Updated May 29, 2023
Introduction to MySQL Collation
MySQL collation is nothing but a set of rules used to compare the characters in a particular character set. The character set, and collations can be set at four levels, and they are at: – server level, database level, table level, and column level. Some rules that need to be considered are: – Two character sets can’t have the same collation. Instead, each character set can have one or more different collations.
Now let us see in detail how we can set the character set among different levels and how to set the collation at different levels, along with the examples.
Syntax:
Below is the syntax to check the character set: –
SHOW CHARACTER SET;Below is the syntax to check the collation: –
SHOW COLLATION LIKE'<characterset_name>';How does MySQL Collation work?
Now let us see the character set and set the character set and collation, along with an example.
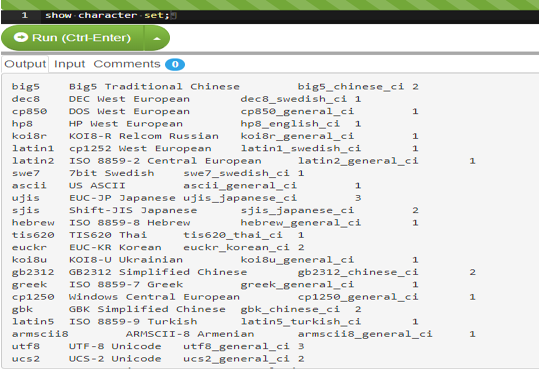
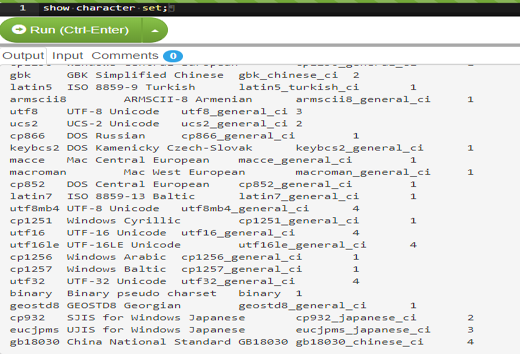
SHOW CHARACTER SET;Output:
In the output, the _ci → case insensitive, _cs→case sensitive, and _bin → binary.
To get all collations for a given character set, you use the SHOW COLLATION statement as follows:
SHOW COLLATION LIKE'ASCII%';How to set Character set and collation at the Server level?
If you want to set the character set and collation at the server level, we use the below syntax. The default character set is “latin1” and the collation is “latin1_swedish_ci”.
mysqld--character-set-server=ascii --collation-server=ascii_general_ci;How to set Character set and collation at the Database Level?
If you want to set the character set and collation at the database level, we use the below syntax.
CREATE DATABASE<databaseName>
CHARACTER SET<characterset_name>;
COLLATE<collation_name>To alter the default setting of the character set and collate, use the below syntax: –
ALTER DATABASE<databaseName>
CHARACTER SET<characterset_name>
COLLATE<collation_name>;How to set Character set and collation at Table Level?
If you want to set the character set and collation at table level, we use the below syntax.
CREATE TABLE TEST_TABLE(
COLUMN1 <DATA_TYPE>,
COLUMN2 <DATA_TYPE>,
COLUMN3 <DATA_TYPE>,
.
.
COLUMNN <DATA_TYPE>,
)
CHARACTER SET<characterset_name>
COLLATE<collation_name>;To alter the default setting of the character set and collate, use the below syntax: –
ALTER TABLE TEST_TABLE(
COLUMN1 <DATA_TYPE>,
COLUMN2 <DATA_TYPE>,
COLUMN3 <DATA_TYPE>,
.
.
COLUMNN <DATA_TYPE>,
)
CHARACTER SET<characterset_name>
COLLATE<collation_name>;How to set Character set and collation at Column Level?
If you want to set the character set and collation at table level, we use the below syntax.
A column of type CHAR, VARCHAR, or TEXT can possess its own character set and collation, which can differ from the default character set and collation of the table.
