Introduction to Mobile Communication Technology
Mobile communication technology is a wireless system that enables people and devices to exchange voice, data, and multimedia information over long distances without physical or wired connections. It uses cellular networks, radio waves, and base stations to keep mobile phones, tablets, and other wireless devices connected as they move from place to place.
In simple terms, mobile communication technology enables calling, messaging, browsing the internet, and sharing data anytime, anywhere on mobile devices.
Table of Contents
- Introduction
- Evolution
- Components
- Types
- Applications
- Advantages and Disadvantages
- Mobile Communication vs Wired Communication
- Security in Mobile Communication
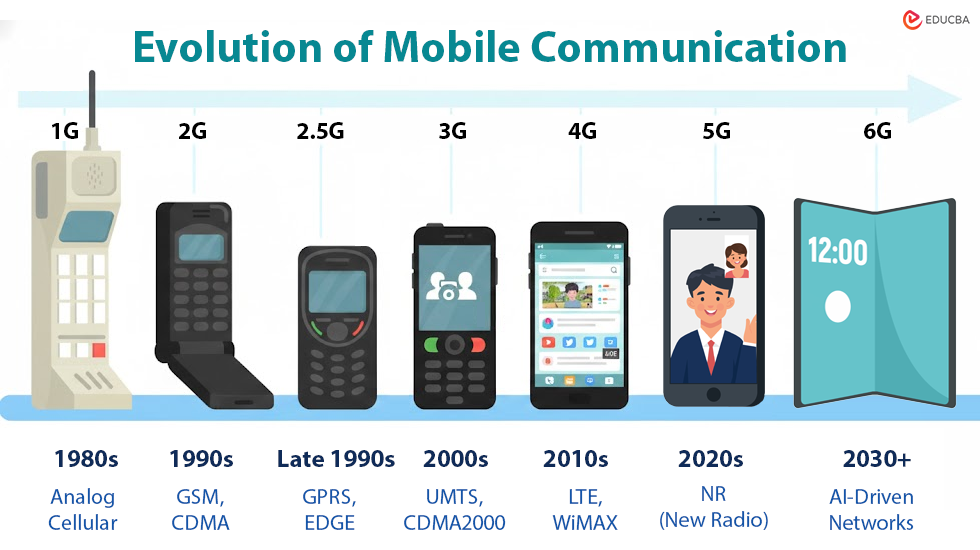
Evolution of Mobile Communication
| Generation | Time Period | Key Technology | Data Speed | Main Features |
| 1G | 1980s | Analog cellular | Up to 2.4 kbps | Voice-only communication, poor call quality, low security, bulky devices |
| 2G | 1990s | GSM, CDMA | Up to 64 kbps | Digital voice calls, SMS, better sound quality, improved security |
| 2.5G | Late 1990s | GPRS, EDGE | Up to 144 kbps | Basic internet access, MMS, email, improved data services |
| 3G | 2000s | UMTS, CDMA2000 | Up to 2 Mbps | Mobile internet, video calling, multimedia services |
| 4G | 2010s | LTE, WiMAX | 100 Mbps – 1 Gbps | High-speed internet, HD video streaming, online gaming, cloud services |
| 5G | 2020s | NR (New Radio) | Up to 10 Gbps | Ultra-low latency, IoT support, smart cities, autonomous vehicles |
| Future (6G) | 2030+ (Expected) | AI-driven networks | Very high (Tbps) | Holographic communication, advanced AI integration, seamless global connectivity |
Components of the Mobile Communication System
A mobile communication system consists of several interconnected components that work together to enable wireless voice and data transmission between users. Each component helps ensure smooth, reliable communication.
- Mobile Station (MS): The mobile station is a user’s device, such as a smartphone or tablet. It includes the handset and the SIM card. The device converts voice into radio signals and receives network signals to enable communication.
- Base Transceiver Station (BTS): The BTS provides the radio interface between the mobile device and the network. It transmits and receives signals within a specific coverage area called a cell and manages communication with multiple users simultaneously.
- Base Station Controller (BSC): The Base Station Controller manages multiple BTS units. It controls handovers, allocates radio channels, and ensures efficient use of network resources while maintaining call quality during movement.
