Updated June 26, 2023
Introduction to Nested Class in Java
A nested class refers to a class that is inside of another class. Java allows us to create nested classes in java. A nested class is one of the members of its outer class. It can also be declared public, private, protected, or default. The nested class has access to the other member of the outer class, while vice versa is not possible. It means the outer class doesn’t have access to a nested class member as the nested class is a member of its enclosing outer class, so dot (.) is used to access the nested class & its members. The nested class doesn’t have any static keywords.
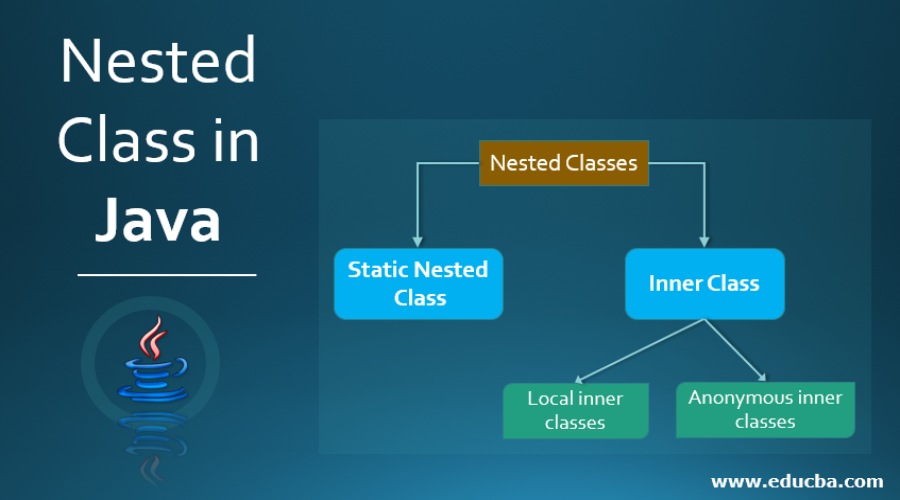
Categories of Nested Class in Java
A nested class is divided into two categories:
- Static Nested Class: We refer to a nested class declared with the keyword “static” as a static nested class. Static Nested classes are accessible by referencing the outer class. The nested class, which has a static class, cannot access the nonstatic variables & methods of the outer class.
- Inner Class: A nonstatic nested class is an inner class that is not statically declared. No static nested classes would have access to all the static & nonstatic variables & methods even if it is declared private. The inner class also has two types.
- Local inner classes
- Anonymous inner classes
Syntax:
In the below syntax, OuterClass has an inside class InnerClass known as the Nested class.
//Outer class
class OuterClass {
//Inner class as a nested class
class InnerClass {
....
}
}Use of Nested Class in Java
In the programming world, the Nested class plays an important role, as given below:
- Nesting of the class is like grouping classes in another class scope. You cannot use nested classes in other places.
- Leads to Readability & Maintainability: Nesting of classes provides better code readability and is easier to maintain as it doesn’t affect the other classes.
- Reduced Code: Using nested classes reduces lines of code, leading to optimization.
- Increases Encapsulation: In nested classes, inner classes have access to the member of its enclosing outer class. At the same time, the outer class cannot access inner-class members directly. Additionally, the inner class is not visible or accessible from outside programs.
Examples of Nested Class in Java
Given below are the examples of Nested Class in Java:
Example #1
In this example, you can observe the instantiation of inner classes by referencing the outer class.
Code:
// Outer class which contains nested class
class Engine{
static double fuel = 20.0;
//static nested class
static class Ignition{
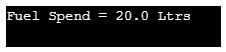
void showFuelSpend() {
System.out.println("Fuel Spend = " + fuel + " Ltrs");
}
}
}
//class uses nested class inside it
public class NestedClassExample{
public static void main(String[] args) {
//creating object of the nested class by referencing parent class
Engine.Ignition engIgnitObj = new Engine.Ignition();
//calling method of the nested class
engIgnitObj.showFuelSpend();
}
}Output:
Example #2
In this example, we can see how the inner class can be instantiated. You will need an instance of the inner class to create an instance of the inner class. After creating an instance of the Outer class, it becomes possible to create an instance of the nested class within it.
Code:
//Outer class
class Volume{
double x, y, z;
Volume(double x, double y, double z) {
this.x = x;
this.y = y;
this.z = z;
}
// Nested inner class
class Measurement{
//method to calculate the total area
void totalArea(double i, double j) {
System.out.println("\nArea for the provided container is " + (i * j));
}
//method to calculate the total volume
void totalVolume(double i, double j, double k) {
System.out.println("\nVolume for the provided container is " + (i * j * k));
}
}
}
public class NestedClassCalcExample {
public static void main(String[] args) {
//passing here all the parameter to constructor
Volume volObj = new Volume(30.0, 25, 18.0);
Volume.Measurement volMeasureObj = volObj.new Measurement();
// calculating total area
volMeasureObj.totalArea(volObj.x, volObj.y);
// calculating total volume
volMeasureObj.totalVolume(volObj.x, volObj.y, volObj.z);
}
}Output:

Example #3
This example demonstrates how the instantiation of a nested class object occurs within an instance of the outer class.
Code:
//outer class
class Electronic{
String circuitName,
String circuitType;
double circuitCost;
//constructor of outer class
Electronic(String name, String type, double cost) {
this.circuitName = name;
this.circuitType = type;
this.circuitCost = cost;
}
String getCircuitName() {
return this.circuitName;
}
//nested class
class Circuit{
String circuitType;
double circuitCost;
void setCircuitType() {
this.circuitType = "Transistor";
this.circuitCost = 430.0;
}
//get circuit type using this method
String getCircuitType(){
return this.circuitType;
}
//get circuit cost using this method
double getCircuitCost(){
return this.circuitCost;
}
}
}
public class Product{
public static void main(String[] args) {
Electronic elObj = new Electronic("Amplifier", "Integrated", 375.0);
Electronic.Circuit circuit = elObj.new Circuit();
//printing here the values before reset it
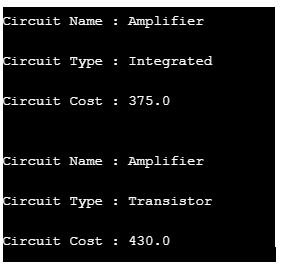
System.out.println("\nCircuit Name : " + elObj.circuitName);
System.out.println("\nCircuit Type : " + elObj.circuitType);
System.out.println("\nCircuit Cost : " + elObj.circuitCost);
//resetting some value
circuit.setCircuitType();
//printing here the values before reset it
System.out.println("\n\nCircuit Name : " + elObj.getCircuitName());
System.out.println("\nCircuit Type : " + circuit.getCircuitType());
System.out.println("\nCircuit Cost : " + circuit.getCircuitCost());
}
}Output:
Conclusion
In the above-given article, we reviewed how the Nested class is essential in java. It is good practice to utilize the nesting of classes. The above article also describes the usability of the Nested class.
Recommended Articles
This is a guide to Nested Class in Java. Here we discuss the basic concept, Use of Nested Class in Java, along with detailed examples. You may also have a look at the following articles to learn more –