You can either specify a character set and a collation for the column in the column’s definition of either CREATE TABLE or ALTER TABLE statement as follows:
CREATE TABLE TEST_TABLE(
COLUMN1 [CHAR | VARCHAR | TEXT](length)
CHARACTER SET<characterset_name>
COLLATE<collation_name>,
COLUMN2 [CHAR | VARCHAR | TEXT](length)
CHARACTER SET<characterset_name>
COLLATE<collation_name>,
.
.
COLUMN_N [CHAR | VARCHAR | TEXT](length)
CHARACTER SET<characterset_name>
COLLATE<collation_name>,
);To alter the default setting of the character set and collate, use the below syntax: –
ALTER TABLE TABLE_NAME MODIFY
COLUMN1 [CHAR | VARCHAR | TEXT](length)
CHARACTER SET<characterset_name>
COLLATE<collation_name>,
COLUMN2 [CHAR | VARCHAR | TEXT](length)
CHARACTER SET<characterset_name>
COLLATE<collation_name>,
.
.
COLUMN_N [CHAR | VARCHAR | TEXT](length)
CHARACTER SET<characterset_name>
COLLATE<collation_name>,
);How to set Character set and collation at Database Level?
If you want to set the character set and collation at the database level, we use the below syntax.
Code:
CREATE DATABASE test
CHARACTER SET ascii
COLLATE ascii_general_ci;To alter the default setting of the character set and collate, use the below syntax: –
Code:
ALTER DATABASE test
CHARACTER SET UTF8
COLLATE utf8_bin;How to Set Character Set and Collation at Table Level?
If you want to set the character set and collation at table level, we use the below syntax.
Code:
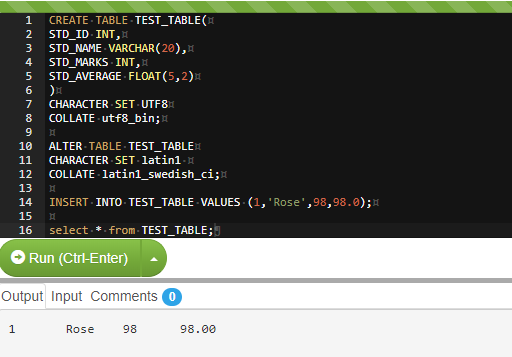
CREATE TABLE TEST_TABLE(
STD_ID INT,
STD_NAME VARCHAR(20),
STD_MARKS INT,
STD_AVERAGE FLOAT(5,2)
)
CHARACTER SET UTF8
COLLATE utf8_bin;To alter the default setting of the character set and collate, use the below syntax: –
Code:
ALTER TABLE TEST_TABLE
CHARACTER SET latin1 COLLATE latin1_swedish_ci;Output:
How to set Character set and collation at Column Level?
Code:
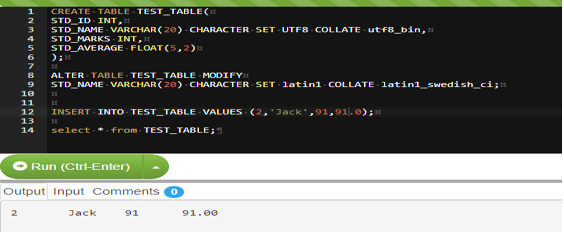
CREATE TABLE TEST_TABLE(
STD_ID INT,
STD_NAME VARCHAR(20)CHARACTER SET UTF8 COLLATE utf8_bin,
STD_MARKS INT,
STD_AVERAGE FLOAT(5,2)
);To alter the default setting of the character set and collate, use the below syntax: –
Code:
ALTER TABLE TEST_TABLE MODIFY
STD_NAME VARCHAR(20) CHARACTER SET latin1 COLLATE latin1_swedish_ci;Output:
Conclusion
Things that need to be put in mind from the above session: –
- MySQL collation is nothing but a set of rules used to compare the characters in a particular character set.
- The character set, and collations can be set at four levels, and they are at: – server level, database level, table level, and column level.
- Some rules that need to be considered are: – Two character sets can’t have the same collation. Instead, each character set can have one or more different collations.
Recommended Articles
We hope that this EDUCBA information on “MySQL Collation” was beneficial to you. You can view EDUCBA’s recommended articles for more information.