Updated May 26, 2023

Introduction to MySQL Cross Join
MySQL Cross Join is a type of MySQL JOINs which is characterized to provide the Cartesian product as a result set from both the tables in the database. Like, INNER JOIN or others, this MySQL Cross Join does not need any common table column to perform the joining query. Here, the Cartesian product is defined as the number of table rows in one table multiplied by the number of table rows in the following table. Thus, using MySQL CROSS JOIN, we should know that it is implemented to get all the available possibilities in the result set, which contains a combination of rows from both tables.
Syntax
The elementary syntax structure mentioned for MySQL CROSS JOIN is provided below:
SELECT TableNameA. ColumnName1, TableNameB.ColumnName2,..............................,TableNameN.ColumnNameN FROM TableNameA CROSS JOIN TableNameB;Explanation: The MySQL CROSS JOIN clause is associated with the SELECT keyword, and join is applied after FROM keyword. Then, the join will retrieve all records from the joined table as output. The TableNameN.ColumnNameN and so on the list the column fields to be joined from respective tablesTableNameA and TableNameB to perform the CROSS JOIN.
How does Cross Join work in MySQL?
Since MySQL JOINS are implemented in MySQL as they are helpful to fetch data from two or multiple database tables. These tables contain PRIMARY KEYs and FOREIGN KEYs through which they are mutually related and, thus, efficient to apply the JOINS queries. Suppose we have two tables with each table having j and k number of rows respectively in a database, and when we apply CROSS JOIN clause query on these tables. The result row set will generate the data in j*k rows.
The query statement below illustrates the working of CROSS JOIN to join two tables and b:
SELECT * FROM Table_a CROSS JOIN Table_b;Remember that this CROSS JOIN clause does not contain a join predicate, unlike the INNER, RIGHT, or LEFT JOIN clauses. In simple terms, we can say that it doesn’t include the USING or ON clause. If we apply a WHERE clause to show a relationship with the two tables, then the CROSS JOIN query works similarly to the INNER JOIN clause. This query becomes like this:
SELECT * FROM Table_a CROSS JOIN Table_b WHERE Table_a.ID = Table_b.ID;The WHERE clause defines that both tables have a common column type to make a relation and produce the result set of INNER JOIN type. But we can use it to define a specific table column condition in the CROSS JOIN query.
Examples to Implement MySQL Cross Join
Let us demonstrate some of the examples to illustrate the working of the CROSS JOIN clause in MySQL server with the related table rows:
Example # 1: Having identical rows and non-NULL values
Step 1: First, we will set up a demo table in a new database. Creating a fresh database empdb using the following query
Code:
CREATE DATABASE IF NOT EXISTS empdb;Step 2: Again, for switching the present data to the newly created database named empdb
Code:
USE empdb;Step 3: After that, let us build up a demo table in the empdb database by the below query statement
Code:
CREATE TABLE products (ProductID INT PRIMARY KEY AUTO_INCREMENT, Product_NameVARCHAR(255) NOT NULL, Cost INT NOT NULL);Step 4: Also, let us input some records into the table products using the query below
Code:
INSERT INTO products(ProductID, Product_Name, Cost) VALUES
('1','Parle G','100')
('2','Maggie','112')
('3','GoodDay Buiscuit','150');Step 5: To display the contents of the table as follows
Code:
SELECT * FROM Products;Output:
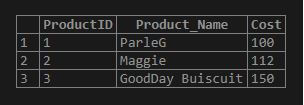
Step 6: Also, we need to create another table as Suppliers having fields as follows
Code:
CREATE TABLE Suppliers(Supplier_ID INT PRIMARY KEY AUTO_INCREMENT, CategoryVARCHAR(255) NOT NULL, Unit VARCHAR(255) NOT NULL);Step 7: Adding some entries into the table Suppliers using the query statement below
Code:
INSERT INTO suppliers(Supplier_ID, Category, Unit, CostEach) VALUES
('10','Snacks','10 pcs'),
('11','Drinks','25 bottles'),
('12','Kitchen Needs','200 packs');Step 8: View the records in the table as
Code:
SELECT * FROM Suppliers;Output:
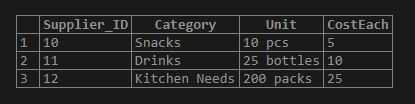
Step 9: Now, let us implement the CROSS JOIN on these tables with the help of the succeeding query command and view the result set
Code:
SELECT ProductID, Supplier_ID, Product_Name, Unit, Cost FROM Products CROSS JOIN Suppliers;Output:
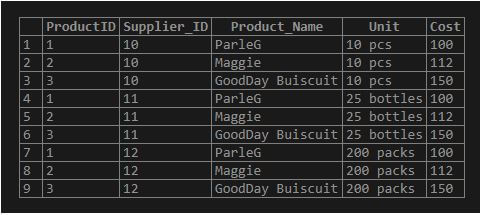
Step 10: We can also write the above query to the following one that will produce the same result
Code:
SELECT ProductID, Supplier_ID, Product_Name, Unit, Cost FROM Products, Suppliers;Output:
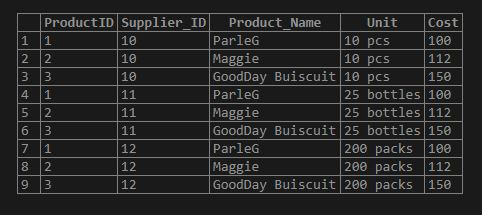
Explanation: Here, the row of one table shows possible combinations one by one with all rows of another table.
