Updated May 12, 2023
Introduction to MySQL GROUP_CONCAT()
MySQL GROUP_CONCAT() function is an aggregate GROUP BY function which is responsive for concatenating data column values from several rows into one field with string values with the help of some MySQL clauses. If the rows group comprises at least a single or no-NULL column value, then the GROUP_CONCAT function returns a sequence value. Otherwise, the result will be NULL. Here are some of the constraints and clauses that can be used with the GROUP_CONCAT() function in MySQL:
Distinct: It is applied to return the unique string values in the group before the function concatenates the values. It removes the repeated values from the result rows.
Order By: By default, the sorted order of the result from the function is ascending, but we can use this clause to categorize the group data in ascending or descending order.
Separator: To separate the string value, we can use the default operator as comma(,) or look for a different literal value.
Syntax
Here is the syntax for the GROUP_CONCAT() function:
SELECT Column1,Column2, …,ColumnNGROUP_CONCAT([DISTINCT] ColumnName1 [ORDER BY {ASC or, DESC}] [SEPARATOR {comma or any literal value}]) FROM TableName GROUP BY ColumnName2;Let us discuss the terms used in the above context:
- Column1,…CoulmnN: Denotes the name of the columns where we apply the function in the table.
- ColumnName1: Defines the column values, which will be concatenated into one row for every group.
- ColumnName2: The GROUP BY clause in MySQL defines the column to be used for grouping the results to be fetched.
- TableName: The database table name where we use the GROUP_CONCAT() function.
How does MySQL GROUP_CONCAT() function work?
- The MySQL GROUP_CONCAT() function returns a result from a table that contains a row with a group of string values separated by a comma or another given value. This function helps fetch records according to a grouping process and collect data for evaluation.
- The MySQL CONCAT() function generates a result limited to a maximum length of 1024 in MySQL, as defined by the system variable group_concat_max_len. However, this limit can be modified at runtime using the SET command as follows:
SET [GLOBAL | SESSION] group_concat_max_len = LengthValue ;LengthValue denotes the variable value to exceed the length of the result produced by the CONCATE() function.
We can use various applications of MySQL CONCAT() function; some are mentioned below:
- We can create comma-separated user roles such as Admin, Editor, Author or Subscriber, etc.
- It can display the list of hobbies of different users separated by commas like Designer, Painter, etc.
- People commonly use MySQL’s GROUP_CONCAT() function to generate tags for articles, blog posts, guest posts, products, etc. For example, tags like “MySQL coding,” “Learn MySQL,” and “clauses” can be generated using this function.
Examples of MySQL GROUP_CONCAT()
Let us try some examples to understand the MySQL CONCATE() function. For this, let us first create a table as a sample one to work with and insert some records into it.
Creating a table:
CREATE TABLE Books (BookID int NOT NULL, BookName varchar(255) NOT NULL, Language varchar(255), Price int, PRIMARY KEY (BookID) );Entering records into the table using the following statement:
INSERT INTO Books (BookID, BookName, Language, Price) VALUES
('101', 'Algebraic Maths', 'English', '2000'),
('102', 'Networking', 'English', '5000'),
('103', 'Nanoscience', 'Hindi', '3000'),
('104', 'Web Design', 'English', '2000'),
('105', 'Nuclear Science', 'English', '2100'),
('106', 'Nuclear Science', 'Hindi', '1980'),
('107', 'Electrical Engineering', 'Hindi', '1500'),
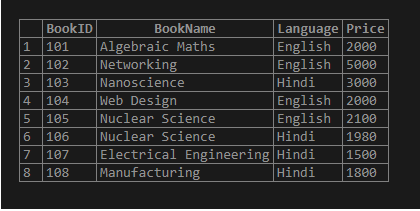
('108', 'Manufacturing', 'Hindi', '1800');Displaying the table:
SELECT * FROM Books;Output:
Now let us start with these examples:
Example #1 – Simple MySQL_CONCAT() function
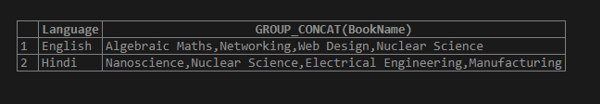
Let us create the statement which returns a list of books separated by a comma in each language group.
