Updated May 31, 2023
Introduction to MySQL ORDER BY Random
MySQL ORDER BY Random is a MySQL technique to randomly query data records from a table in a specific MySQL database. This MySQL command helps to fetch the table rows with the ORDER BY clause unsystematically. For example, suppose we need to use this MySQL ORDER BY Random for selecting the following records from the table:
- Few random posts in a blog and show them in the particular sidebar.
- A random quote for presenting, “Latest Quote of the Day,” like in the widget section.
- Random images in a gallery and implement them as highlighted images.
MySQL has no built-in statement to choose unplanned table rows from a database table. Therefore, we will apply the MySQL RAND() function.
Syntax
Let us view the basic syntax structure that shows the working for the ORDER BY RAND() function:
SELECT * FROM TableName ORDER BY RAND() LIMIT1;The explanation of the above syntax query:
- The MySQL RAND() function produces a random value for every table row.
- After this, the ORDER BY clause helps to sort all the table rows by the random value or number produced by the function RAND() in MySQL.
- Next is the LIMIT clause, which picks the initial table row in a set of results that are ordered randomly.
Presume that you want to select random rows of records from the table in the database with the value ‘n,’ then we need to modify the LIMIT clause value as below:
SELECT * FROM TableName ORDER BY RAND() LIMIT N;How does ORDER BY Random work in MySQL?
- The ORDER BY RAND() technique in MySQL works to select the column values or records from the database table displayed randomly. The SELECT statement is used to query this technique.
- We will sort the records fetched with a query in MySQL using a specific function RAND(). Especially we can use this method to shuffle the song list while building up a music player so that each new playlist is generated from songs in the database than the previous list.
- This randomly selecting records makes it useful for the tables to have a small amount of data rows. Moreover, it works fast for query execution and result display.
- However, when used in a large table, this may slow down the process of execution using the ORDER BY RAND() function. MySQL needs to sort the whole table to find the random values, which is time-consuming.
- Therefore, the speed of this command query will depend on the number of rows available in a database table. So, if the table consists of more records, producing the random values in the result set for each row will require more time.
Examples of MySQL ORDER BY Random
We will evaluate the demonstration of this MySQL technique using the following examples:
Example #1 – Using ORDER BY RAND()
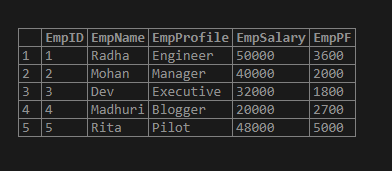
Let us take a sample database table named Employeeshaving fields EmpID, EmpName, EmpProfile, EmpSalary, and EmpPF.
select * from employees;Output:
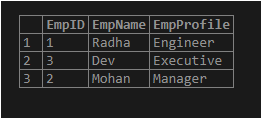
Suppose we will randomly fetch three employee rows from this table using the following query:
SELECT EmpID, EmpName, EmpProfile FROM Employees ORDER BY RAND() LIMIT 3;Output:
We can view that the provided result is somewhat different from the general one due to the randomized result query.
Example #2 – Using ORDER BY RAND() and INNER clause
For this example, we need the demo table whose fields have attributes: PRIMARY KEY and Auto Increment. Also, there should be no gap in the order series.
Now, based on the primary key table column, we have written the below query to produce the random number row values:
SELECT ROUND( RAND() * (SELECT MAX(Col_ID) FROM TableName)) AS Col_ID;With the result set provided by the above query, we will join the table as follows:
SELECT y.* FROM TableName AS y INNER JOIN
(SELECT ROUND( RAND() * (SELECT MAX(Col_ID) FROM TableName) ) AS Col_ID )
AS x WHERE y.Col_ID>= x.Col_ID LIMIT 1;Applying this process, we need to execute the command more than once to fetch multiple rows randomly. Increasing the command limit will only provide the serial rows that begin randomly from the row selected.
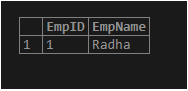
SELECT y.EmpID, y.EmpName FROM Employees AS y JOIN
(SELECT ROUND( RAND() * (SELECT MAX(EmpID) FROM Employees) ) AS EmpID)
AS x WHERE y.EmpID >= x.EmpID LIMIT 1;Output:
Example #3 – Using ORDER BY RAND() using a Subquery
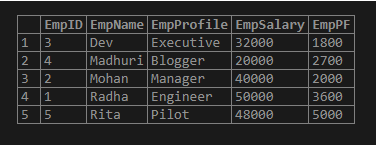
With the previous query technique, we can apply a subquery to sort randomly and view the name in either ascending or descending order as follows:
SELECT * FROM (SELECT * FROM Employees ORDER BY RAND() LIMIT 5)Empsub ORDER BY EmpName;Output:
Example #4 – Using ORDER BY RAND() using variables
Assuming that the database table includes an id column with the values falling in the range 1,..,n and consists of no gab. Then we need to follow the steps:
Firstly, select the random numbers within the 1,..,n range.
Next, we will choose the records based on random numbers. To accomplish this, we will use the following query:
SELECT TableName.* FROM (SELECT ROUND( RAND() * (SELECT MAX(Col_ID) FROM TableName) ) RandomVal, @val:=@val + 1 FROM (SELECT @val:=0)AS y , TableName LIMIT n )AS x, TableName AS a WHERE x.RandomVal = a.Col_ID;Remember that the user-defined variables are known to be connection-specific. This means that the proceeding technique cannot be implemented along with the connection pooling. For this purpose, we must also confirm that the column field in the specified table having PRIMARY KEY should be of data type integer. In addition, the table column values should also be in the defined series without any gap.
Conclusion
The MYSQL ORDER BY RAND() is essential to display the results to be ordered randomly. Like any information related to articles, pages, links, etc., that we want to show in the order sorted randomly from several databases.
Applying the ORDER BY RAND() technique in MySQL can be significant. However, if the table being queried is large, generating the results using ORDER BY RAND() can be time-consuming. Otherwise, tables having fewer records gives faster results.
Recommended Articles
We hope that this EDUCBA information on “MySQL ORDER BY Random” was beneficial to you. You can view EDUCBA’s recommended articles for more information.