Updated May 12, 2023
Introduction to MySQL REGEXP
The following article provides an outline for MySQL REGEXP. A regular expression is used with SELECT queries to search for patterns, generally strings, in the database. We can consider the REGEXP as a search tool to understand easily. This operation is similar to the “LIKE …%” operator, which also does pattern matching. REGEXP can be combined with almost all operators from the keyboard. The regular expression operator (REGEXP) can be considered a separate set of languages.
Syntax:
The syntax for the REGEXP function is as follows:
expression REGEXP patternHere, the ‘expression’ stands for the column name or the expression to be looked at from the database. The term ‘pattern’ represents the string to be searched in the DB.
While using a real query, the REGEXP will be as follows:
SELECT * from table_name where expression REGEXP pattern;The pattern will be mentioned with single quotes.
How RANK() works in MySQL?
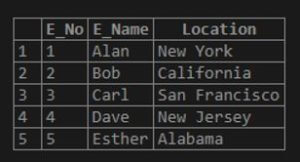
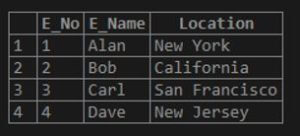
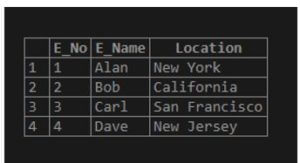
Consider the table emp as below:
Code:
select * from emp;Output:
Example #1
Here we need to get the details of employees with the character ‘a’ in their names.
Code:
select * from emp where E_Name REGEXP 'a';Output:
To analyze the query, we have described it to select all details from table ’emp’ with the character’ a’ in their E_Name field. And as we look at the output, we can understand that out of 5 employees, 3 have the character ‘a in their names: Alan, Carl, and Dave.
So we wrote the query for selecting details with a string in it. Here we just mentioned selecting data with a character. The specified character could be anywhere in the word.
Example #2
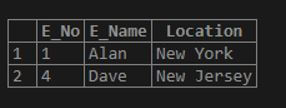
Here we see how to select the details of an employee whose name starts with a specific character.
Code:
select * from emp where E_Name REGEXP '^a';Output:
Here, we used the operator ‘^’ along with the pattern to be searched and thus got the details of employees whose name starts with the character ‘a’.
So far, the characters or strings considered as the pattern were not case-sensitive.
Example #3
Here we make it more specific by making it case-sensitive.
Code:
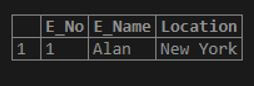
select * from emp where E_Name REGEXP BINARY '^a';Output:
Since we specified the lowercase character ‘a’ in the query, no results could be retrieved.
Example #4
Here let’s make it upper case and try to retrieve the output.
Code:
select * from emp where E_Name REGEXP BINARY '^E';Output:
Here we got the details of employees with the character ‘E’ in upper case at the beginning.
Example #5
Here we can search a part of a word as well.
Code:
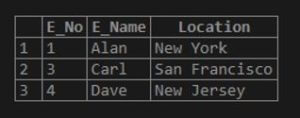
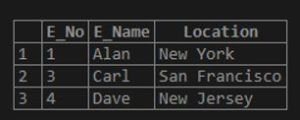
select * from emp where Location REGEXP BINARY '^New';Output:
The query says to select the entries for which the location field starts with the word ‘New’. And from the sample table, we get two rows satisfying the condition, which are New York and New Jersey. Also, since the BINARY function is mentioned in the query, it will check for case sensitivity too.
Example #6
Here we see how to search for an ending character/ word/ part of the word.
Code:
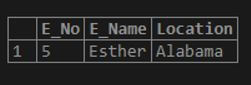
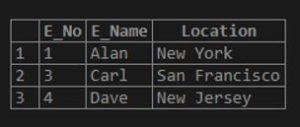
select * from emp where Location REGEXP 'a$';Output:
The query specifies to select entries from the employee table for which the location field ends with the character ‘a’. And as the output picked two entries from the table, which have character ‘a’ at the final character of the location, California and Alabama. So far, we have discussed searching for a single character, word, or a portion of a word.
Example #7
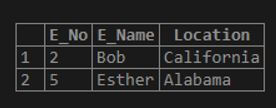
Here we can see how to search for a set of characters and a range of characters.
For example, let’s assume we need to identify the rows from the employee table with any of the characters’ a,’ b’, and ‘c’ in the E_Name column. We can put this exact requirement in two ways, first by mentioning all three characters as an array and second by mentioning the range of characters from ‘a’ to ‘c’.
Code:
select * from emp where E_Name REGEXP '[abc]';Output:
Example #8
Code:
select * from emp where E_Name REGEXP '[a-c]';Output:
Query 7 and 8 will give the same output. Query 7 picks rows with characters specified within the ‘[..]’ under column E_Name. We have mentioned characters ‘a, ‘b’, and ‘c’ within the square bracket. So the four rows will be selected to display. Here, note that the characters should be mentioned ‘without’ comma operator inside the square brackets.
Query 8 will pick those rows with characters within the range specified within the square bracket ‘[….]’. So those employee names, which include any characters ranging from ‘a’ to ‘c’, will be picked and displayed.
Example #9
Let’s write a query with the ‘OR’ operator, ‘ |’ in MySQL.
Code:
select * from emp where Location REGEXP 'new|san';Output:
The query is to search for locations with either ‘new’ or ‘san’ in the word. And there, we get three outputs with either of the words mentioned within the quotes.
Another operator generally used along with REGEXP is the number of characters in the word. Suppose we have to search for employee names with the same four characters; then we need to specify four instances of ‘.’ between the beginning and closing strings, which are ‘^’ and ‘$’.
Example #10
Here let’s write the query to identify names with four characters.
Code:
select * from emp where E_Name REGEXP '^....$';Output:
Conclusion – MySQL REGEXP
In this article, we have seen the REGEXP operator, which searches for characters or patterns in a table. Now we have gained familiarity with various string operators commonly used with the REGEXP operator, along with their syntax. We can use almost all string operators with the REGEXP operator in MySQL.
Recommended Articles
We hope that this EDUCBA information on “MySQL REGEXP” was beneficial to you. You can view EDUCBA’s recommended articles for more information.