Updated June 1, 2023
Definition
MySQL table size is determined in multiple ways; we can use various commands to retrieve MySQL table size. The “”how table status””command returns the information about the MySQL table; it also includes the size of the table. The total size of the MySQL table is a combination of index and data length. Add the index length with the data length to retrieve the original size of the MySQL table.
Key Takeaways
- Table size is crucial in the performance of a database, as we know that a larger table shows down the performance of the database and it will also increase the time to process the data.
- We can determine the table size using the amount of data stored, data type, and index of tables.
Introduction to MySQL Table Size
MySQL provides metadata about tables and databases. It will refer to the amount of disk space used to store the data and the indexes the table. The table size is essential for multiple reasons; it includes optimization, disk usage, and performance. The larger table size will lead the slower performance because the MySQL server needs to read more data from the disk and needs to process it. This is true for a large query that scans the whole table of MySQL to process the data.
To monitor the size of the table is to ensure the availability of disk space on the server that was used efficiently. If the table size is large, we can reduce it by optimizing the data and data types of the column. We can also delete unwanted data from the table. Table size also impacts capacity planning; it indicates the disk space that is required to store the data in the future.
Methods to Check MySQL Table Size
There are three methods used to check the size of the MySQL table.
1. Using phpMyAdmin
To check the size using phpMyAdmin, follow the below steps as follows.
1. Open the phpMyAdmin in the browser. We can open phpMySQL in the browser and install it in our system.
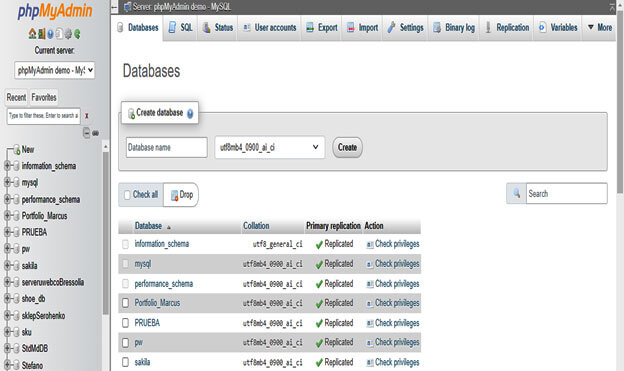
2. Below, we have enabled the database statistics as follows. To check the size of the table, first, we need to allow the statistics.
