Updated June 2, 2023
Difference between MySQL Text vs Varchar
MySQL Varchar defines a data type string with a variable length that stores a value as a length prefix of 1-byte or 2-byte plus actual data. Besides Varchar and Char data types, the MySQL server supports the TEXT data type, including additional features that the previous two do not contain. In this topic, we will learn about MySQL text vs varchar.
MySQL Text is a data type in MySQL responsible for storing a text data value in the database table. The Text type is beneficial to store the long-form text strings from length 1 byte to 4 GB. Unlike Varchar; we do not need to specify the length storage using Text type for a table column. The length prefix denotes the number of bytes present in a value. Suppose a table column needs less than 255 bytes; then a 1-byte length prefix is used. Also, when the column needs more than 255 bytes a 2-byte length prefix is used. But the total length for all columns should be to a maximum size of 65,535.
Head-to-Head Comparison Between MySQL Text vs Varchar (Infographics)
Below are the top differences between MySQL text and Varchar
Key differences between MySQL text vs Varchar
Below are the key differences between MySQL text vs varchar:
1. VARCHAR
VARCHAR follows the standard ASCII character. This data type uses dynamic memory allocation. For Varchar, the maximum length for table row size is up to 65,535 characters. It means that the columns available in a database table should be of a total length of less than the max size. Suppose let us illustrate the above with the following example:
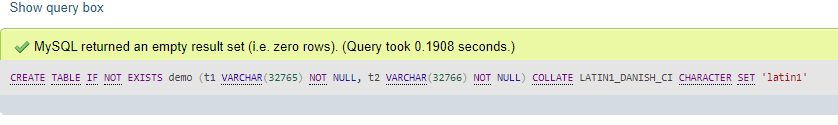
We are creating a table with two columns, t1, and t2, consisting of 32765 & 32766, i.e., +2 for length prefix. Here, you can evaluate the row size as 32765+2+32766+2=65535, the max size. The query is:
CREATE TABLE IF NOT EXISTS demo (t1 VARCHAR(32765) NOT NULL, t2 VARCHAR(32766) NOT NULL) COLLATE LATIN1_DANISH_CI CHARACTER SET 'latin1';Output:
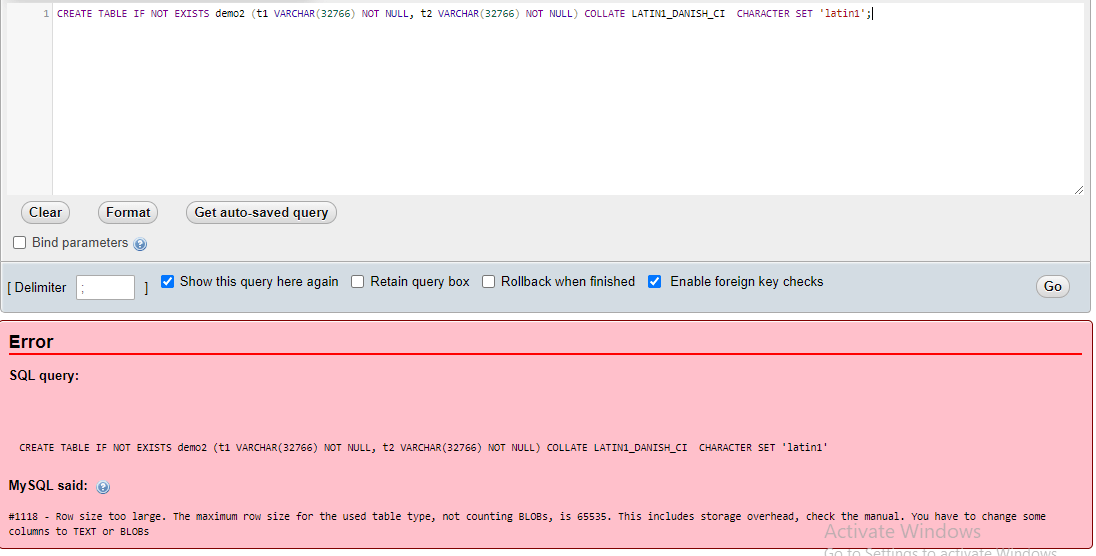
The above query will create the table named demo. But when we increment the length size of column t1 by 1 for another table demo2, then the query is executed as follows:
CREATE TABLE IF NOT EXISTS demo2 (t1 VARCHAR(32766) NOT NULL, t2 VARCHAR(32766) NOT NULL) COLLATE LATIN1_DANISH_CI CHARACTER SET 'latin1';Output:
The server will generate the error message because as we have increased the column size by1 then, the total row size becomes 65536, which is too big. Thus, the query statement becomes fails.
