtime environment. It is a recommended feature for Node.JS installers. It can manage packages that are local dependencies of a particular project and is the world’s largest online repository.
Node.js allows us to build highly scalable web applications with the help of frameworks. The popular frameworks for Node.js are Express.js, Sails.js, Meteor.js, Total.js, and many more. The frameworks provide us with a way to build the applications effortlessly. The non-blocking I/O model (asynchronous programming) and the event-driven nature make Node.js efficient and lightweight.
Advantages of Nodejs
Below are some of the advantages.
- Single-threaded nature
- Asynchronous programming (non-blocking I/O operations)
- Event-driven
- No buffering
- Node Package Manager (NPM)
- Advantage of Caching
- Open Source
- Performance
- Highly Extensible
Conclusion
Thus we studied Nodejs architecture based on the Single-Threaded Event Loop Model. It helped us understand how a particular request is handled through the concept of Event Queue and Thread Pool; how a request that contains any blocking input-output operations is placed in the event queue, and a thread is assigned to carry the request forward and send back the response to the client once the response is prepared.
We also looked through the concept of the Node.js Platform, the popular frameworks available to build data-intensive, highly scalable Node.js applications, and its advantages.
Recommended Articles
This is a guide to Nodejs Architecture. Here we discuss the Single-threaded nature and how Node.js handles a particular request. You may also have a look at the following articles to learn more –


