Updated May 12, 2023
Introduction to MySQL WHILE LOOP
The MySQL WHILE LOOP allows us to repeatedly execute one or multiple MySQL statements or queries until a certain condition is met and returns the corresponding result value.It is also known to be a pre-test conditional loop among the three-loop MySQL statements WHILE, LOOP, and REPEAT because the search condition is tested initially before the code statement execution. WHILE loop, when iteratively processed, executes the SQL statements as a result sets as long as the conditional expression is TRUE. Each statement in the WHILE loop terminates with the inclusion of a semicolon. The loop iteration occurs whenever the condition is evaluated. The result depends on the code flow. But if the MySQL WHILE loop condition is FALSE when the expression evaluates between while and end while statements, it exits the loop.
Syntax
We represent the elementary syntax for the WHILE loop as follows:
[Label_to _begin:] WHILE SearchCondition DO
SQL statement(s)
END WHILE [Label_to_end]Explanation of the above syntax terms:
- Using the label name, we can provide an optional label to the WHILE loop during the beginning or end of the MySQL execution of the query statement.
- A search condition is specified right after the WHILE keyword
- At the beginning of each iteration, the condition is checked.
- If it evaluates TRUE, then the WHILE loop executes the other lists of statements until the search condition results generate TRUE.
- Between the DO and END WHILE Loop keywords, one or multiple statements specified will be executed.
- If the WHILE condition evaluates to FALSE, the loop terminates and ends.
- The loop works on stored programs and returns
Flowchart
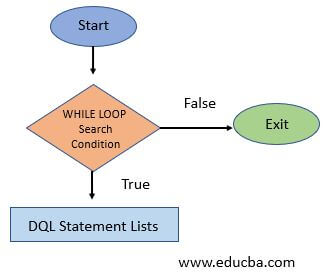
We can better understand the MySQL WHILE loop process with the help of a flowchart. This diagrammatic illustration will clarify our concepts regarding the TRUE and FALSE evaluations in a WHILE loop and execution of SQL statements.
The flowchart specifies the necessary arrangement of the WHILE loop iterative process in MySQL.
How does WHILE LOOP work in MySQL?
- The visual symbolic diagram above also represents the simple design notion and meaning of the WHILE loop algorithm in MySQL.
- Firstly, the WHILE loop execution is started; for each loop iteration, the condition defined is evaluated, then based on the result of the WHILE condition, the SQL statement is determined. The code flow statements will be executed when the WHILE loop results in TRUE.
- Secondly, if the WHILE loop execution tends to produce any FALSE result according to the search condition, the code flow will be withdrawn, and the WHILE loop will stop further processing. And suppose it will be accomplished if any SQL statement is available outside the WHILE loop.
Example to Implement WHILE LOOP in MySQL
Let us discuss some of the examples of WHILE loop MySQL statements to execute the SQL query code as follows:
- Let’s consider a table named Calendar_Data to store the values of the WHILE loop and execute the statements accordingly. Let us write the SQL query to create the MySQL table, which will store the dates and other derived information such as year, month, day, and quarter. Here is the SQL CREATE Statement:
Code:
CREATE TABLE Calendar_Data (CID INT AUTO_INCREMENT, CDate DATE UNIQUE, CDay TINYINT NOT NULL, CMonth
TINYINT NOT NULL, CQuarter TINYINT NOT NULL, CYear INT
NOT NULL, PRIMARY KEY(CID));- After this, we must make a new stored procedure in the Calendar_Data table to enter a date value. The MySQL query for this is below:
Code:
DELIMITER $$
CREATE PROCEDURE EntryCalendar(cdt DATE)
BEGIN
INSERT INTO Calendar_Data(CDate, CDay, CMonth, CQuarter, CYear) VALUES(cdt, EXTRACT(DAY FROM cdt), EXTRACT(MONTH FROM cdt), EXTRACT(QUARTER FROM cdt),
EXTRACT(YEAR FROM cdt));
END$$
DELIMITER;
DELIMITER $$- In the third step, we will generate a new stored procedure, i.e., LoadCalendar_Data(), responsible for loading several days into the Calendar_Data initialized by the start date.
Code:
CREATE PROCEDURE LoadCalendar_Data(startDate DATE, day INT)
BEGIN
DECLARE counter INT DEFAULT 1;
DECLARE cdt DATE DEFAULT startDate;
WHILE counter <= day DO
CALL EntryCalendar(cdt);
SET counter = counter + 1;
SET cdt = DATE_ADD(cdt,INTERVAL 1 day);
END WHILE;
END$$
DELIMITER;Here, the LoadCalendar_Data stored procedure comprises and accepts two parameters in the function:
- In MySQL, the DATE data type of startData denotes the start date that we insert in the Calendar_Data table.
- day parameter in the procedure loads the number of days starting from the startDate into the table.
In this loading procedure:
- Before the WHILE loop begins, we declare the variables counter, and cdtto holds the immediate values. By default, the counter and cdt variables values are one and startDatecorrespondingly.
- Now, with MySQL WHILE Loop’s help, we will detect if the variable counter value is equal to or less than the day parameter value on execution.
If the result goes yes, then:
- To enter the row values in the Calendar_Datatable, we call a stored procedure named EntryCalendar.
- Again, as the loop iterates, we increase the counter by one, and we increment cdt by one day using the DATE_ADD() function in MySQL.
The WHILE loop repeats the counter condition unless the variable counter value is identical to the day parameter value and respectively inserts the date values into the columns in the Calendar_Datatable.
Example
Finally, we will use the following query statement to call the LoadCalendar_Data() stored procedure that holds 15 days row values records into the Calendar_Data table starting from 1st January 2020.
Code:
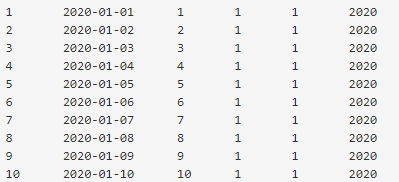
CALL LoadCalendar_Data('2020-01-01',10);We can view the Calendar_Data records using the WHILE loop and stored programs using the SELECT keyword.
SELECT * FROM Calendar_Data;Output:
Conclusion
A WHILE loop in MySQL works to execute a block of code statements while a search condition or say WHILE loop condition remains TRUE. When the part of the code has a stated condition, the loop continues to execute the SQL part. Otherwise, the loop ends if no WHILE condition occurs. A MySQL-stored program structure implements a WHILE loop to work fast.
Recommended Articles
We hope that this EDUCBA information on “MySQL WHILE LOOP” was beneficial to you. You can view EDUCBA’s recommended articles for more information.