Updated May 17, 2023
Differences Between MySQL vs MongoDB
MySQL is a database system used in Web Development. It is developed, marketed, and supported by MySQL AB, a Swedish company. MySQL is very fast, easy-to-use. It uses a standard form of the well-known SQL data language. It supports large databases, up to 50 million rows or more in a table. MongoDB is a NoSQL Database. It is a cross-platform, document-oriented database with high availability, performance, and easy scalability. MongoDB works on the concept of collection and document.
MySQL
- You have nothing to pay to use it because MySQL is released under an open-source license. It works on many operating systems and with many languages, including C++, JAVA, PHP, PERL, C, etc. The open-source GPL license allows programmers to modify the MySQL software to fit their specific environments.
- The default file size limit for a table is 4GB. We can increase this (if our operating system can handle it) to a theoretical limit of 8 million terabytes (TB). It works very quickly and works well even with large datasets. It handles a large subset of the functionality of the most expensive and powerful database packages.
- Compiles on many platforms. It is named after co-founder Monty Widenius’s daughter: My. Data is stored in MySQL tables; Tables are collections of related data. Tables have rows and columns to store data; different keys like primary keys, Foreign keys, etc., relate tables.
MongoDB
- A collection is a group of MongoDB documents. It is the equivalent of an RDBMS table. A collection exists within a single database. Collections do not enforce a schema.
- A document is a set of key-value pairs. Documents have a dynamic schema. Dynamic schema means that documents in the same collection do not need the same set of fields or structures, and common fields in a collection’s documents may hold different types of data.
MySql Stores date in from Tables Example given below
| ID | FirstName | LastName | Age | |
| 312 | John | Roy | 44 | [email protected] |
MongoDB stores data in the form of Documents Example given below.
{
_id: ObjectId(7df38ad8902c)
title: 'MongoDB Test',
description: 'MongoDB is no sql DB',
by: 'by me',
url: 'http://www.xyz.com',MySQL vs MongoDB
tags: ['mongodb', 'database', 'NoSQL'],
likes: 100,
comments: [
{
user:'user1',
message: 'thinking to ask question',
dateCreated: new Date(2011,1,21,2,15),
like: 0
},
{
user:'user2',
message: 'how we are going to use please help me',
dateCreated: new Date(2011,1,27,7,45),
like: 5
}
]
}In the above documents _id is a 12 bytes hexadecimal number, which assures the uniqueness of every document. We can provide _id while inserting the document. MongoDB offers a unique id for every document if we don’t provide one. These 12 bytes are the first 4 bytes for the current timestamp, the next 3 bytes for the machine id, the next 2 bytes for the process id of the MongoDB server, and the remaining 3 bytes are simple incremental values.
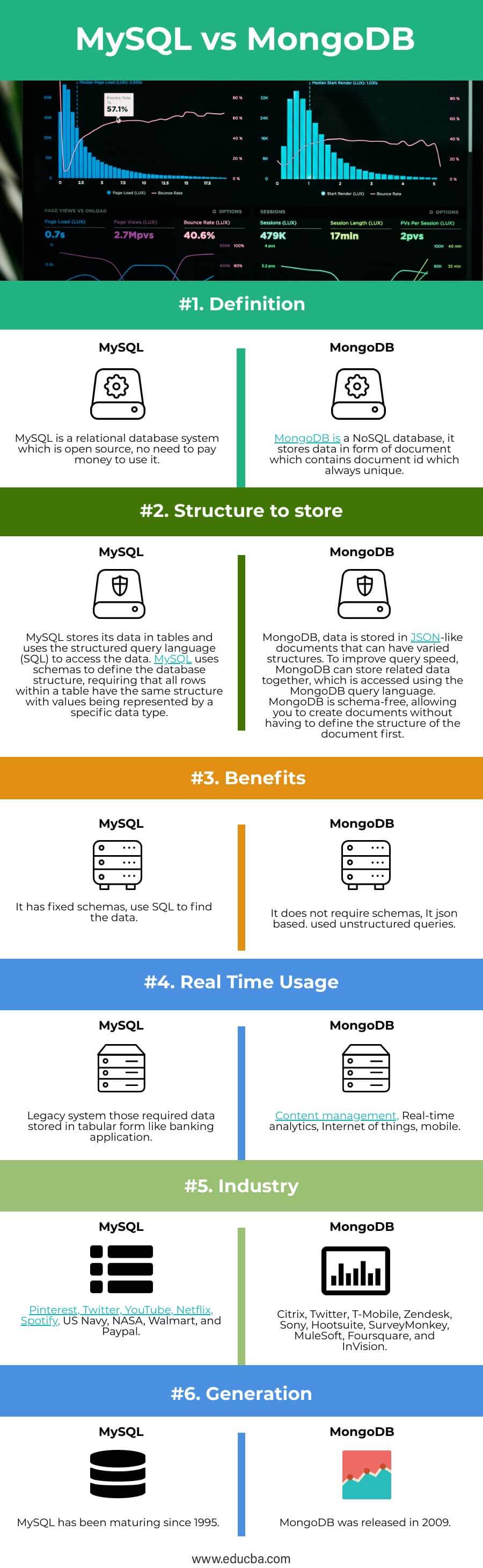
Head to Head Comparison Between MYSQL vs MongoDB (Infographics)
Below are the top 6 differences between MYSQL and MongoDB:
Key Differences Between MYSQL and MongoDB
Let us discuss some of the significant differences between MYSQL and MongoDB:
In MySQL: if an index is not defined, the database engine must scan the entire table to find all relevant rows.