SELECT Language, GROUP_CONCAT(BookName) FROM Books GROUP BY Language;Output:
Example #2 – MySQL CONCAT() function with DISTINCT clause
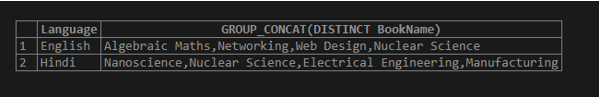
Here, the MySQL query returns unique string values as grouped by Language, removing the duplicate ones if present for each group in the column values using GROUP_CONCAT() function.
SELECT Language, GROUP_CONCAT(DISTINCT BookName) FROM Books GROUP BY Language;Output:
Example #3 – MySQL CONCAT() function with ORDER BY Clause
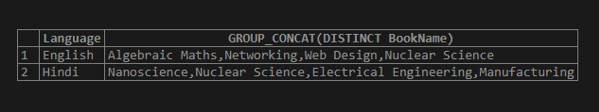
In this example, we will use the MySQL statement to retrieve a list of distinct BookName values separated by commas. As you see in the result, the fetched rows are sorted in ascending order using the ORDER BY clause; you can also use DESC sorting.
SELECT Language, GROUP_CONCAT(DISTINCT BookName) FROM Books GROUP BY Language ORDER BY GROUP_CONCAT(DISTINCT BookName) ASC;Output:
Example #4 – MySQL CONCAT() function with Separator
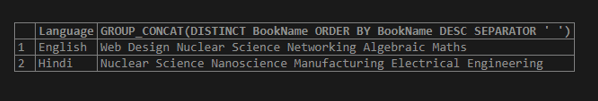
In this example, the MySQL CONCAT() function will return the list series of BookName grouped by Language with distinct string values but separated by adding a specific separator (“) space. We can also use other literal values like semicolon(;), colon(:), etc. The SELECT MySQL query below includes an option to display the result rows in descending order.
SELECT Language, GROUP_CONCAT(DISTINCT BookName ORDER BY BookName DESC SEPARATOR ' ') FROM Books GROUP BY Language;Output:
Example #5 – MySQL CONCAT() function: some mistakes
Since the result returned by the GROUP_CONCAT function is a single string, not a list of values, it concatenates all the values in one list denoted as a single string. Experts do not recommend using the GROUP_CONCAT() function for the operator IN within an inner query in MySQL.
For example, the result of values: 21,2 and 23 when applied GROUP_CONCAT() function will be as a string:’ 21,22,23′.
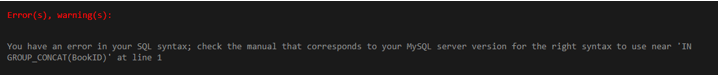
IN operator receives a series of values but not a string, including the list of column values. Therefore if you provide this type of result using IN operator in MySQL, you do not get the expected result, and the query below will not work as shown in the output.
SELECT BookID, BookName FROM Books WHEREBookID IN GROUP_CONCAT(BookID);Output:
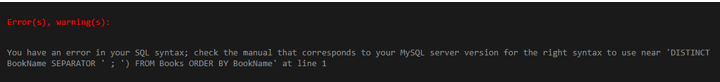
We need to use the ORDER BY clause in the GROUP_CONCAT properly () function query statement to get the desired output. This is an aggregate function, so we should use ORDER BY inside the function but not in the SELECT statement part.
The succeeding query represents the incorrect usage of such a mistake:
SELECT GROUP_CONCATE(DISTINCT BookName SEPARATOR ' ; ') FROM Books ORDER BY BookName;Output:
Conclusion
- The MySQL CONCAT() function on execution results in binary or non-binary string values, which depend on the particular arguments or parameters provided in the function during code definition.
- This function can be beneficial to return the column values displaying in a single field using ORDER BY and GROUP BY clauses, respectively, to get the desired result from column table values.
Recommended Articles
We hope that this EDUCBA information on “MySQL GROUP_CONCAT()” was beneficial to you. You can view EDUCBA’s recommended articles for more information.