Updated June 6, 2023
Introduction to MySQL User Permissions
The MySQL user account is assigned user permissions, which determine the actions that the user is allowed to perform on the server. The degrees of rights these user permissions apply to for various query executions may vary. Administrative permissions are global privileges not specified to a specific MySQL database that enables the account users to regulate the admin operations in the MySQL server.
User Permissions also provide rights for database objects within a particular database, such as indexes, tables, stored routines, and views, along with data types. Also, it can be applied generally for all data objects available in all databases.
How to Apply User Permissions in MySQL?
- In MySQL, the administration concept is more than just executing query statements. We manage the database records for security and data maintenance using user access available to this data and permissions. In more giant corporations, we may have several users with permission to access the table’s data. We can restrict some admin-level access to a few users and implements special permission for each user.
- When any user account is created in MySQL, we have to allocate some consent to it for any primary tasks. There is a difference between other database platforms and MySQL servers in that the hostname and user are the primary keys to determining user permissions. Here, MySQL’s hostname recognizes users holding access to specific hosts defined. For demonstration, suppose that we have a user named ‘admin,’ but we only require to provide myadmin the local database access. Due to this, my admin users will have access to only the local host but cannot access the remote hosting server. The hostname can be an IP address, a wholly qualified name, or a wildcard hostname that provides access to different databases.
- MySQL database administrators may allocate privileges to columns, tables, or whole databases. For illustration, assume we have a table having information about the products. To know specific data about product prices, we can only give access to table columns for a particular number of users. Here, we will not provide the right to access the Product id or security code if present. Still, for instance, we can provide access to a few columns such as product name, category, unit, and supplier so that the reports can be prepared. This type of access control in the database is denoted as column-level security.
Examples of MySQL User Permissions
Let us elaborate on some examples and query commands to show the MySQL User Permissions in the server:
When we work on a server like a localhost, we know that we have already installed MariaDB or MySQL server on our system. We have to execute all commands in the MySQL shell as an admin user or root user. We must use CREATE USER and GRANT privileges command to create user account permissions. This user account in MySQL includes two sections host name and user name. Now, if we want to create a new user account in MySQL, then we need to query the following command:
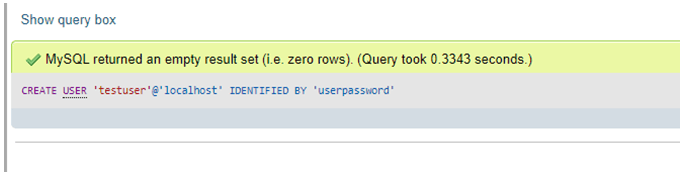
CREATE USER 'testuser'@'localhost' IDENTIFIED BY 'userpassword';Output:
Here, it would be best to use the actual username in place of the test user and the associated password as the user password.
Suppose we want to replace or modify the hostname with any other grant access with the remote IP address, then we can use the command like this:
CREATE USER 'testuser'@'10.2.0.8' IDENTIFIED BY 'userpassword';The hostname and associated password for remote access from a device with IP 10.2.0.8 are set to establish a new user.
Also, there may be a case where we want to connect the user from any host or machine address. Then, in such a case, we will apply the symbol ‘%’ that denotes wildcard to define the hostname. View the query below for this:
CREATE USER 'testuser'@'%' IDENTIFIED BY 'userpassword';Now, let us discuss more types of privileges that a user account can grant. Following is the list of permissions of the user account that MySQL supports:
- ALL PRIVILEGES: Allows all permissions to a user account.
- CREATE: Permits a user account to create databases and tables in the MySQL server.
- DROP: Allows a user account to remove tables and databases in the server.
- DELETE: Permits a user to drop rows from a particular table in the server.
- INSERT: Allows a user to enter rows into a specific table in the database.
- SELECT: Permits a MySQL user to view or read the database present on the server.
- UPDATE: Allows a user to alter the table rows in the database server.
If we want to show all the permissions provided to the MySQL User Account for any specific databases, then we will use the following:
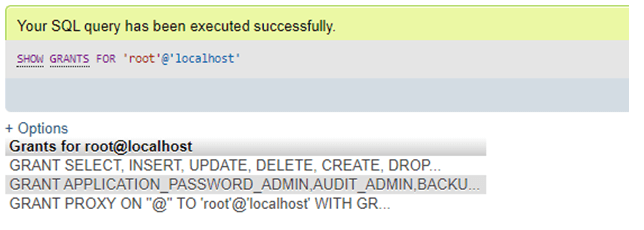
SHOW GRANTS FOR 'database_user'@'localhost';Query:
SHOW GRANTS FOR 'root'@'localhost';Output:
Again, to provide multiple permissions to a MySQL user account over a particular database:
GRANT SELECT, INSERT, DELETE ON DatabaseName.* TO 'Database_User'@'localhost';Similarly, if we need to cancel or revoke all permissions from a MySQL user account over a specific MySQL database, we need to execute the following query:
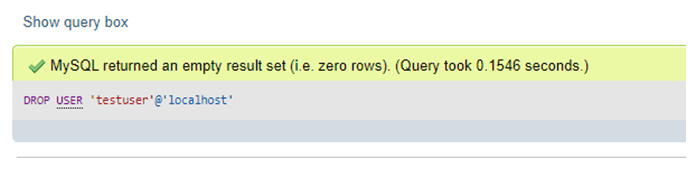
REVOKE ALL PRIVILEGES ON DatabaseName.* FROM 'Database_User'@'localhost';At last, if we want to remove any current MySQL user account, including its permissions, then we can run the following query:
DROP USER 'testuser'@'localhost';Output:
Conclusion
MySQL, a well-known database storage and management system, is responsible for storing, organizing, and retrieving data as needed. However, one must be given particular user permissions at different authority levels to do the server actions. The root user can access the whole database and administer all related activities. User permissions can be only specified to tables or table columns and not the full database in the server, which is useful in the security of data records and server maintenance.
Recommend ed Articles
We hope that this EDUCBA information on “MySQL User Permissions” was beneficial to you. You can view EDUCBA’s recommended articles for more information.