Updated May 2, 2023
Definition of MongoDB User
MongoDB users are used to accessing the database as per specified grants that the user-defined. The user is more important and useful in every database to access the database through the client. In MongoDB, we have to use the db.createUser method to create a new user; when adding any user into the MongoDB database, we can assign a role to the user to privileges. We can also update the user after creating; we can change the user name and password and grant or revoke the privileges of the user. After adding a user to the database, we can create a user-specific database.
MongoDB User Operations and Roles
- Access control on the database is more important when we are working with users and roles in MongoDB.
- By default, authorization to the database is disabled; we need to enable this using adding authorization in configuration files.
- The below examples show the use of security options in MongoDB.
#Security
Authorization: enabled
cat /etc/mongod.conf
- The authorization setting in MongoDB will enable and disable the role-based access control.
- The below syntax shows that create a user in MongoDB, the db.createUser method is used to create a new user in MongoDB.
Syntax:
db.createUser (user_info, Writeconcern)
Parameter:
Below is the parameter description syntax for creating a user in MongoDB.
- Create User: Create user is a method that was used to create a new user in MongoDB. Using create user method, we have to create new users as per the operation specified in MongoDB.
- User or user_info: The type of user parameter is a document in creating the user method. This parameter will contain the document and authentication of the user. User info contains usernames and privileges, which we have defined for the user.
- Write concern: This is an optional parameter to create a user method in MongoDB. The get last error command takes the same field as the write concern in MongoDB.
MongoDB User and Role Operations
- To create a role with authentication restrictions in MongoDB, we must have set authentication restrictions on the database that we have using.
1. Create a Role in MongoDB to Manage Current Operations
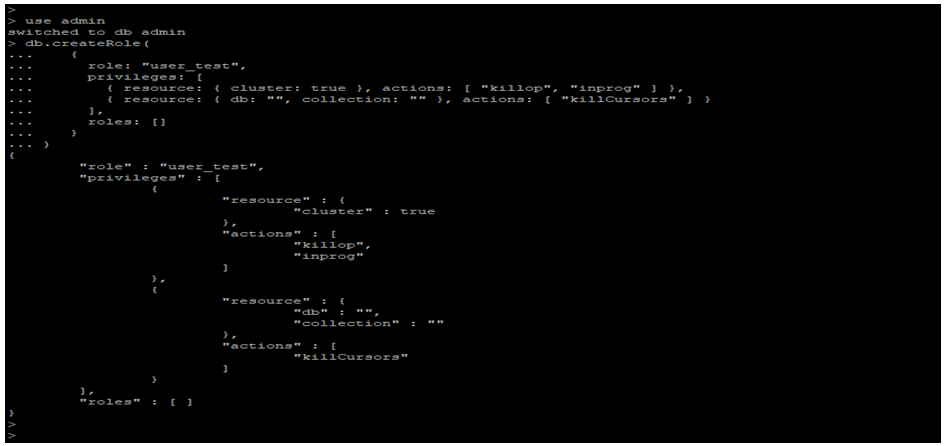
- In the following example, we have created a role name as user_test, which is used to run only the db.currentOp () and db.killOp () commands.
- For creating any user in MongoDB, we need to connect the MongoDB instance.
Example:
use admin
db.createRole (
{
role: "user_test",
privileges: [
{ resource: { cluster: true }, actions: [ "killop", "inprog" ] },
{ resource: { db: "", collection: "" }, actions: [ "killCursors" ] }
],
roles: []
})
- To create a user in MongoDB, we need to use the admin database first and then create a user name as user_test.
2. Create a User to Run Mongostat Command
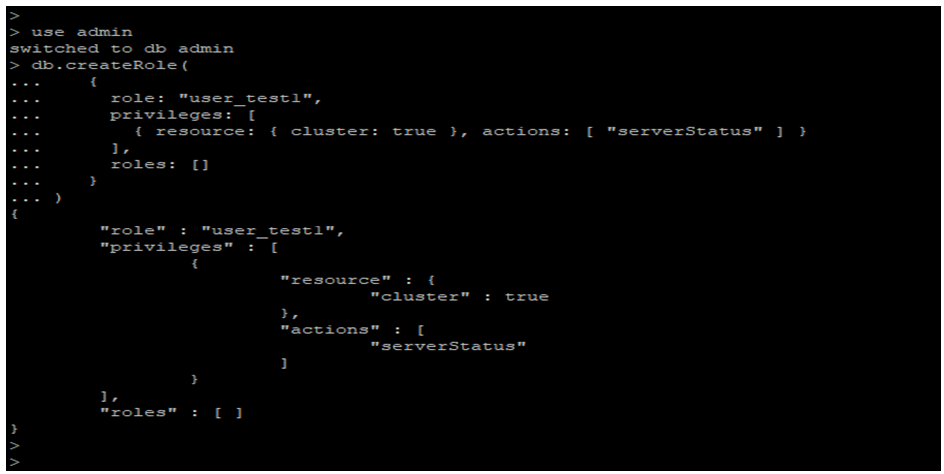
- In the below example, we have to create a role name as user_test1, which is used to provide the privileges that run only a command name as mongostat.
