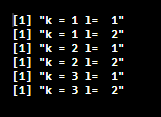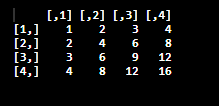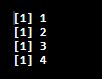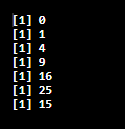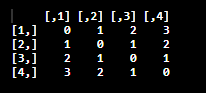Updated July 3, 2023
Introduction to Nested For Loop in R
In Nested For Loop in R, R uses the control structures to manage the execution of the expression; one such control structure is Nested For Loop, similar to basic ‘for’ loop executes. It can be defined as placing one ‘for’ loop inside the first ‘for’ loop is called a nesting or loop of loops in some terms, which takes the responsibility of two loops such that the outer loop controls the number of repetitions of the whole inner detailed information until it is false, in other words, the inner loop executes n-times of every execution of the outer for loop, and also it’s a great tool to work with R Programming Language.
Syntax:
The basic syntax is given below:
for (variable in sequence) {
for (variable in sequence)
{
expression // expression statements can be a single statement of R or group of statements.
} }
Here variable implies iteration value used in a sequence and sequence is a set of values or objects that could be numbers or characters.
Sample:
for(i in 1:n)
{
for(j in 1:n)
{
// block of statement
}
}
In the above general syntax, we could see two loop statements. Nested Loops are primarily meant for multi-dimensional array storage purposes, which the data scientist widely uses. We can use numeric as well as character indices.
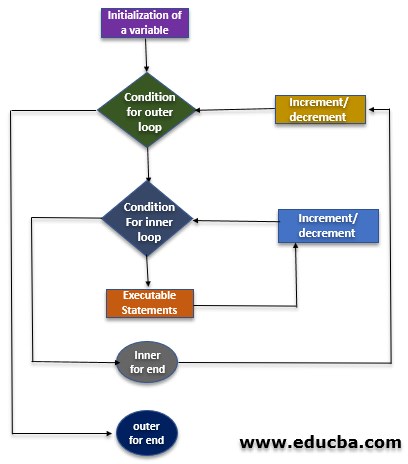
Flowchart Structure
The flowchart below shows the R for Loop structures: The loop gets executed in the diagram below for each value in the sequence. When there is no value, it returns to the end. Flowchart representing the steps of Nested ‘For’ Loop:
How Nested For Loop Works in R?
Nested-for loops are used to manipulate a matrix by making a specific setting to a particular value and are considered a foundation skill in R Programming. This is more beneficial if we wish to extract a specific value from the corresponding row and column index. For instance, let’s take the following code:
Steps:
- Initially, the outer loop assigns k=1L and executes its statement to the inner loop; meanwhile, the inner for loop assigns l=1L and prints k=1, l=1. And now, the inner loop executes itself as the information is true, and now ‘l’ is incremented to 1, will be set to l=2L, and the K value remains the same, and we get the result as k=1 l=2. Similarly, do it for the next inner loop k=1 l=3.
- Now the inner loop is made false and finished, and we proceed with the first outer loop where it takes k=2L and executes its following statement, which is to be an Inner loop and assigns the same as the above process l=1L. Repeat the following iterations until the loop exits.
for (k in 1:3) {
for (l in 1:2) {
print(paste("k =", k, "l= ",l))
}
}
Let’s see how it works in a two-dimensional array by taking the mathematical concept matrix. First, create a code for a nested loop representing several rows and columns as integer positioned.
res = matrix(nrow=4, ncol=4) # create a 4 x 4 matrix (of 4 rows and 4 columns)
for(i in 1:nrow(res)) // Assigned a variable ‘i’for each row
{
for(j in 1:ncol(res)) // Assigned a variable ‘j for each column
{
res[i,j] = i*j // calculating product of two indices
}
}
print(res)
Examples of Nested For Loop in R
Below is the example of Nested For Loop in R:
Example #1
Using Simple For Structure.
Code:
for(i in 1:4)
{
for(j in 1:1)
{
print(i*j);
}
}
Output:
Example #2
Performing nest for loop along with if statement to do some complicated tasks. In the example below, we shall declare a matrix using a matrix () function and check the variables i=j using an if statement.
Code:
mt= 5
nt=5
cter=0
mym = matrix(0,mt,nt)
for (i in 0:mt) {
for (j in 0:nt) {
if(i==j) {
break;
} else
{
mym[i,j] = i*j
cter=cter+1
}
}
print(i*j)
}
print(cter)
Output:
Example #3
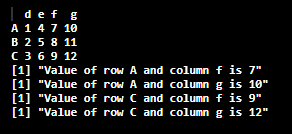
Implementing a matrix to print the letters according to the rows and columns. Here I have created a matrix 3×4 matrix.
Code:
res <- matrix(1:12, ncol = 4,
dimnames = list(LETTERS[1:3], letters[4:7]))
print(res)
for (rname in c("A", "C")) {
for (cname in c("f", "g")) {
print(paste("Value of row", rname, "and column",
cname, "is", res[rname, cname]))
}
}
Output:
Example #4
Displaying Positive Absolute value Using Math function abs().
Code:
z <- matrix(NA_integer_, nrow = 4, ncol = 4)
for (m in 1:4) {
for (n in 1:4) {
z[m, n] <- abs(m - n)
}
}
print(z)
Output:
Example #5
Implementation with data frames in R Language using Nested For loop -matrix.
Code:
x=5; y=5;
mat<-replicate(x, rnorm(y))
mydfr=data.frame(mat)
system.time(
for (m in 1:x) {
for (n in 1:y) {
mydfr[m,n]<-mydfr[m,n] + 5*sin(0.62*pi)
}
}
)
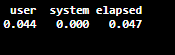
Created normal random numbers with a data frame of 5 observations and 5 variables to check the execution time using the system.time() function.
Output:
Conclusion
So now, to conclude, the for loops in R programming are by far the most famous and important concept, and their structure states that the number of iterations is known in advance and fixed. What happens if the number of iterations is not known in advance or predictable to overcome this problem while loop is used? Therefore, in this R article, we have studied their syntax and how to operate them with a different sequence with an example.
Recommended Articles
This is a guide to Nested For Loop in R. Here we briefly overview Nested For Loop in R, its Examples, and its Code Implementation. You can also go through our other suggested articles to learn more –