- Mobile Switching Center (MSC): The MSC is the core of the cellular network. It handles call routing, call setup, call termination, and mobility management. It also connects the mobile network to other networks such as PSTN and the internet.
- Home Location Register (HLR): The Home Location Register stores permanent subscriber information, including user identity, service details, and current location. It helps authenticate users and manage roaming services.
- Visitor Location Register (VLR): The Visitor Location Register temporarily stores information about subscribers roaming in a particular area. It works with the HLR to provide seamless service when users move between different network regions.
- Authentication Center (AuC): The Authentication Center ensures network security by verifying subscribers’ identities. It protects the system from unauthorized access and fraud.
- Transmission System: The transmission system connects different network components using optical fiber, microwave links, or satellite communication. It helps transfer data quickly and reliably across the network.
- Core Network: The core network manages data routing, billing, authentication, and service delivery. It supports voice calls, SMS, multimedia services, and internet access.
Types of Mobile Communication
Mobile communication can be categorized based on how information is transmitted, the purpose of communication, and the underlying technology. Each type plays a vital role in modern digital connectivity.
1. Voice Communication
Voice communication enables users to transmit spoken messages over mobile networks. It was the primary purpose of early mobile phones and remains essential today. Modern voice communication uses digital compression and packet switching to improve call clarity and reduce noise.
With advancements such as VoLTE (Voice over LTE) and VoNR (Voice over New Radio), users now experience HD voice quality, faster call connections, and fewer call drops. People widely use voice communication for personal, business, emergency, and customer support services.
Key Benefits:
- Real-time interaction
- Wide network coverage
- Reliable for emergency communication.
2. Data Communication
Data communication allows mobile devices to transmit and receive digital data through cellular networks. It supports internet access, application usage, and cloud-based services. This type of communication has grown rapidly with the rise of smartphones and mobile applications.
Higher generations, such as 4G and 5G, provide high-speed data transfer, low latency, and better bandwidth efficiency. Data communication is essential for online learning, remote work, e-commerce, and social media platforms.
Key Benefits:
- High-speed internet access
- Supports modern mobile applications
- Enables cloud computing and remote services.
3. Video Communication
Video communication enables the transmission of both video and audio signals in real time. 4G LTE and 5G networks efficiently support it by providing high data speeds and stable network connections.
This type of communication supports virtual meetings, online education, telemedicine, and video conferencing on a wide scale. Improved compression techniques and network optimization have enhanced video quality while reducing data consumption.
Key Benefits:
- Face-to-face interaction from remote locations
- Improved collaboration and learning
- Supports telehealth and remote consultations.
4. Messaging Communication
Messaging communication involves sending text, images, videos, and audio messages through mobile devices. It includes both traditional messaging services (SMS, MMS) and internet-based instant messaging platforms.
Modern messaging services offer features such as end-to-end encryption, group chats, voice notes, and file sharing. Messaging communication is cost-effective, fast, and widely used for both personal and professional communication.
Key Benefits:
- Quick and asynchronous communication
- Low bandwidth requirement
- Supports multimedia content.
5. Machine-to-Machine (M2M) Communication
Machine-to-Machine communication allows devices to communicate automatically without human intervention. It supports smart, automated systems used in industries such as manufacturing, healthcare, and transportation.
M2M communication uses mobile networks to monitor, collect, and transmit data in real time. It improves efficiency, reduces operational costs, and enables predictive maintenance.
Key Benefits:
- Automation of processes
- Real-time data monitoring
- Increased operational efficiency.
6. Internet of Things (IoT) Communication
IoT communication connects physical objects to the internet using mobile communication technologies. These devices collect and exchange data to provide intelligent insights and automated control.
Mobile networks such as NB-IoT, LTE-M, and 5G support large-scale IoT deployments. IoT communication connects devices across smart homes, healthcare monitoring systems, agriculture, and smart cities to efficiently collect and exchange data.
Key Benefits:
- Remote monitoring and control
- Data-driven decision-making
- Supports smart and connected environments.
7. Satellite Mobile Communication
Satellite mobile communication provides connectivity in areas where traditional cellular networks are unavailable. It uses satellites to transmit signals over long distances, making it ideal for remote and disaster-prone regions.
This type of communication is essential for aviation, maritime operations, defense, emergency response, and remote exploration. Although satellite communication has higher latency and higher costs, it provides global coverage.
