Updated May 26, 2023
Introduction to MySQL DELETE JOIN
Mysql delete join is used to delete rows and records from a table and the matching records of another table. Matching records or rows in the join statements depends on the join we apply in our query, like whether we use inner, outer, full, etc.
Case Study for MySQL DELETE JOIN
Below we will learn about two different cases to study in MySQL DELETE JOIN:
Case #1
Let’s start explaining mysql delete join with the inner join clause. The inner join clause selects the records or rows that match values in another table.
Below is the inner join clause to select the matching records of the given two tables, table1, and table2:
Select col_name1,col_name2...col_namen from table1 INNER JOIN table2 ON table1.col_name=table2.col_name;In MySQL, we use the inner join clause to delete rows or records that have matching values in the table. For example, the following statement deletes records from table1 and table2 that satisfy a given condition:
Delete table1,table2 from table1 INNER JOIN table2 on table1.joining_col=table2.joining_col where condition;In the above statement, table1.joining_col =table2.joining_col, the expression is the matching condition between table1 and table2 that needs to be deleted. Also, the condition followed by the where clause will result in rows in table1 and table2 that need to be deleted.
If we remove table1, the delete statement is only applied to table2 and will only delete rows from table2. Similarly, if we remove table2, the delete statement is only used to table1 and will only delete rows from table1.
Examples to Implement
The examples mentioned are as follows:
Example #1
To explain delete inner join, we have created tables in the database named table1 and table2 and inserted five rows into them.
Code #1 – Creating table1
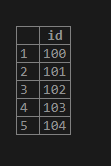
create table table1(id int primary key auto_increment);
insert into table1 values(100);
insert into table1 values(101);
insert into table1 values(102);
insert into table1 values(103);
insert into table1 values(104);
select * from table1;Output:
Code #2 – Creating table2
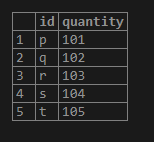
create table table2(id varchar(100) primary key,quantity int not null);
insert into table2(id,quantity) values('p',101);
insert into table2(id,quantity) values('q',102);
insert into table2(id,quantity) values('r',103);
insert into table2(id,quantity) values('s',104);
insert into table2(id,quantity) values('t',105);
select * from table22;
delete table1,table2 from table1 inner join table2 on table2.quantity=table1.id where table1.id=100;Output: of the above query in the output console:
It indicates that the deletion process has affected two rows.
Example #2
Now we will create another two table student and contact to explain delete inner join:
Code #1: The two tables created are student and contact.
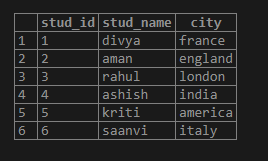
create table student(stud_id int, stud_name varchar(150),city varchar(150));
insert into student values (1,'divya','france');
insert into student values(2,'aman','england');
insert into student values(3,'rahul','london');
insert into student values(4,'ashish','india');
insert into student values(5,'kriti','america');
insert into student values (6,'saanvi','italy');
select * from student;Output: Of the student table is displayed in the below output console:
Code #2
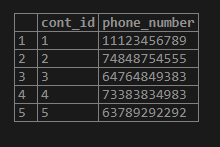
create table contact (cont_id int, phone_number varchar(150));
insert into contact values (1,'11123456789');
insert into contact values (2,'74848754555');
insert into contact values (3,'64764849383');
insert into contact values (4,'73383834983');
insert into contact values (5,'63789292292');
select * from contact;
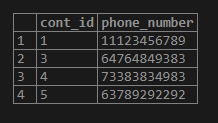
delete student,contact from student inner join contact on student.stud_id=contact.col_id where student.stud_id=2;After the successful execution of the above query, the output will be displayed on the output console:
We can also verify our result by using a select query as given below.
Code #2
select * from contact;Output:
Case #2
Mysql delete joins with left join:
The left join clause is used to select all rows from the left table, even if they have or don’t have matching in the right table. The delete left join table is used to delete rows from the left table that do not have matching records in the right table.
Below is the syntax for deleting rows with a left join that does not have matching rows in another table:
Delete table1 from table1 LEFT JOIN table2 ON table1.col_name=table2.column2 where table2.col_name is NULL;Output: As expected, the above query returns an empty set as the result.
Example to Implement
We will create two tables, customer and contact, and insert values into them to explain delete left join:
Code #1
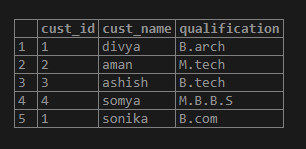
create table customer (cust_id int, cust_name varchar(100),qualification varchar(100));
insert into customer values (1,'divya','B.arch');
insert into customer values(2,'aman','M.tech');
insert into customer values(3,'ashish','B.tech');
insert into customer values(4,'somya','M.B.B.S');
insert into customer values(1,'sonika','B.com');
select * from customer;Output: The output console displays the customer table.
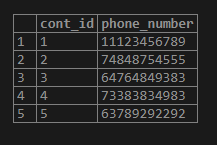
Code #2
select * from contact;Output:
Code #3
Delete customer from customer LEFT JOIN contact ON customer.cust_id=contact.cont_id where phone_number is NULL;Output: After the successful execution of the above query, the output will be displayed on the output console.
Conclusion
In this article, we have learned about mysql delete join query. We have learned how to delete records from two or more tables joined by a joint clause. In this article, we have taken two cases of join, i.e., inner and left join. We have also learned how to select rows from two or more tabled joints together by joint clause before deleting them. This article also provides screenshots of the output console for all queries executed to understand the reader better.
Recommended Articles
We hope that this EDUCBA information on “MySQL DELETE JOIN” was beneficial to you. You can view EDUCBA’s recommended articles for more information.