Updated May 15, 2023

Introduction to MySQL Datetime
The following article provides an outline for MySQL Datetime. Suppose we want to store a value of date that contains both date and time in it. Then we use the Datetime format. Datetime stores the data in year, month, date, hour, minutes, and seconds. The Datetime uses 5 bytes for storage. We can also store the fraction, but holding the fraction would increase the storage. Considering precision and wanting to keep the precision fraction(0) takes 0 storage bytes. Suppose fraction (1, 2) takes 1 byte. Fraction (3,4) takes 2 bytes, and a fraction (5, 6) takes 3 bytes of storage. A total of 3 bytes would need extra for the storage of fractions.
Syntax:
<column_name>datetime;To define a column as a datetime type, we define it as the above.
How does MySQL Datetime work?
Now let us create a table with a column data type as datetime and get the result.
Code:
CREATE TABLE TEST_DATETIME1
(
ORDER_ID VARCHAR(10),
ORDER_DATE DATETIME
);Let us insert the data into the table:
INSERT INTO TEST_DATETIME1 VALUES ('O1','2019-01-01 12:00:00');
INSERT INTO TEST_DATETIME1 VALUES ('O2','2019-02-02 12:00:00');
INSERT INTO TEST_DATETIME1 VALUES ('O3','2019-03-03 12:00:00');
INSERT INTO TEST_DATETIME1 VALUES ('O4','2019-04-04 12:00:00');
INSERT INTO TEST_DATETIME1 VALUES ('O5','2019-05-05 12:00:00');
INSERT INTO TEST_DATETIME1 VALUES ('O6','2019-06-06 12:00:00');
INSERT INTO TEST_DATETIME1 VALUES ('O7','2019-07-07 12:00:00');
INSERT INTO TEST_DATETIME1 VALUES ('O8','2019-08-08 12:00:00');
INSERT INTO TEST_DATETIME1 VALUES ('O9','2019-09-09 12:00:00');
INSERT INTO TEST_DATETIME1 VALUES ('O10','2019-10-10 12:00:00');
select * from test_datetime1;Output:
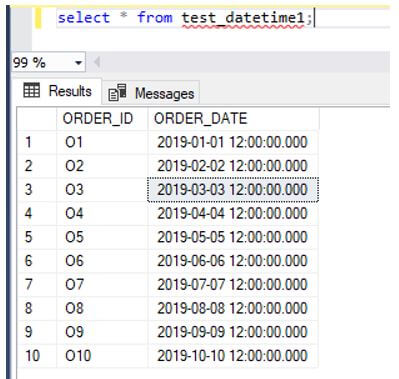
Here we check the data for the “order_date.” We could see that the storage taken for the column is 7 bytes as it saves the precision fraction of (3, 4).
If we see the value of “ Date_time “ value:
2019-01-01 12:00.00.000
Given below is the format of the above data:
yyyy-mm-ddhh:mm:ss:ff
- YYYY: Is the year – 2019
- MM: Is month – 01
- DD: Is Date -01
- HH: Hour – 12
- MM: Month – 00
- SS: Second – 00
- FF: Fraction seconds – 000
As per the above example:
‘2019-01-01 12:00.00.000’
Code:
CREATE TABLE TEST_DT
(
SERIAL_NUMBER INT,
DATE_TIME DATETIME
);Now let us insert into the table with the current date:
INSERT INTO TEST_DT VALUES (1,'2019-01-01 09:22:08:123');
INSERT INTO TEST_DT VALUES (2,'2019-01-02 10:22:08:123');
INSERT INTO TEST_DT VALUES (3,'2019-01-03 11:22:08:123');
INSERT INTO TEST_DT VALUES (4,'2019-01-04 12:22:08:123');
INSERT INTO TEST_DT VALUES (5,'2019-01-05 13:22:08:123');
INSERT INTO TEST_DT VALUES (6,'2019-01-06 14:22:08:123');
INSERT INTO TEST_DT VALUES (7,'2019-01-07 15:22:08:123');
INSERT INTO TEST_DT VALUES (8,'2019-01-08 16:22:08:123');
INSERT INTO TEST_DT VALUES (9,'2019-01-09 17:22:08:123');
INSERT INTO TEST_DT VALUES (10,'2019-01-10 18:22:08:123');
INSERT INTO TEST_DT VALUES (11,'2019-01-11 19:22:08:123');
INSERT INTO TEST_DT VALUES (12,'2019-01-12 20:22:08:123');
select * from TEST_DTOutput:
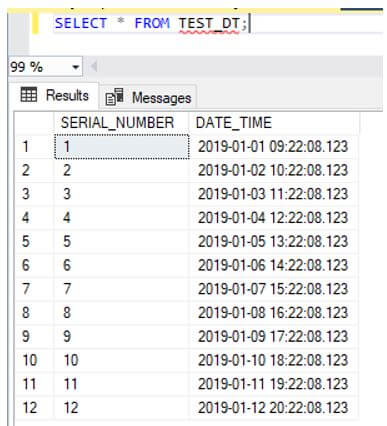
Here we check the data for the “order_date”. We could see that the storage taken for the column is 7 bytes as it saves the precision fraction of (3,4).
If we see the value of “ Date_time “ value:
2019-01-01 09:22.08.123
Given below is the format of the above data:
yyyy-mm-ddhh:mm:ss:ff
- YYYY: Is the year – 2019
- MM: Is month – 01
- DD: Is Date – 01
- HH: Hour – 09
- MM: Month – 22
- SS: Second – 08
- FF: fraction seconds -123
Output:

