Updated May 24, 2023
Introduction to MySQL Interval
The MySQL Interval Operator uses the binary search algorithm to find the items from the list and returns the values in range 0 to N. It can also be said that it returns the index of the argument, which is greater than the first argument passed in the interval function.
It outputs 0(zeroth index) if 1st number is less than the 2nd number and 1(index 1) if 1st number is less than the 3rd number like this, it goes on and checks for the last element in the function, and if the first element is null, it will return -1 as an output.
All elements or arguments passed in the function acts as an integer.
Syntax
Below is the syntax of MySQL interval function
select interval(n1,n2, n3…..nn)If n<n1, then it returns 0. If n<n2, then it will return 1, n<n3, it will return 2, and so on. All the arguments must be in ascending order to function like n1<n2>n3……nn. Otherwise, it will not work properly.
Interval Function
The table below describes the unit associated with the interval function’s expression.
| unit | Expression |
| DAY | DAYS |
| DAY_HOUR | ‘DAYS HOURS’ |
| DAY_MICROSECOND | ‘DAYS HOURS:MINUTES:SECONDS. MICROSECONDS’ |
| DAY_MINUTE | ‘DAYS HOURS:MINUTES’ |
| DAY_SECOND | ‘DAYS HOURS:MINUTES:SECONDS’ |
| HOUR | HOURS |
| HOUR_MICROSECOND | ‘HOURS:MINUTES:SECONDS.MICROSECONDS’ |
| HOUR_MINUTE | ‘HOURS:MINUTES’ |
| HOUR_SECOND | ‘HOURS:MINUTES:SECONDS’ |
| MICROSECOND | MICROSECONDS |
| MINUTE | MINUTES |
| MINUTE_MICROSECOND | ‘MINUTES:SECONDS.MICROSECONDS’ |
| MINUTE_SECOND | ‘MINUTES:SECONDS’ |
| MONTH | MONTHS |
| QUARTER | QUARTERS |
| SECOND | SECONDS |
| SECOND_MICROSECOND | ‘SECONDS.MICROSECONDS’ |
| WEEK | WEEKS |
| YEAR | YEARS |
| YEAR_MONTH | ‘YEARS-MONTHS’ |
Examples to Implement MySQL Interval
Below are the examples of implementing MySQL Interval:
Example #1
Code:
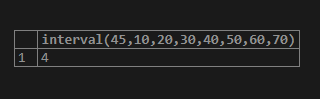
select interval(45,10,20,30,40,50,60,70);Output:
Example #2
Code:
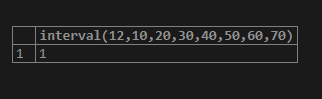
select interval(12,10,20,30,40,50,60,70);Output:
Example #3
Code:
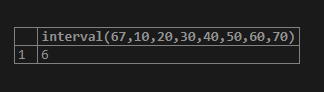
select interval(67,10,20,30,40,50,60,70);Output:
Example #4
Code:
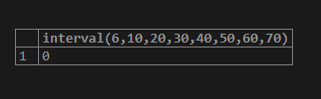
select interval(6,10,20,30,40,50,60,70);Output:
Example #5
Code:
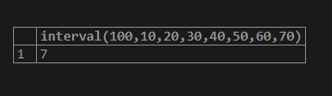
select interval(100,10,20,30,40,50,60,70);Output:
Example #6
Code:
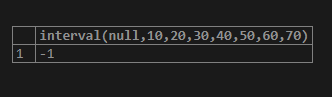
select interval(null,10,20,30,40,50,60,70);Output: Since the first argument is null, the above query returns -1 as an output in the output console.
MySQL interval operator is mainly used for date and time calculations. The below expression is used to create an interval:
Syntax:
INTERVAL expression unitThe expression defines the interval value, and the unit determines the unit of the interval.
Example: interval 5 day
The above example explains how 5 days are created.
- Date + interval expression unit
- Date + interval expression unit
Generally, the interval values are calculated with date, time,date_add,date_subfunctions, etc.
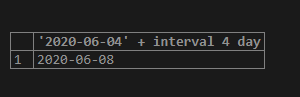
The below statement adds four days to June 4, 2020that returns on June 8, 2020:
Example #7
Code:
select '2020-06-04' + interval 4 day;Output:
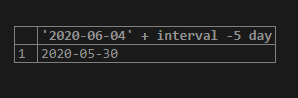
When an interval value is used in a date, and datetime expression that involved value and the interval value will be on the right-hand side of the expression, we can use the negative date and date-time value in the expression as shown in the below example:
Example #8
Code:
select '2020-06-04' + interval -5 day;Output:
Example #9
Code:
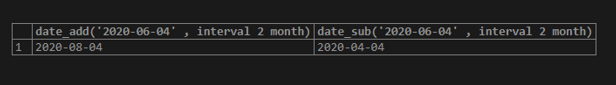
select date_add('2020-06-04' , interval 2 month), date_sub('2020-06-04' , interval 2 month);In the above query, two months are added on 2020-06-04 with the date_add() function, and then two months are subtracted from 2020-06-04 with the date_sub() function.
Output:
Example #10
Code:
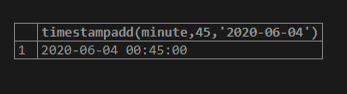
select timestampadd(minute,45,'2020-06-04');In the above query, timestampadd function uses three arguments unit, interval, and expression, which adds 45 minutes in the given date: 2020-06-04
Output:
Mysql interval keyword is also used with now() and curdate()
Below is the query that explains how the interval is used with the now() and curdate() function
Example #11
Code:
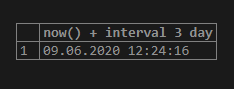
select now() + interval 3 day;In the above query, three days are added in the now function. Now function gives us the date plus the current time of the system.
Output:
Example #12
Code:
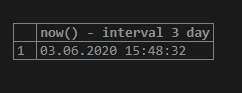
select now() - interval 3 day;In the above query, 3 days are subtracted from now.
Output:
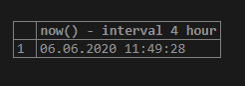
Example #13
Code:
select now() - interval 4 hour;In the above query, 4 hours is subtracted from the current date and time. Therefore, the output will be in date and time format.
Output:
Example #14
Code:
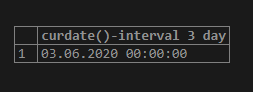
select curdate()-interval 3 day;In the above query, 3 days is subtracted from the current date. Therefore, the output will be only the 3 day less than the current date.
Output:
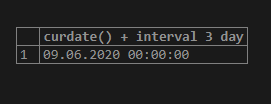
Example #15
Code:
select curdate() + interval 3 day;Output:
Conclusion
In this article, we have learned about the interval function. We have also learned about how it is used with different MySQL functions like the date(), time(), date_add(), date_sub(), now(), curdate(), etc. In this article, we have tried to cover every concept of interval easily. In this article, all the concepts of the interval are explained with MySQL query along with the screenshot of the output console to provide a better understanding to the reader.
Recommended Articles
We hope that this EDUCBA information on “MySQL Interval” was beneficial to you. You can view EDUCBA’s recommended articles for more information.