Key Benefits:
- Communication in remote areas
- High reliability during emergencies
- Global network coverage.
8. Wireless Broadband Communication
Wireless broadband communication offers high-speed internet access over mobile networks without physical cables. It supports high-bandwidth applications such as video streaming, online gaming, and cloud services.
Technologies such as LTE, WiMAX, and 5G enable fast, reliable broadband access, especially in areas where wired infrastructure is limited or unavailable.
Key Benefits:
- High-speed data transmission
- Easy deployment and scalability
- Supports multimedia and real-time applications.
Applications of Mobile Communication Technology
Mobile communication technology is not just about making calls or sending messages. Its applications span multiple sectors, transforming how we live, work, and interact. Here are the key areas where mobile communication plays a vital role:
1. Healthcare
- Telemedicine and remote consultations allow doctors to diagnose and treat patients from a distance.
- Mobile health apps monitor vital signs, track fitness, and remind patients to take medication.
- Emergency services use mobile communication to provide quick responses during accidents or disasters.
2. Education
- E-learning platforms and online classrooms use mobile networks for interactive learning.
- Students can access digital libraries, tutorials, and collaborative tools on mobile devices.
- Distance education is made possible for rural and remote areas.
3. Banking and Financial Services
- Mobile banking apps allow account management, fund transfers, and bill payments.
- Mobile wallets (such as UPI, PayPal, and Google Pay) facilitate cashless transactions.
- Banks use mobile notifications for real-time alerts and security verification.
4. Transportation and Navigation
- GPS-enabled mobile devices provide accurate navigation and route planning.
- Ride-hailing and delivery services (Uber, Ola, Zomato, Swiggy) rely on mobile communication.
- Fleet management uses mobile networks to track and optimize vehicles.
5. Business and Remote Work
- Mobile communication supports virtual meetings, emails, and instant messaging.
- Businesses use mobile devices for real-time decision-making and collaboration.
- Remote work is feasible anywhere with mobile internet connectivity.
6. Disaster Management
- Mobile networks enable emergency alerts, disaster warnings, and relief coordination.
- Mobile communication enables quick rescue operations and the dissemination of information.
7. Smart Cities and IoT
- Traffic management, street lighting, and surveillance systems use mobile networks.
- Mobile-connected devices monitor air quality, water usage, and energy consumption.
- IoT devices communicate via mobile infrastructure to enable automation and efficiency.
8. Entertainment and Social Media
- Streaming services, video calls, and online gaming depend on high-speed mobile networks.
- Social media platforms rely on mobile communication for instant sharing and connectivity.
9. Retail and E-commerce
- Mobile apps enable shopping, order tracking, and digital payments.
- Retailers use mobile technology to engage customers and offer personalized offers.
Advantages and Disadvantages of Mobile Communication Technology
| Advantages | Disadvantages |
| Provides instant communication anytime, anywhere. | Overdependence on mobile devices may reduce face-to-face interactions. |
| Facilitates access to the internet and multimedia services. | Mobile networks are vulnerable to hacking and data breaches. |
| Supports business operations and remote work. | Health concerns related to prolonged mobile usage (e.g., radiation, eye strain). |
| Enables real-time navigation, GPS, and location services. | Expensive infrastructure and maintenance for network providers. |
| Enhances emergency response through alerts and notifications. | Network congestion can reduce communication quality. |
| Improves social connectivity and networking. | Privacy issues due to tracking and data collection. |
| Supports mobile banking, e-commerce, and digital transactions. | Mobile devices can be lost, stolen, or damaged. |
| Encourages technological innovations and app development. | Dependence on electricity and network coverage limits accessibility in remote areas. |
Mobile Communication vs Wired Communication
Mobile and wired communication are the primary modes for transmitting data and voice. Knowing the differences helps you pick the best technology for your needs.