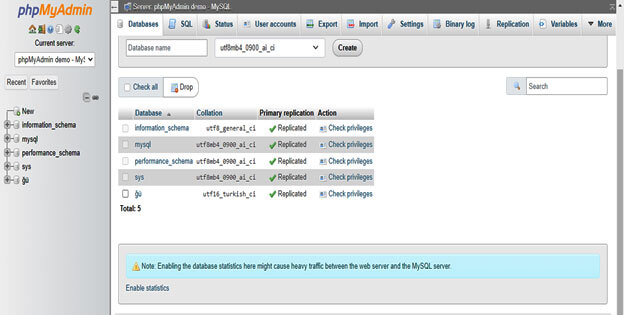
3. After opening the phpMyAdmin, now in this step, we have checked the size of all databases as follows.
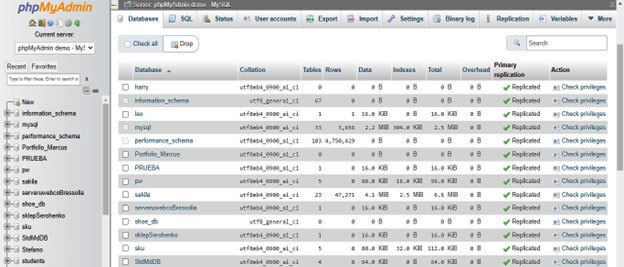
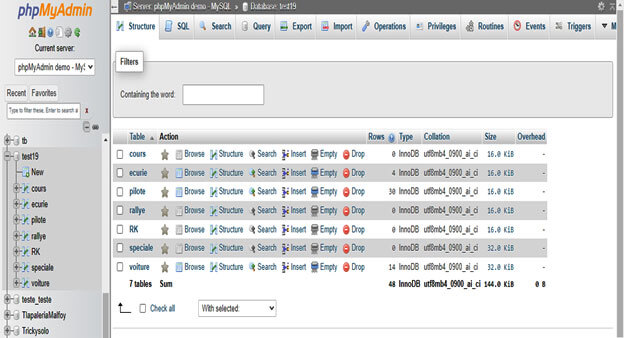
4. In this step, we have checked the size of all tables as follows.
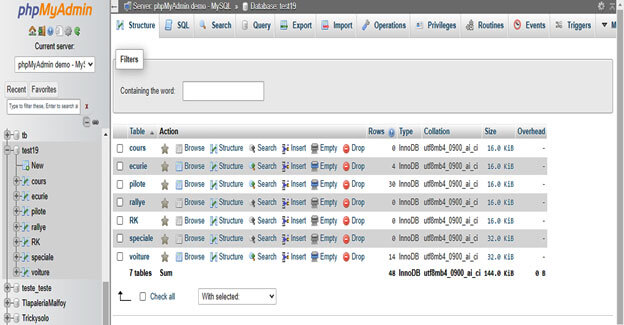
5. In this step, we have checked the size of single tables as follows.
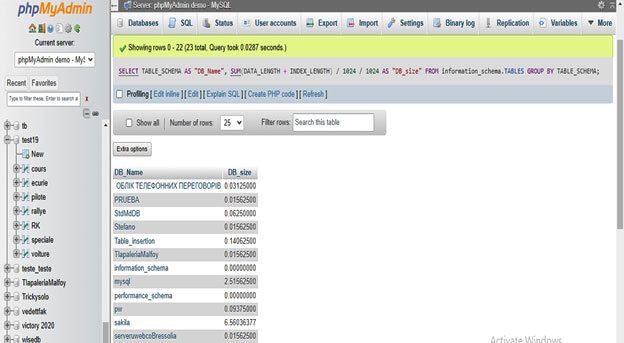
6. We can also get the size of all databases using SQL command in phpMyAdmin as follows.
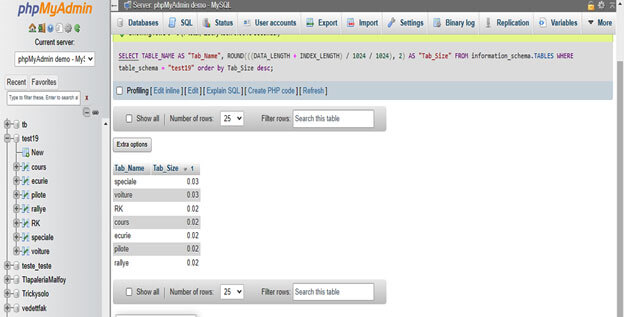
SELECT TABLE_SCHEMA AS "DB_Name", SUM(DATA_LENGTH + INDEX_LENGTH) / 1024 / 1024, 2 AS "DB_size" FROM information_schema.TABLES GROUP BY TABLE_SCHEMA;7. We can also get the size of all tables using SQL command in phpMyAdmin as follows.
SELECT TABLE_NAME AS "Tab_Name", ROUND(((DATA_LENGTH + INDEX_LENGTH) / 1024 / 1024), 2) AS "Tab_Size" FROM information_schema.TABLES WHERE table_schema = "test19" order by Tab_Size desc;2. Using the Command Line
Below steps show to find the size using the command line as follows.
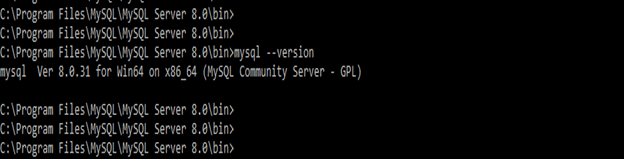
The pre-requisite is to check the size using the MySQL command line and install the MySQL client and server in our system. To check the MySQL client and server installation, execute the below command.
mysql –version1. In the first step, login into the MySQL server.
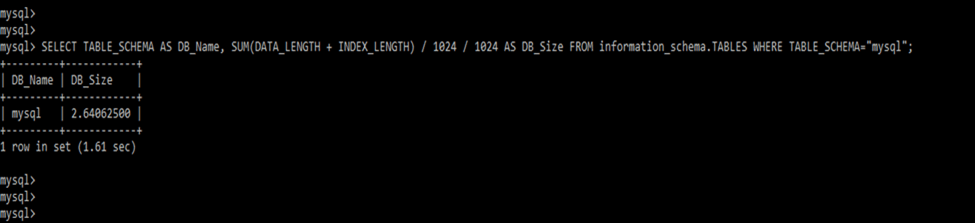
mysql –u root -p2. After logging in MySQL server, now in this step, we execute the select command to find the size of the specific database as follows. In the below example, we have seen the database size in MB.
