Updated May 24, 2023
Introduction to MySQL Transaction
Mysql transactions can be defined as the atomic unit comprising multiple SQL query statements that must be executed completely or rollbacked when an issue occurs. Filing any of the database operations will result in inconsistencies and application inefficiency. For this, we use the transactions in Mysql. Mysql transactions allow you to perform a set of database operations. Suppose an error occurs due to factors such as table locking. In this case, the system will perform either a complete execution of all the commands and commit the transaction, or it will refrain from executing any of the commands and roll back the transaction. As a result, the database will remain unchanged. This article focuses on transactions in MySQL, including their properties, transactional statements, and how to utilize transactions in MySQL through an example.
Properties of MySQL Transaction
InnoDB provides complete ACID support among the different storage engines supported by MySQL. By the term ACID, we refer to the properties of the transactions.
The transaction supports four properties, namely:
- Atomicity
- Consistency
- Isolation
- Durability
Whose acronym is ACID. The following are the explanations of all four properties:
1. Atomicity: All the operations within a work unit need to be completed successfully. Suppose any problem or failure occurs while executing the operation. In that case, the system should roll back all the operations of that work unit and restore the state of the database to its previous state. The rollback should ensure no effect on the work unit operations on the database. The atomicity property ensures the completeness of work unit execution.
2. Consistency: It ensures the changes made to the database if the transaction is successfully committed.
3. Isolation: All the transactions work independently and are transparent to each other.
4. Durability: If the system fails, the changes made to the database need to be persisted.
Transactional statements in MySQL
MySQL provides certain statements that we can use to define the behavior of execution and control transactions. We mention all the transaction-related statements below.
1. START TRANSACTION, BEGIN, and BEGIN WORK: The START TRANSACTION statement is used to begin the transaction in MySQL. BEGIN and BEGIN WORK statements also provide the same functionality.
2. COMMIT: When all statements inside the transaction or work unit are completely executed, the transaction can be committed using the COMMIT statement.
3. ROLLBACK: In case there is a failure in the execution of specific queries inside the transaction, then the database effects of all the previously executed queries of the same transaction need to be rollbacked. We can achieve this by utilizing the ROLLBACK statement in MySQL.
4. SET autocommit: By default, all the operations in MySQL are automatically committed, and their changes are saved permanently. We have to set the autocommit property to off or 0 to remove the auto commitment working. By utilizing the SET autocommit statement, you can achieve this task.
You can accomplish this task using the following method:
SET autocommit = OFF;Or
SET autocommit = 0;To again reset the autocommit mode to yes, you can use the following statement:
SET autocommit = ON;Or
SET autocommit = 1;Examples to Implement MySQL Transaction
Consider that we need to add the developers and the technologies that the developers are aware of and use in the database. For this, we will need to store the data in two different tables as a single developer may use and be aware of multiple technologies. So, by applying normalization concepts, we will create two tables: developers and used_technologies. In the table of technologies, we will have to store the reference of the developer id, so there will be a foreign key to the developer’s table from the used_technologies table. So, our queries will be as follows –
Code:
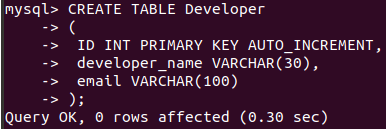
CREATE TABLE Developer
(
ID INT PRIMARY KEY AUTO_INCREMENT,
developer_name VARCHAR(30),
email VARCHAR(100)
);Output:
Code:
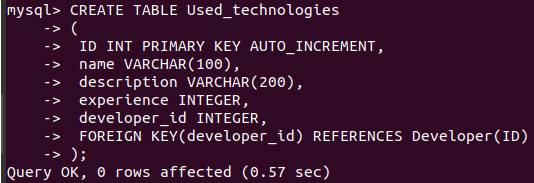
CREATE TABLE Used_technologies
(
ID INT PRIMARY KEY AUTO_INCREMENT,
name VARCHAR(100),
description VARCHAR(200),
experience INTEGER,
developer_id INTEGER,
FOREIGN KEY(developer_id) REFERENCES Developer(ID)
);Output:
The system should create a mechanism that simultaneously inserts all the technologies known by a developer into the used_technologies table whenever a new entry is made for a developer in the developer’s table. If a problem occurs while inserting the technologies related to the developer, then no entry should also be seen in the developer’s table. That means the system should either insert all the developer and related technologies entries or not insert any of them.
For this, we can use the transactions in the following way:
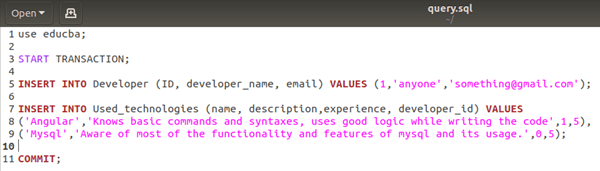
Code:
SET autocommit = 0;
START TRANSACTION;
INSERT INTO Developer (ID, developer_name, email) VALUES
(1,'anyone','[email protected]');
INSERT INTO Used_technologies (name, description,experience, developer_id) VALUES
('Angular','Knows basic commands and syntaxes, uses good logic while writing the code',1,5),
('Mysql','Aware of most of the functionality and features of MySQL and its usage.',0,5);
COMMIT;Output:
You can store this transaction code in a file; for example, we will store it in query.sql. Then using the pipe command as follows can run the transaction code on the MySQL server using the terminal:
cat query.sql |sudo mysql -u root -pOutput:
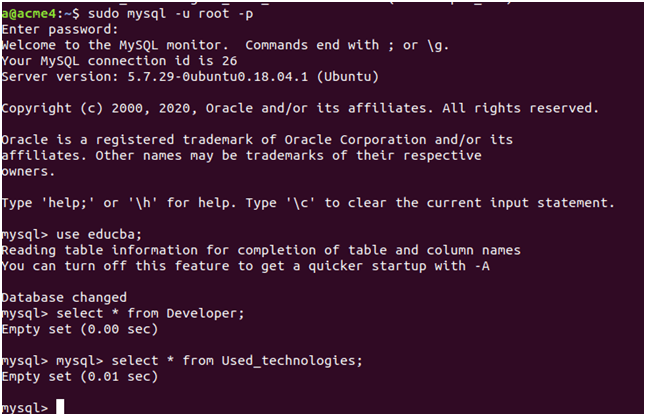
Let us check the contents of the Developer table and Used_technologies table by logging in to SQL and using the educba database in which they reside:
sudo mysql -u root -pOutput:
This is because we specified the developer_id value as 5, which does not exist in the Developer table. We inserted the developer record with an ID of 1. The system also rolled back the insert command on the developer’s table because we were using a transaction, as the second insertion command on Used_technologies failed. Try executing the two insert queries without a transaction and compare the results of using a transaction versus not using a transaction.
Conclusion
Transactions help us execute the statements following the acid properties, thus maintaining the integrity and consistency of the MySQL database.
Recommended Articles
We hope that this EDUCBA information on “MySQL Transaction” was beneficial to you. You can view EDUCBA’s recommended articles for more information.