Example:
use admin
db.createRole(
{
role: "user_test1",
privileges: [
{ resource: { cluster: true }, actions: [ "serverStatus" ] }
],
roles: []
}
)
3. Create a User and Provider Privileges to Drop System Views in Collection Across Databases
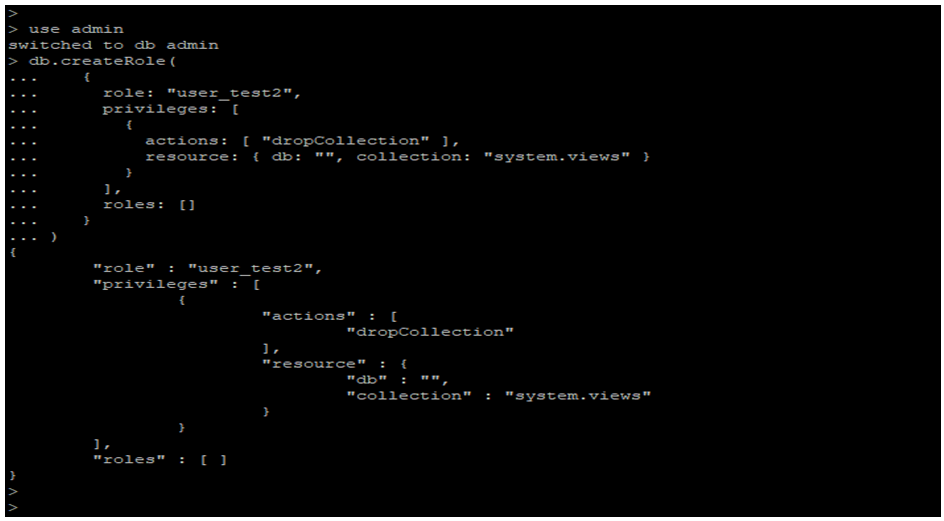
- In the below example, we have created a user name as user_test2 and provided permission to drop the system view collection.
Example:
use admin
db.createRole(
{
role: "user_test2",
privileges: [
{
actions: [ "dropCollection" ],
resource: { db: "", collection: "system.views" }
}
],
roles: []
}
)
4. Change the user Password in MongoDB
- We can change the password of the existing user by using the change user password method in MongoDB.
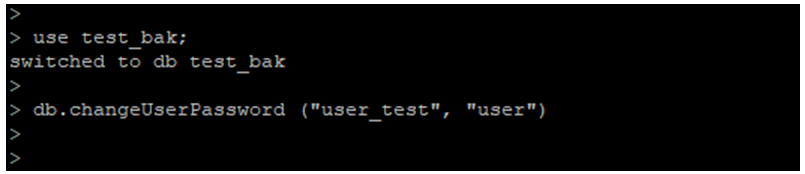
- We have to change the user_test user password to “user.” We need to pass the user’s current username and password to change the user’s password in MongoDB.
- We need to specify the user name when we want to change the user password in MongoDB.
use test_bak;
db.changeUserPassword ("user_test", "user")
- To modify the password of any or existing user, we need to use the change user password method in MongoDB.
5. Modify the user access in MongoDB
- We can modify the access of the existing or any user in MongoDB. We can give access and revoke the privileges of an existing user.
- Below is the access which was available in MongoDB.
- Revoke grants from the role.
- Grant privileges to role.
1. Revoke a Grant from the Role
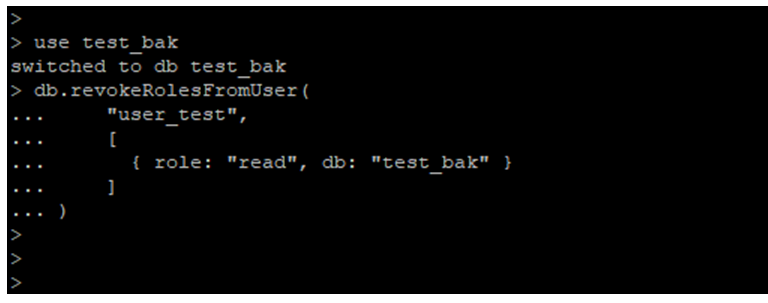
- We can revoke the role of the existing user by using the db.revokeRolesFromUser () method.
- In the below example, we have revoked the grant of user_test user. We have revoked the read grants from the user_test user.
Example:
use test_bak
db.revokeRolesFromUser("user_test",
[ { role: "read", db: "test_bak" }
])
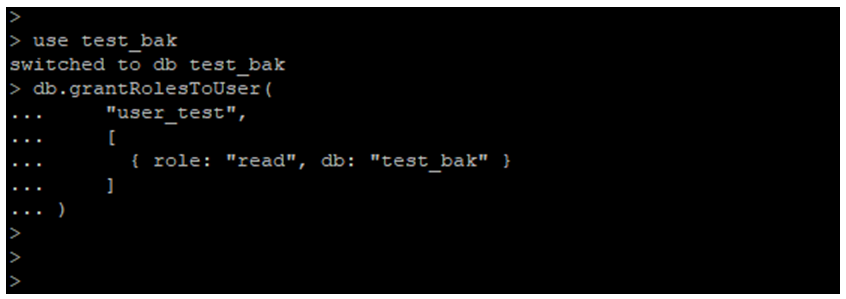
2. Grant Privileges to Role
- We can provide grants to the role or existing user by using the db.grantRolesToUser () method.