Example #2: Having different rows and NULL values
Step 1: We have created two tables simultaneously to apply the CROSS JOIN clause using the queries below
Code:
CREATE TABLE Employees(EmpID INT PRIMARY KEY, EmpName VARCHAR(255), EmpProfile VARCHAR(255), EmpSalary INT NOT NULL, EmpPF INT);
CREATE TABLE Payment(CustomerID INT PRIMARY KEY, CustomerName VARCHAR(255), PAmount INT);Step 2: Also, let us enter some records like this:
Code:
INSERT INTO employees(EmpID, EmpName, EmpProfile, EmpSalary, EmpPF) VALUES ('210','Radha','Engineer','50000','3600'),
('211','Mohan','Manager','40000','2000'),
('212','Dev','Executive','32000','1800'),
('213','Madhuri','Blogger','20000',NULL),
('214','Rita','Pilot','48000','5000');
INSERT INTO payment(CustomerID, CustomerName, PAmount) VALUES
('101','Anita','3400'),
('102','Rita',NULL),
('103','Sahil','7000');Step 3: The table records are inserted into the tables simultaneously. We can view the contents of those tables in the database using the SELECT statements below.
Code:
SELECT * FROM employees;Output:
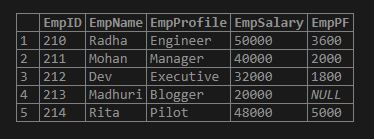
Code:
SELECT * FROM payment;Output:
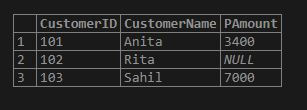
Step 4: Now, let us execute the query statement combining both tables with matching each record from one table to every row in another to generate a joined table. For this, the CROSS JOIN query is as follows.
Code:
SELECT * FROM Employees CROSS JOIN Payment;Output:
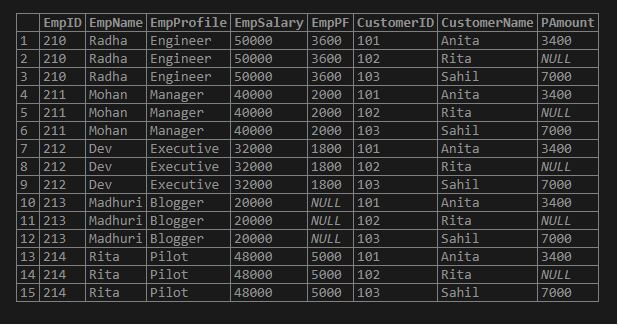
Explanation: It is clear that if there are NULL values in any columns, then after the CROSS JOIN implementation, you can see that those values are also combined to perform the Cartesian product in the joined table, and it produces the result set.
Conclusion
We have study about the application of the MySQL CROSS JOIN clause to answer a few interesting data questions in MySQL. Hence, the CROSS JOIN does not need any column in common and helps to return the Cartesian product set of rows with the tables joined together. This allows producing all possible combinations of rows from each table.
Recommended Articles
We hope that this EDUCBA information on “MySQL Cross Join” was beneficial to you. You can view EDUCBA’s recommended articles for more information.