While storing the VARCHAR type values, the MySQL server does not remove spaces. However, the server will maintain the trailing spaces during the insertion or selection of Varchar values.
2. TEXT
Conversely, the Text type values are not kept in the server’s database memory. Hence, whenever a user queries Text data, the MySQL server has to view it from the disk. This is a much slower process in comparison to Varchar.
MySQL supports four types of Text data: Text, TinyText, MediumText, and LongText.
Let us view the size of all four Text types using a character set (1 byte to store a character):
3. TINYTEXT
This Text type can store a maximum of 255 characters (255 Bytes). If a table column needs less than 255 characters, contains inconsistent length, and does not need sortings like the excerpt for a summary of an article or a blog post. To illustrate this, let us view the example below:
CREATE TABLE Books (BookID INT AUTO_INCREMENT PRIMARY KEY, BookName VARCHAR (255), Summary TINYTEXT);4. TEXT
This TEXT type holds up to 65,535 characters (64KB) and needs a 2-byte overhead. In addition, the text type can contain the body of an article. For example:
CREATE TABLE Books (BookID INT AUTO_INCREMENT PRIMARY KEY, BookName VARCHAR (255), Body TEXT NOT NULL);5. MEDIUMTEXT
This type of Text can store a maximum of 16,777,215 characters (16MB). For the text data, it needs 3-bytes overhead. This Text kind is beneficial for storing quite big data such as the text of a white paper, book, etc.
CREATE TABLE Books (BookID INT AUTO_INCREMENT PRIMARY KEY, BookName VARCHAR (255), Body MEDIUMTEXT NOT NULL);6. LONGTEXT
This Text type can hold 4,294,967,295 characters (4 GB), which is a lot and needs 4-bytes overhead. View an example below:
CREATE TABLE Books (BookID INT AUTO_INCREMENT PRIMARY KEY, BookName VARCHAR (255), Body LONGTEXT NOT NULL, Price INT NOT NULL);Hence, the TEXT type supports a family column kind aimed to be a high-capacity character storage data type. The tiniest TEXT type, TINYTEXT, bonds the same character length as VARCHAR. The TEXT type holds character strings other than collation and binary character sets. Therefore, the sorting and comparisons take place based on this character set. If the truncation of trailing spaces from the Text values is exceeded when inserted into the table columns, MySQL often produces a warning irrespective of the SQL mode. This is because the Text table column does not contain any DEFAULT value.
