Updated June 2, 2023
Introduction to MySQL SELECT INTO Variable
Sometimes there is a need to store the values of the retrieved fields inside the variables in MySQL. We can do this by using the clause INTO to store the values of the retrieved fields, whether column values of aggregate values or any other expressions retrieved in the SELECT query statement. In MySQL, we access and declare variables using the format of ‘@’ before the variable name. In this article, we will learn how to save the fetched values of the query statement into the variables in MySQL and learn its syntax and implementation with the help of some examples.
Syntax
The syntax of storing the selected values in the variables of the select query is as follows –
SELECT column1, column2, column3, ... INTO @variable1, @variable2, @variable3,... FROM tablename WHERE condition or restriction;- column1, column2, column3, … – These are the names of the columns you are retrieving from the table named tablename. You can retrieve any number of columns from the select statement.
- @variable1, @variable2, @variable3,… – These are the names of the variables into which you want to store the retrieved column values. Note that the number of columns and variables should be the same. Additionally, it is essential to note that the correct sequence should be followed when retrieving columns and specifying variables. The system will store each value in its respective variable. For instance, the value obtained from column1 will be stored in @variable1, the value from column2 will be stored in @variable2, and so forth.
- tablename – this is the table name from which you want to retrieve the values of columns.
- Condition or restriction – This is optional, allowing you to specify specific conditions or restrictions on the columns, filtering the results accordingly during retrieval.
Working of MySQL SELECT INTO Variable
The retrieved result set of the query should contain one or no records. If the query statement retrieves multiple records, MySQL generates an error. If the query returns no rows, MySQL issues a warning, and the values of the variables used for storage remain unchanged. Only when a single record is retrieved will the correct values be assigned to the variables.
Hence, we can use the MySQL LIMIT clause to avoid errors when retrieving multiple records. This clause helps us retrieve only the specified number of rows even if the actual query resultset may retrieve too many rows. We can set LIMIT 1 at the end of our select query to avoid the error. This helps us ensure that, at maximum, only one row is retrieved from the query statement.
Examples of MySQL SELECT INTO Variable
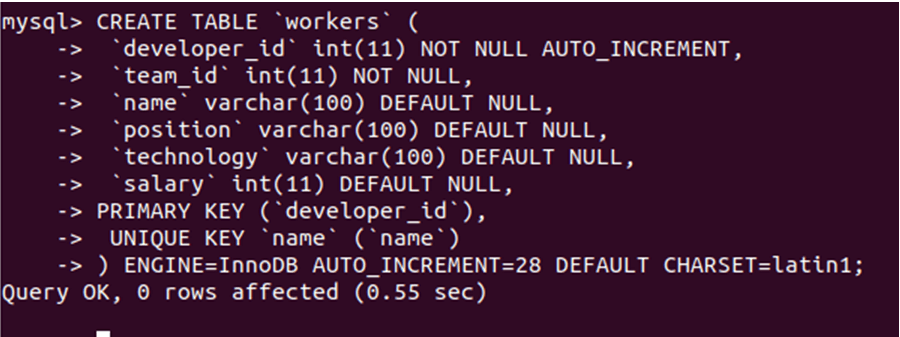
Consider a table named workers that have the following structure,
CREATE TABLE 'workers' (
'developer_id' int(11) NOT NULL AUTO_INCREMENT,
'team_id' int(11) NOT NULL,
'name' varchar(100) DEFAULT NULL,
'position' varchar(100) DEFAULT NULL,
'technology' varchar(100) DEFAULT NULL,
'salary' int(11) DEFAULT NULL,
PRIMARY KEY (`developer_id`),
UNIQUE KEY `name` (`name`)
) ENGINE=InnoDB AUTO_INCREMENT=28 DEFAULT CHARSET=latin1;that gives the following output after the execution of the query
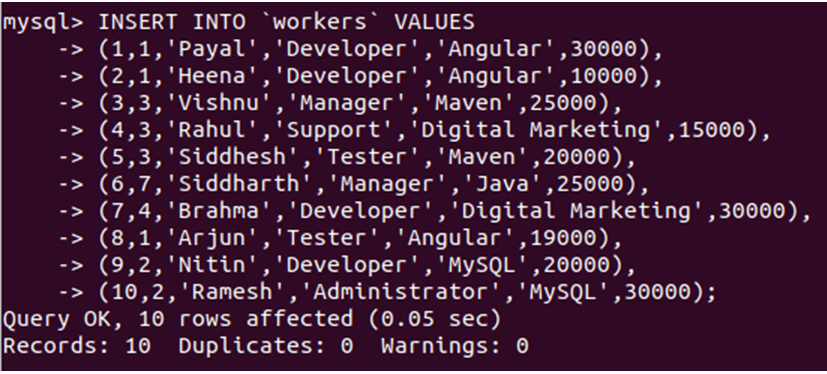
Let us insert some records in the table workers by using the following insert query statement –
INSERT INTO 'workers' VALUES
(1,1,'Payal','Developer','Angular',30000),
(2,1,'Heena','Developer','Angular',10000),
(3,3,'Vishnu','Manager','Maven',25000),
(4,3,'Rahul','Support','Digital Marketing',15000),
(5,3,'Siddhesh','Tester','Maven',20000),
(6,7,'Siddharth','Manager','Java',25000),
(7,4,'Brahma','Developer','Digital Marketing',30000),
(8,1,'Arjun','Tester','Angular',19000),
