Updated May 23, 2023
Introduction to MYSQL Database
MySQL Database is a Relational Database Management System that is available freely as an open-source and based on SQL (Structured Query Language) language for data access and retrieval processes.MySQL Database software is provided under the terms of the GNU General Public License and also under other proprietary licenses. Also, a Database is defined as a Data Structure used to store any data and information on the server in an organized manner. The Database contains tables, and records are inserted or saved in those tables in columns and rows so data manipulation can be done quickly.
How to Create a Database in MySQL?
We can create MySQL Database using different methods, but as it is based on SQL, let us consider the following.
Syntax:
CREATE Database Database_name;You can also create MySQL Database using the command line interface on your desktop and pass the SQL queries to view the result.
1. you can still execute the SQL instructions using the WAMP server. You can install WAMP or XAMPP, both of which are open source, on your computer by downloading them. To access WAMP’s homepage, run localhost.
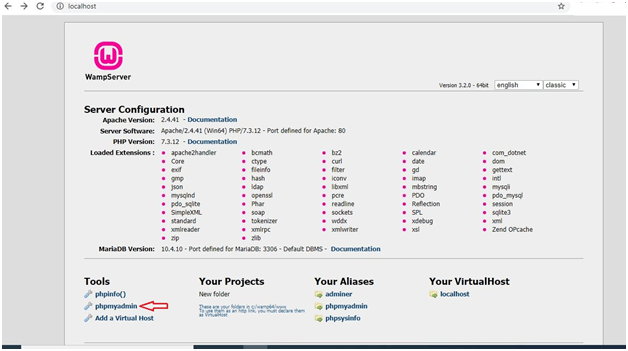
2. You will find the PHPMyAdmin option, the MySQL server, which uses root as username and password (blank if not set) and helps access the database and perform any SQL query commands.
3. You can access the database and tables to manipulate any field’s data.
4. You can either execute the SQL query through the query editor area and manage the databases on the MySQL server or write PHP code to connect the database and make changes.
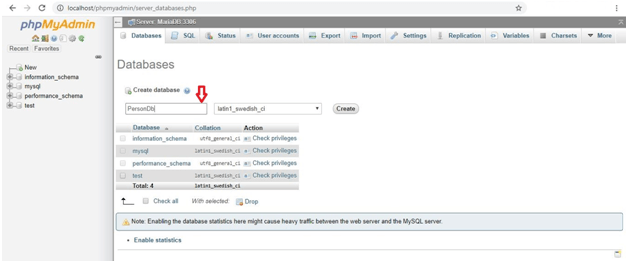
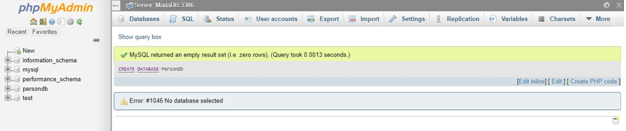
5. For example, a database named ‘PersonDb’ in the database option is created as follows using the WAMP server:
Code:
CREATE Database PersonDb;Output:
6. Using SQL command:
Code:
CREATE DATABASE PERSONDB;Output:
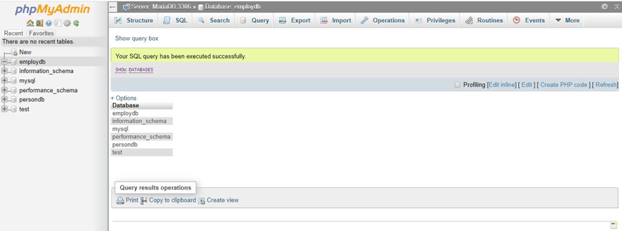
7. Once the database is created, you can view it in the lists of databases on the server using the following query:
Code:
SHOW DATABASES;Output:
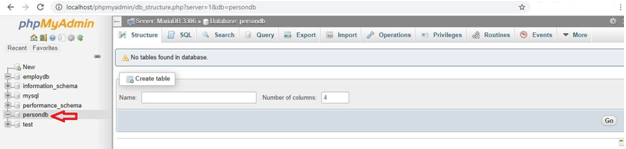
8. You can view the database by clicking on a database on the left menu bar, where you can add tables:
9. Further, you can use PHP scripts to integrate the SQL query and establish a connection of any webpage to the database for insertions and other manipulations to store data.
