Introduction to MongoDB Remove
- MongoDB Remove method is implemented to remove any specific documents from a collection. This method is defined as db. collection.remove() structure code.
- This remove() method provides a WriteResult() object which includes the status of the operation. After the success of the operation, the WriteResult() object includes info on the number of documents removed: WriteResult({“nRemoved”: 3}).
- The method includes a query part which is required and other two optional parts such as justOne and writeConcern options included in the remove() method which delivers two different syntaxes for the MongoDB remove() method.
- When we execute the remove() method applied on any collection in MongoDB database then, the writeResult object will return the status of the operation performed.
Syntax
The MongoDB Remove method includes two basic syntaxes implemented for removing any collection from MongoDB database described as follows:
Syntax where the MongoDB remove() method takes a query document with an optional Boolean ‘justOne’ is:
Db.collection.remove(<query>, <justOne>)
And, syntax, where the MongoDB remove() method, takes a query document with an optional remove options document:
It is modified in version 5.0.,
Db.collection.remove(
<query>,
{justOne: <boolean>,
writeConcern: <document>,
let: <document> //supplemented in MongoDB 5.0
})
Let us explain the parameters used in the above syntaxes:
1. Query: It is a document type that states deletion criteria by means of query operators. This method removes all documents in a collection when we pass an empty document ({}).
2. justOne: It is Boolean type and optional one but is used for limiting the deletion operation to only a single document when set to true. The user should omit to use the value as false which is the default one and remove all documents which match the deletion criteria.
3. writeConcern: It is a document type that is optional where a document expresses the write concern. One should avoid applying the default write concern. The user should not set the write concern externally for the operation if executed in a transaction.
4. Collation: It is a document type that states the collation for using the operation. This collation permits users to define language-specific rules like rules for lettercase and accent marks for string comparison. This option specifies the below syntax:
Collation: {
Locale: <string>,
caseLevel: <boolean>,
caseFirst: <string>,
strength: <int>,
numericOrdering: <boolean>,
alternate: <string>,
maxVariable: <string>,
backwards: <boolean>
}
While defining the collation, locale field is compulsory; whereas all other fields of collation are optional. If the collation is not stated but still the collection takes a default collation value which is specified for the collection when executed.
If a collection is stated with any collation or for the operations, then MongoDB applies the basic binary comparison implemented in preceding versions for the string comparisons.
For an operation, we cannot define many collations. Suppose, many collations per field cannot be defined, or maybe executing a find with a sort, one cannot apply one collation for the find and additional for the sort.
It is new in the MongoDB version 3.4.
5. Let: It is a document type parameter optionally defined. It states a document having a list of variables allowing the user for enhancing command readability through separation of variables from the query text. Its syntax has the below structure:
{<variable_name_1>: <expression_1>, ……., <variable_name_n>: <expression_n>}
The variable will be set to the value resulted by the expression which cannot be altered afterwards. For accessing the value of a variable present in the command, we will apply the double dollar sign prefix i.e. $$, together with having the variable name in the form $$<variable_name>. E.g. $$Totalsum.
It should be noted that to apply a variable to filter results, one must access the variable inside the $expr operator. It is new in version 5.0.
The MongoDB remove() method outputs an object which consists of the status of the operation. It results in a WriteResult object which includes the status of the operation.
How remove works in MongoDB?
Discussing the working of remove () method in MongoDB, we will illustrate the behavior of MongoDB Remove() method:
Write Concern:
The MongoDB remove() method implements the delete command that applies the default parameter i.e. writeConcern. But if we want to state a distinct write concern, then we must consist the write concern in the options parameter.
Query Considerations:
This remove() method will remove all documents by default which will match the query expression. We can define the justOne option for limiting the operation to remove just one document. Also, we can use the method findAndModify(), for deleting only a document sorted by a particular order.
When deleting multiple documents, this remove() method operation may incorporate additional read and/or write operations in MongoDB to the collection.
Capped Collections:
The MongoDB remove() method cannot be implemented with a capped collection.
Time Series Collections:
The MongoDB remove() method cannot be implemented on a time series collection.
Sharded Collections:
For a sharded collection, all remove() operations that define the justOne: true option must include the shard key or even the _id field on the query specification. Thus, the remove() operations stating justOne: true in a sharded collection that do not include either the _id field or the shard key result an error.
Transactions:
MongoDB remove method as, db.collection.remove(), can be implemented within multi-document transactions. If executed in a transaction, we must not externally set the parameter, write concern for the operation. We need to study some rules for applying the write concern with transactions.
Example
Let us illustrate some examples to view the working of this Mongo remove() method:
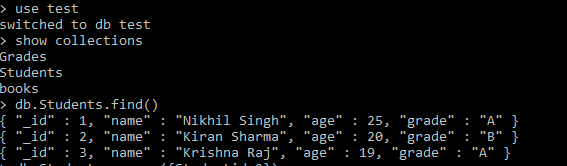
Suppose, we have a db ‘test’ and few collections created in it, where details of the collection named ‘Students’ is shown below:
use test
show collections
db.Students.find()
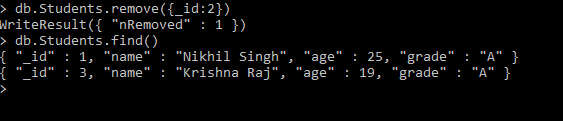
Now, we will code to demonstrate how to remove any particular document from the collection.
Db.books.({_id:2)
When the above code is executed with success then it will remove the documents that have the student id as 2 generating the output as:
WriteResult({“nRemoved” : 1})
db.Students.find()
Output:
Also, if we want to remove all documents from any collection, then call remove() having an empty query as, db.books.remove({}).
Conclusion
- In MongoDB, we will use the remove() method to delete such documents from a specific collection which matches certain deleting criteria mentioning in the query function as parameters.
- But to remove the entire documents of a collection, it may be more resourceful to implement the method as drop() that consists of indexes and after that we may reconstruct collection as well as restructure the collection indexes simply.
Recommended Articles
This is a guide to MongoDB Remove. Here we discuss the definition, How remove works in MongoDB? with examples respectively. You may also have a look at the following articles to learn more –