In MongoDB: if an index is not found, every document within a collection must be scanned to select the documents that match the query statement.
Selecting records from the customer table:
In MySQL: SELECT * FROM customer In MongoDB: db.customer.find()
Inserting records into the customer table:
In MySQL: INSERT INTO customer (cust_id, branch, status) VALUES (‘appl01’, ‘main’, ‘A’)
In MongoDB: db.customer.insert({ cust_id: ‘appl01’, branch: ‘main’, status: ‘A’})
Updating records in the customer table:
In MySQL: UPDATE customer SET branch = ‘main’ WHERE custage > 2
In MongoDB: db.customer.update( { custage: { $gt: 2 } }, { $set: { branch: ‘main’ } }, { multi: true } )
MySQL is written in C and C++ and has binaries for the following systems: Microsoft Windows, OS X, HP-UX, Linux, AIX, BSDi, FreeBSD, IRIX, NetBSD, and more.
The developers wrote MongoDB in C++, C, and JavaScript, and they created binaries for the following systems: Linux, OS X, Solaris, and Windows.
MySQL: MySQL supports master-slave replication and master-master replication (as of MySQL 5.7.6 and later). Multisource replication allows you to replicate from several masters in parallel.
MongoDB: MongoDB supports built-in replication, sharding, and auto-elections. Using auto-elections, you can set up a secondary database to automatically take over if the primary database fails. Sharding allows for horizontal scaling, which is difficult to implement in MySQL.
MYSQL and MongoDB Comparison Table
Below is the comparison table between MYSQL and MongoDB.
| Basis Of Comparison | MYSQL | MongoDB |
| Definition | MySQL is an open-source relational database system; there is no need to pay money to use it. | MongoDB is a NoSQL database; it stores data in the form of a document that contains a document id that is always unique. |
| Structure to store | MySQL stores its data in tables and uses the structured query language (SQL) to access it. MySQL uses schemas to define the database structure, requiring all rows within a table to have the same structure with values represented by a specific data type. | MongoDB, data is stored in JSON-like documents that can have varied structures. MongoDB can store related data together to improve query speed, which is accessed using the MongoDB query language. It is schema-free, allowing you to create documents without defining the document’s structure first. |
|
Benefits |
It has fixed schemas, uses SQL to find the data | It does not require schemas; json based. Used unstructured queries. |
| Real-Time Usage | Legacy systems require data stored in a tabular form like a banking application. | Content management, Real-time analytics, Internet of things, mobile. |
| Industry | Pinterest, Twitter, YouTube, Netflix, Spotify, US Navy, NASA, Walmart, and Paypal | Citrix, Twitter, T-Mobile, Zendesk, Sony, Hootsuite, SurveyMonkey, MuleSoft, Foursquare, and InVision |
| Generation | MySQL has been maturing since 1995. | MongoDB was released in 2009. |
Conclusion
Both MySQL and MongoDB have advantages and disadvantages, .which one has to use depend on our project requirements. If we are dealing with a banking system that maintains users’ transactions or a legacy system, in these cases, MySQL selection will be the best choice while in the case of an Internet of things, Mobile, Content Management, and analytics MongoDB will be the best choice.
Recommended Articles
We hope that this EDUCBA information on “MYSQL vs MongoDB” was beneficial to you. You can view EDUCBA’s recommended articles for more information.