Code:
<?php
$dbhost = "localhost"; // Host/Server name
$dbuser = "root"; // Host user name
$dbpassword = " "; //use password if exists
$con = mysql_connect ($dbhost, $dbuser, $dbpassword);
if (! $con)
{
die ('No Connection Established: ' . mysql_error());
}
echo "Connection Established successfully";
$sql = 'CREATE DATABASE PersonDb';
$query = mysql_query ($sql, $con);
if (! $query){
die ('Could not create Database: ' . mysql_error());
}
echo "Database created successfully\n";
mysql_close ($con);
?>Here, the mysql_connectparameter is used to open a connection with the MySQL server, and CREATEquery creates a database, whereas mysql_queryfunction checks if the database is created with the connection or not and returns TRUE on success and FALSE on failure.
How to Select a Database from Multiple Databases?
Generally, we use the SQL SELECT statement to select a particular database from multiple databases and display its tables of records. This is required when many databases exist on MySQL servers, and we need to work only with one of them.
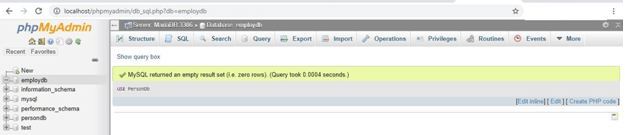
We use the USE SQL command for this with the following:
Syntax:
USE Database_name;Example
USE PersonDb;Output:
How to Drop a Database?
1. We need admin access for deleting any database from the server. The following syntax is used to delete any database from the MySQL server:
Syntax:
DROP DATABASE Database_name;Example
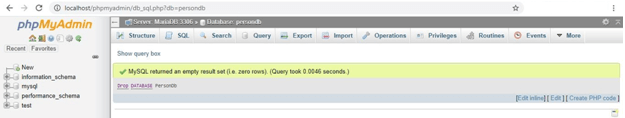
DROP DATABASE PersonDb;Output:
2. Dropping a database may not be simple; you must lose all the tables with records if you delete any database. So be careful; the DROP SQL statement destroys all the data in that database.
3. When you proceed or execute this query, a warning or message is displayed asking to confirm whether we want to delete this database.
4. While deleting the database in the PHP script, it does not prompt to ask whether you want to delete the database or not, so be careful before executing the code:
Code:
<?php
$dbhost = "localhost";// Host/Server name
$dbuser = "root";// Host user name
$dbpassword = " "; // Use password if exists
$con = mysql_connect ($dbhost, $dbuser, $dbpassword);
if (! $con)
{
die ('No Connection Established: ' . mysql_error());
}
echo "Connection Established successfully";
$sql = 'DROP DATABASE PersonDb';
$query = mysql_query ($sql, $con);
if (! $query){
die ('Could not drop the Database: ' . mysql_error());
}
echo "Database deleted successfully\n";
mysql_close ($con);
?>Conclusion
- MySQL Database application is used to maintain and store records for various purposes such as E-Commerce, Data Warehousing, and logging applications. But the most important use of MySQL Database is as Web Database.
- Some significant benefits of MySQL Database are Data safety, On-Demand Scalability, High Presentation, Round-the-Clock Uptime, Wide-ranging Transactional Provision, Complete Workflow Mechanism, Concentrated Total Cost of Proprietorship, etc.
- For example, a company database holds tables for different areas like employee info, services records or financial transactions, and so on.
- Thus, MySQL Database, being a fast, reliable, and stable RDBMS, saves us money and time because we can use SQL queries to manipulate the records.
Recommended Articles
We hope that this EDUCBA information on the “MYSQL Database” was beneficial to you. You can view EDUCBA’s recommended articles for more information.