Example of MySQL Datetime
Given below is the example mentioned:
Code:
CREATE TABLE TEST_DT1
(
SERIAL_NUMBER INT,
DATE_TIME DATETIME
);Now let us insert into the table with the current date:
INSERT INTO TEST_DT1 VALUES (11,'2019-01-11 09:22:08:123');
INSERT INTO TEST_DT1 VALUES (22,'2019-01-12 10:22:08:123');
INSERT INTO TEST_DT1 VALUES (33,'2019-01-13 11:22:08:123');
INSERT INTO TEST_DT1 VALUES (44,'2019-01-14 12:22:08:123');
INSERT INTO TEST_DT1 VALUES (55,'2019-01-15 13:22:08:123');
INSERT INTO TEST_DT1 VALUES (66,'2019-01-16 14:22:08:123');
INSERT INTO TEST_DT1 VALUES (77,'2019-01-17 15:22:08:123');
INSERT INTO TEST_DT1 VALUES (88,'2019-01-18 16:22:08:123');
INSERT INTO TEST_DT1 VALUES (99,'2019-01-19 17:22:08:123');
INSERT INTO TEST_DT1 VALUES (110,'2019-01-21 18:22:08:123');
INSERT INTO TEST_DT1 VALUES (111,'2019-01-22 19:22:08:123');
INSERT INTO TEST_DT1 VALUES (122,'2019-01-23 20:22:08:123');
Select * from TEST_DT1;Output:

If we check the data for the “Date_time,” we can see that the storage taken for the column is 7 bytes as it saves the precision fraction of (3, 4).
If we see the value of “ Date_time “ value:
2019-01-11 09:22.08.123
Given below is the format of the above data:
yyyy-mm-ddhh:mm:ss:ff
- YYYY: Is the year – 2019
- MM: Is month – 01
- DD: Is Date – 11
- HH: Hour – 09
- MM: Month – 22
- SS: Second – 08
- FF: Fraction seconds – 123
Conclusion
If we want to store a value of date that contains both date and time, then we use the Datetime format. Datetime stores the data in year, month, date, hour, minutes, and seconds. The Datetime uses 5 bytes for storage. We can also store the fraction, but holding the fraction would increase the storage. Considering precision and wanting to keep the precision fraction (0) takes 0 storage bytes. Suppose fraction (1, 2) takes 1 byte. Fraction (3, 4) takes 2 bytes, and fraction (5, 6) takes 3 bytes of storage. A total of 3 bytes would need extra for the storage of fractions.
Recommended Articles
We hope that this EDUCBA information on “MySQL Datetime” was beneficial to you. You can view EDUCBA’s recommended articles for more information.