For demonstration:
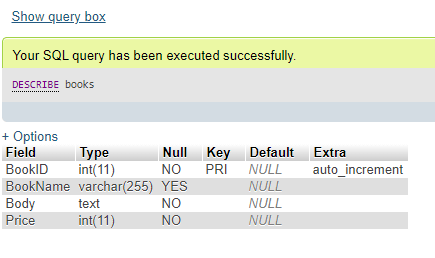
CREATE TABLE Books (BookID INT AUTO_INCREMENT PRIMARY KEY, BookName VARCHAR (255), Body TEXT NOT NULL, Price INT NOT NULL);
Describe Books;Output:
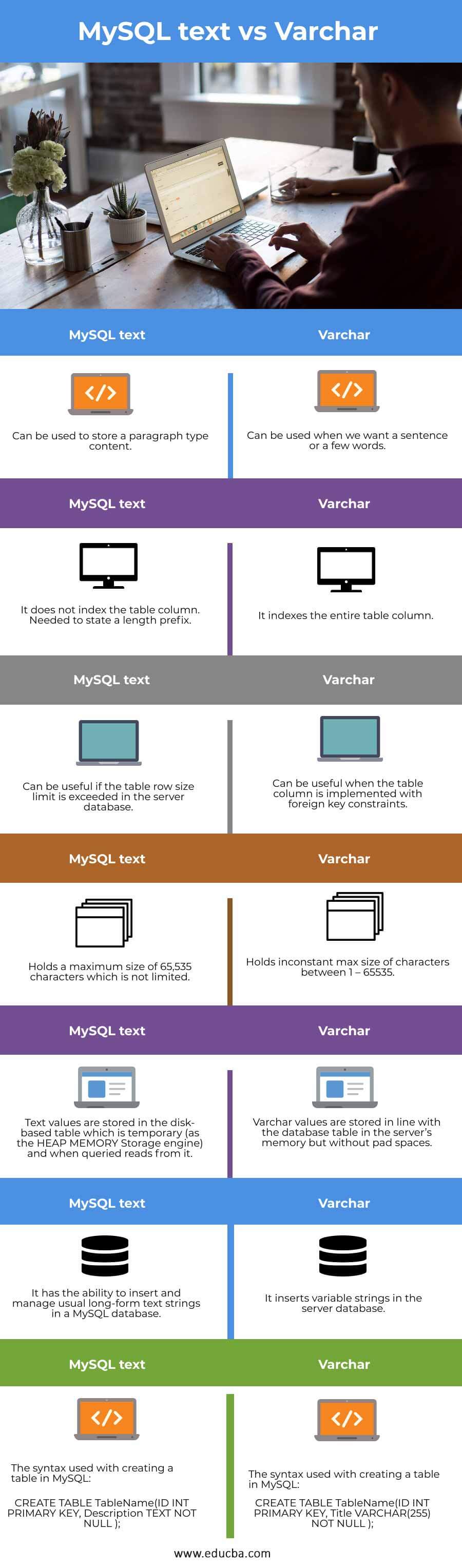
Comparison Table of MySQL text vs Varchar
Following is the comparison table between TEXT and VARCHAR data types in MySQL:
| TEXT | VARCHAR |
| It can be used to store paragraph-type content. | It can be used when we want a sentence or a few words. |
| It does not index the table column. I needed to state a length prefix. | It indexes the entire table column. |
| It can be useful if the server database’s table row size limit is exceeded. | It can be useful when the table column is implemented with foreign key constraints. |
| It holds a maximum size of 65,535 characters which is not limited. | Holds an inconstant max size of characters between 1 – 65535. |
| Text values are stored in the disk-based table, which is temporary (as the HEAP MEMORY Storage engine) and when queried, reads from it. | Varchar values are stored in line with the database table in the server’s memory but without pad spaces. |
| It can insert and manage usual long-form text strings in a MySQL database. | It inserts variable strings in the server database. |
| The syntax used for creating a table in MySQL:
CREATE TABLE TableName(ID INT PRIMARY KEY, Description TEXT NOT NULL ); |
The syntax used for creating a table in MySQL:
CREATE TABLE TableName(ID INT PRIMARY KEY, Title VARCHAR(255) NOT NULL ); |
Conclusion
The VARCHAR data type in MySQL can usually be applied for data that includes values like title, name, profile, product name, company names, etc., which holds short content in the table column.
Generally, the data type TEXT in MySQL stores the article content body in the production description and news sites in websites using e-commerce products.
Recommended Articles
We hope that this EDUCBA information on “MySQL text vs varchar” was beneficial to you. You can view EDUCBA’s recommended articles for more information.