SELECT TABLE_SCHEMA AS DB_Name, SUM(DATA_LENGTH + INDEX_LENGTH) / 1024 / 1024 AS DB_Size FROM information_schema.TABLES WHERE TABLE_SCHEMA="mysql";3. After getting the size of specific databases, now,, in this step, we execute the select command to find the size of all databases as follows.
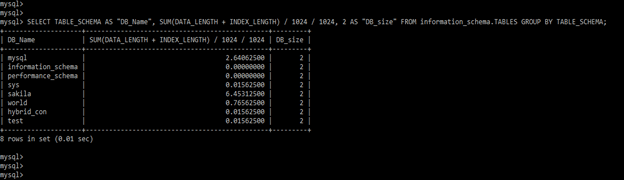
SELECT TABLE_SCHEMA AS "DB_Name", SUM(DATA_LENGTH + INDEX_LENGTH) / 1024 / 1024, 2 AS "DB_size" FROM information_schema.TABLES GROUP BY TABLE_SCHEMA;4. After getting the size of all databases, now in this step, we are executing the select command to find the size of all tables of specified DB as follows.
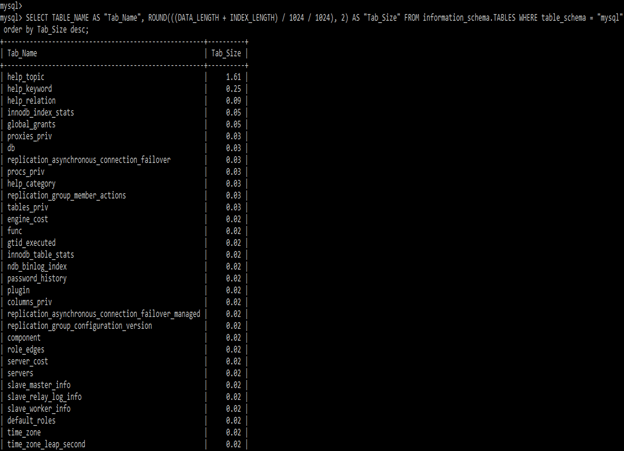
SELECT TABLE_NAME AS "Tab_Name", ROUND(((DATA_LENGTH + INDEX_LENGTH) / 1024 / 1024), 2) AS "Tab_Size" FROM information_schema.TABLES WHERE table_schema = "mysql" order by Tab_Size desc;3. Using Workbench
Below steps show to find the size using MySQL workbench as follows.