- In the below example, we have granted privileges to the user_test user. We have provided a read role on test_bak database to the user_test user.
Example:
use test_bak
db.grantRolesToUser(
"user_test",
[
{ role: "read", db: "test_bak" }
]
)
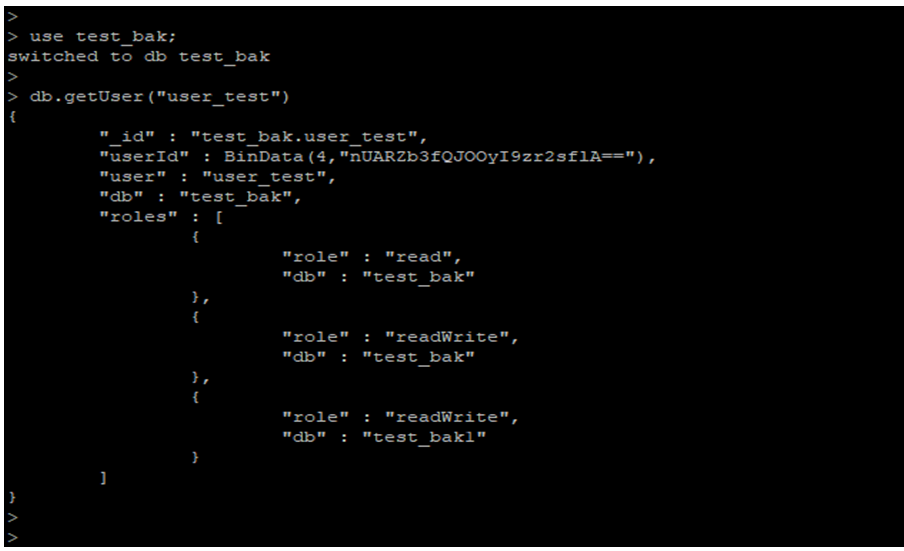
6. View user role
- We can check the user role by using the db.getUser method in MongoDB. We have to check all the details of the user_test user.
- We have to use the database name before using the method of db.getUser in MongoDB.
Example:
use test_bak;
db.getUser("user_test")
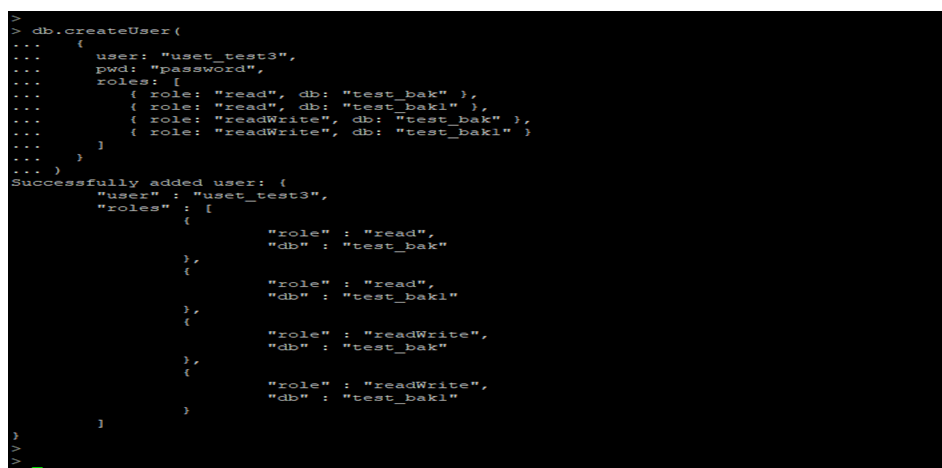
7. Create a User and Provider Read Write Grant to The User
- In the below example, we have created a user name as user_test3 and can read and write on the database.
- We have provided read and write roles on the test_bak and test_bak1 databases.
Example:
db.createUser(
{
user: "uset_test3",
pwd: "password",
roles: [
{ role: "read", db: "test_bak" },
{ role: "read", db: "test_bak1" },
{ role: "readWrite", db: "test_bak" },
{ role: "readWrite", db: "test_bak1" }
]
}
)
How to list all users in the MongoDB
To list all the users in MongoDB, you can use the show users command in the MongoDB shell.
1. First, connect to your MongoDB instance using the Mongo shell:
2. Switch to the admin database:
3. Run the show users command:
This will output a list of all the users in your MongoDB instance. If you have a large number of users, you can use the pretty() method to format the output for better readability:
You need to have appropriate privileges to execute this command. In particular, you need to have the viewUser privilege on the admin database or the clusterMonitor privilege on the entire MongoDB instance.
Recommended Articles
This is a guide for MongoDB Users. Here we also discuss the definition and MongoDB users’ operations and roles, along with different examples and its code implementation. You may also have a look at the following articles to learn more –