(9,2,'Nitin','Developer','MySQL',20000),
(10,2,'Ramesh','Administrator','MySQL',30000);That provides the following output after execution of the query –
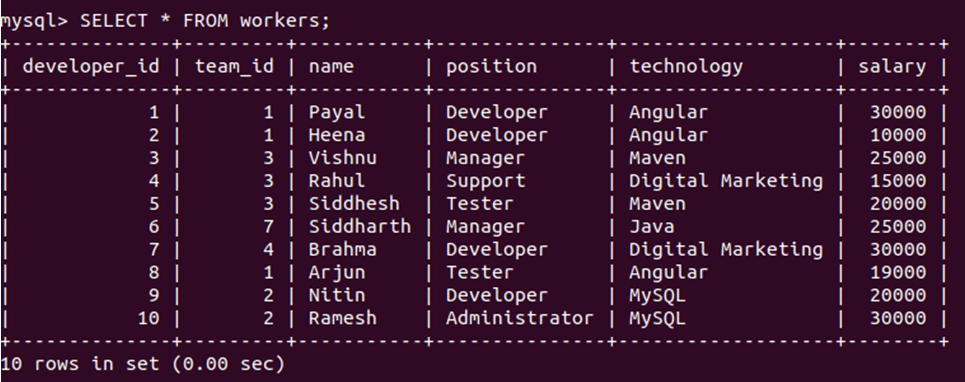
Let us retrieve all the records of the worker’s table by using the following query statement –
SELECT * FROM workers;that gives the following output after execution of the query –
We will see the first example that will get only one variable in the select query. Let us store the name of the administrator in the variable admin by using the following query statement –
SELECT name INTO @admin FROM workers WHERE position = 'Administrator';that gives the following output after the execution of the query –
We can see that the query executed successfully affects one row, as now, the @admin variable will contain the administrator’s name. From the above resultset of the table records, we can observe that the worker with the name Ramesh is the administrator; hence, the Ramesh value should be stored in the @admin variable. Let us select that variable and observe what value gets retrieved.
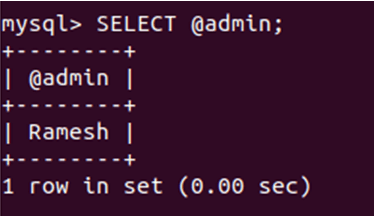
SELECT @admin;that gives the following output after the execution of the query –
Here we go; The value @admin refers to Ramesh, which can be stored and retrieved from the variable.
Let us see one more example where we will insert two variable values from the selected contents of the select query statement. We will store the name and position of the worker with Java technology in the variable @javaperson and @javaoperator using the following query statement –
SELECT name, position INTO @javaperson, @javaoperator FROM workers WHERE technology = 'Java';that gives the following output after the execution of the query –
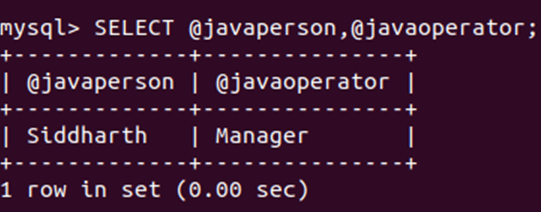
We can see that the query executed successfully affects one row as now, @javaperson and @javaoperator variables will contain the name and position of the Java technology-related person. Analyzing the table results, we can determine that the manager’s name is Siddharth, and they are associated with Java technology. Therefore, we should store the value of Siddharth in the @javaperson variable and the manager’s value in the @javaoperator variable. Let’s select those variables and see what value is retrieved.
SELECT @javaperson, @javaoperator;that gives the following output after the execution of the query –
Let us try storing values with Angular technology the same as Java but with more than one record.
SELECT name, position INTO @angularperson, @angularoperator FROM workers WHERE technology = 'Angular';that gives the following output after execution of the query –
We observe that it throws an error indicating the retrieval of more than one row. Let us use LIMIT 1.
SELECT name, position INTO @angularperson, @angularoperator FROM workers WHERE technology = 'Angular' LIMIT 1;that gives the following output after the execution of the query –
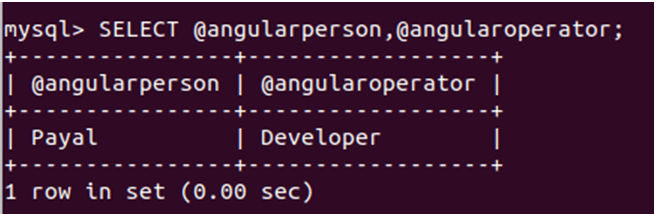
SELECT @angularperson,@angularoperator;That gives the following output after the execution of the query –
We have saved the initial entry for a developer called “payal” who works with angular technology in variables @angularperson and @angularoperator, respectively.
Conclusion
We can use the SELECT INTO clause to get the retrieved values of the SELECT query statement into the variables. We need to be careful about the number and order of variables and columns while doing so. Also, the number of rows retrieved should not exceed one record.
Recommended Articles
We hope that this EDUCBA information on “MySQL SELECT INTO Variable” was beneficial to you. You can view EDUCBA’s recommended articles for more information.