1. In the first step, open the MySQL workbench.
2. In this step, we show the MySQL table size by GUI option as follows.
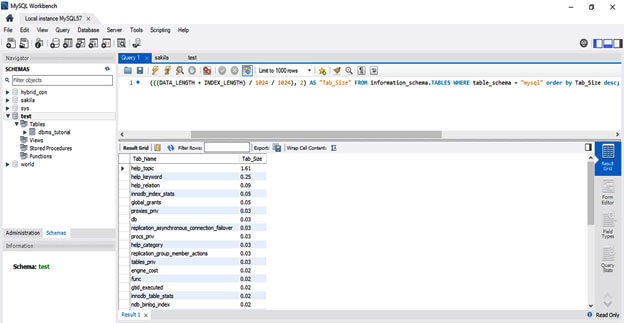
3. We can also find the table size using the SQL query tool in MySQL workbench as follows.
SELECT TABLE_NAME AS "Tab_Name", ROUND(((DATA_LENGTH + INDEX_LENGTH) / 1024 / 1024), 2) AS "Tab_Size" FROM information_schema.TABLES WHERE table_schema = "mysql" order by Tab_Size desc;List of MySQL Tables ordered by Sizes
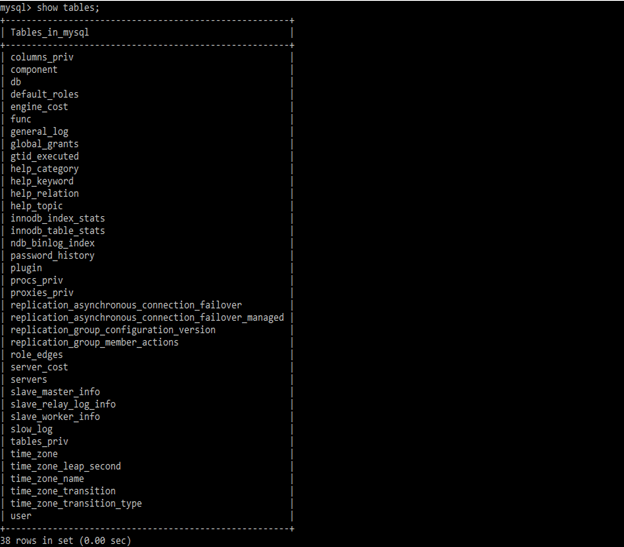
We can find the table size by using information_schema.tables. Below example shows to display a list of all tables from the specified schema.
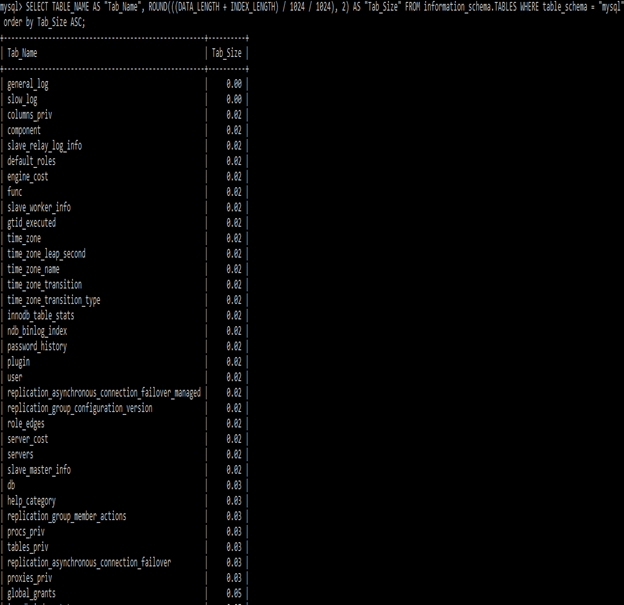
show tables;In the below section, we have retrieved the table size in ascending order. We can retrieve table size in ascending and descending order as follows.
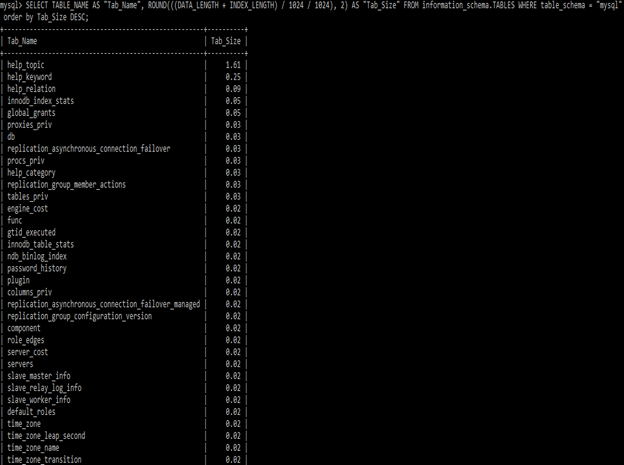
SELECT TABLE_NAME AS "Tab_Name", ROUND(((DATA_LENGTH + INDEX_LENGTH) / 1024 / 1024), 2) AS "Tab_Size" FROM information_schema.TABLES WHERE table_schema = "mysql" order by Tab_Size ASC;In the below section, we have retrieved the table size in descending order.
SELECT TABLE_NAME AS "Tab_Name", ROUND(((DATA_LENGTH + INDEX_LENGTH) / 1024 / 1024), 2) AS "Tab_Size" FROM information_schema.TABLES WHERE table_schema = "mysql" order by Tab_Size DESC;Conclusion
Understanding the size of MySQL database and table is essential to manage the whole database. The table size impacts query performance. To determine the table size, we use the select command and the and phpMyAdmin tool. We can also use other tools like dbeaver to find the size of the MySQL table.
Recommended Article
We hope that this EDUCBA information on “MySQL table size” was beneficial to you. You can view EDUCBA’s recommended articles for more information.