| Feature | Mobile Communication | Wired Communication |
| Connectivity | Uses wireless signals like radio waves or microwaves. | Uses physical cables such as fiber optic, coaxial, or copper wires. |
| Mobility | Highly portable; users can communicate on the move. | Limited mobility; devices must remain connected to cables. |
| Installation | Easier and faster to deploy, especially in remote areas. | Installation is complex and expensive, especially over long distances. |
| Speed | Generally slower than wired for stable, high-volume data transfer (though 5G is bridging the gap). | Provides faster and more stable connections for high-speed data transfer. |
| Reliability | Susceptible to interference, signal loss, and network congestion. | More reliable, consistent, and less affected by environmental factors. |
| Cost | Lower initial infrastructure cost, but recurring costs for spectrum and maintenance. | Higher installation cost, but lower recurring costs for maintenance. |
| Security | Vulnerable to hacking and unauthorized access if not secured. | More secure due to physical access requirements; harder to intercept. |
| Use Case | Smartphones, IoT devices, remote monitoring, field operations. | Data centers, office networks, industrial automation, and high-bandwidth applications. |
Security in Mobile Communication
Mobile communication carries sensitive data, making security a critical aspect. Mobile networks use multiple measures to protect users and prevent unauthorized access.
- Encryption: Encryption changes data into a secret code that only approved devices can read. Modern mobile networks use advanced encryption standards to secure voice calls, text messages, and internet data. This ensures that sensitive information, such as banking transactions or personal messages, cannot be easily intercepted.
- Authentication: Authentication checks the identity of users and devices before allowing them to access the network. SIM-based authentication, passwords, and biometric verification (like fingerprint or face recognition) help prevent unauthorized access and reduce the risk of identity theft.
- SIM security: SIM cards store user identity information and encryption keys. Advanced SIM security mechanisms, such as PIN codes, remote SIM locking, and embedded secure elements, prevent misuse or cloning of SIM cards.
- Mobile malware threats: Mobile devices are vulnerable to malware, spyware, and phishing attacks. Threats can compromise personal data or network security. Regular software updates, antivirus apps, and cautious downloading practices help mitigate these risks.
- Secure communication protocols: Mobile communication networks rely on secure protocols such as GSM, LTE, and 5G NR, which include built-in encryption and authentication. Secure communication protocols prevent eavesdropping, data tampering, and other cyber threats.
Final Thoughts
Mobile communication technology has transformed the way we connect, work, and live. From simple voice calls in the 1G era to ultra-fast, low-latency 5G networks, mobile technology continues to evolve and expand possibilities. It enables instant communication, supports business operations, powers smart devices, and facilitates essential services like healthcare, education, and disaster management.
As mobile networks advance, security, reliability, and accessibility remain crucial to ensuring safe, seamless connectivity. Whether it enables IoT, smart cities, or remote work, mobile communication plays a pivotal role in shaping a connected, efficient world.
Understanding its components, generations, types, and applications helps individuals and organizations leverage mobile technology to its fullest potential. With future innovations like 6G on the horizon, mobile communication will continue to revolutionize global connectivity, making communication faster, smarter, and more integrated than ever before.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
Q1. How do mobile communication technologies handle network congestion?
Answer: Techniques like dynamic load balancing, network slicing in 5G, and advanced routing protocols help distribute traffic efficiently and maintain service quality during peak usage.
Q2. How do mobile networks ensure call quality and low latency?
Answer: Mobile networks use quality of service (Quality of Service) mechanisms, optimized routing, handover management, and advanced modulation techniques to maintain clear voice calls and low-latency data transmission.
Q3. What are the environmental impacts of mobile communication networks?
Answer: Mobile towers and data centers consume energy, and network infrastructure can contribute to electromagnetic radiation. 5G and future networks aim to reduce energy consumption using energy-efficient technologies.
Q4. How is mobile communication evolving with AI?
Answer: AI helps optimize network management, predicts traffic congestion, improves security through anomaly detection, and supports intelligent services for users, such as predictive text and smart routing.
Q5. What is VoLTE, and how is it different from regular voice calls?
Answer: VoLTE (Voice over LTE) transmits voice calls over the 4G LTE network instead of traditional 2G/3G channels, offering higher call quality, faster connections, and simultaneous voice and data use.
Q6. Can mobile communication networks support emergency services?
Answer: Yes, mobile networks provide real-time alerts, disaster warnings, GPS tracking, and emergency call routing to help coordinate relief and save lives during disasters.
Recommended Articles
This is a guide to Mobile communication technology. Here we discuss what Mobile communication technology which is an important part of our daily life, is. We hope you will find this article helpful. You may also have a look at the following articles to learn more –

